Table of Contents
In this article, we will discuss the four VTP modes namely client mode, server mode, transparent mode, off mode and three versions, VTP v1, VTP v2 and VTP v3, their differentiation and parameters.
VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol that propagates the information of Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN) on the whole local area network. VTP protocol carries VLAN information to all the switches in a VTP domain. VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) reduces administration in a Layer 2 network.
When you configure a new VLAN on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. VTP protocol is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that is available on most of the Cisco Catalyst series products.
VTP Modes
VTP operates in different modes, each with a specific purpose. While VTP version 1 and 2 support 3 modes of operation i.e. Server/Client/ Transparent, VTPs latest version 3 has introduced a new mode “Off“.
Server Mode
This is the default mode .It can create, modify and delete VLANs. The changes are advertised to other switches in the same VTP domain. It stores VLAN info in NVRAM (i.e., VLAN database is persistent after a reboot). You need at least one switch in server mode for VTP to work.
Client Mode
Client mode cannot create, modify, or delete VLANs. It receives updates from VTP servers and applies them. It does not store VLAN info in NVRAM (rebooting will lose VLAN info unless received again). It is useful for keeping VLANs consistent across the network.
Transparent Mode
transparent mode does not participate in VTP advertisements. It forwards VTP messages to other switches. It can create, modify, and delete VLANs, but changes are local only. VLAN info is stored in NVRAM, but not shared.
Off Mode
Off Mode is basically VTP Version 3 only. It disables VTP completely hence no VLAN updates are sent or received. The VLAN configuration is local only.
VTP Versions
While VTP has evolved over time, its key for us to understand how and what are the differentiating parameters of various versions of VTP – (VTP v1 , VTP v2 and VTP v3)
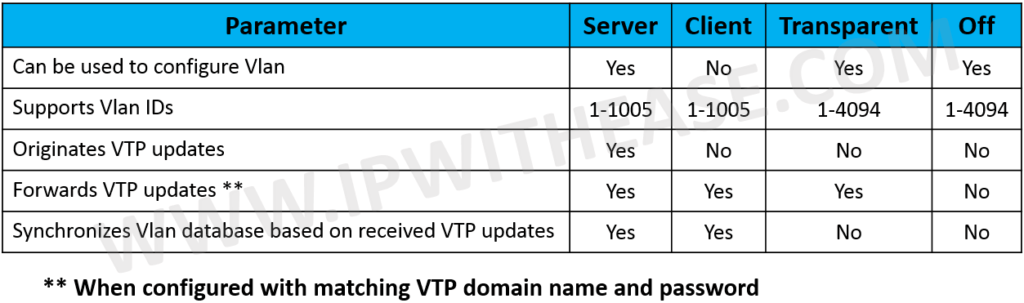
| Parameter | VTP v1 | VTP v2 | VTP v3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mode | Server / Client / Transparent | Server / Client / Transparent | Server / Client / Transparent / Off |
| Token Ring support | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Unrecognized Type-Length-Value (TLV) Support | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Version-Dependent Transparent Mode | In VTP version 1, a VTP transparent network device inspects VTP messages for the domain name and version and forwards a message only if the version and domain name match | VTP version 2 forwards VTP messages in transparent mode without checking the version | VTP version 2 forwards VTP messages in transparent mode without checking the version |
| Consistency Checks | Not Supported | Supported | Supported |
| Propagation of extended Vlan range | 1 to 1000 | 1 to 1000 | 1 to 4094 |
| Private VLANs | Not Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Support for propagation of any database in a domain | a VTP server is used to back up | a VTP server is used to back up | Supported |
| Authentication | Plain text password | Plain text password | Encrypted password |
Download the comparison table: VTP v1 vs VTP v2 vs VTP v3
VTP v3 Enhancements
- Extended VLANs: Can now manage VLANs 1006–4094.
- Private VLANs: Supports configuration sharing for PVLANs.
- MST support: Can propagate MST region information.
- Primary Server Role: Only the primary server can make VLAN changes, reducing config errors.
- Improved security: Optionally enforces secure updates and stronger authentication.
- Persistent configuration: VLAN data is saved in the switch config, not just a separate database.
VTPv3 is highly recommended if you are deploying in larger or more complex environments that use extended VLANs, MST and Private VLANs.
Continue Reading
How to Reset Revision Number in VTP?
Are you preparing for your next interview?
If you want to learn more about VTP, then check our e-book on VTP Interview Questions and Answers in easy to understand PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj