Table of Contents
GenAI or Generative AI is a buzz word and very popular due to its capabilities to create new content and ability to produce human-like images, audio, content and text. GenAI based first consumer robot was released in the market in the year 2022. It is used in a wide range of consumer and business applications and helps in improving operations, reducing operational costs, replacing repetitive tasks with automation and so on.
In this article we will learn more in detail about Generative AI or GenAI, its key characteristics and understand about six layers of Gen AI.
Understanding GenAI
GenAI is a subset of AI learning technologies which has the ability to produce content in response to text-based prompts. In November 2022 ChatGPT was released which was an OpenAI GPT3.5 neural network. In the early 1960’s MIT had developed ELIZA but it was largely rule-based and lacked contextual understanding like humans. The generative AI models now emerging do not operate on pre-set rules or attributes, they are primitive open neural networks which learn via real-world training data.
GenAI usage is not just limited to technology organizations but it is being used in healthcare for medical imaging, medicine development, in the financial sector it is used for AI risk modelling, fraud detection, customer service, in E-commerce GenAI is used to provide dynamic product descriptions, customer support responses etc.
Related: Generative AI vs ChatGPT
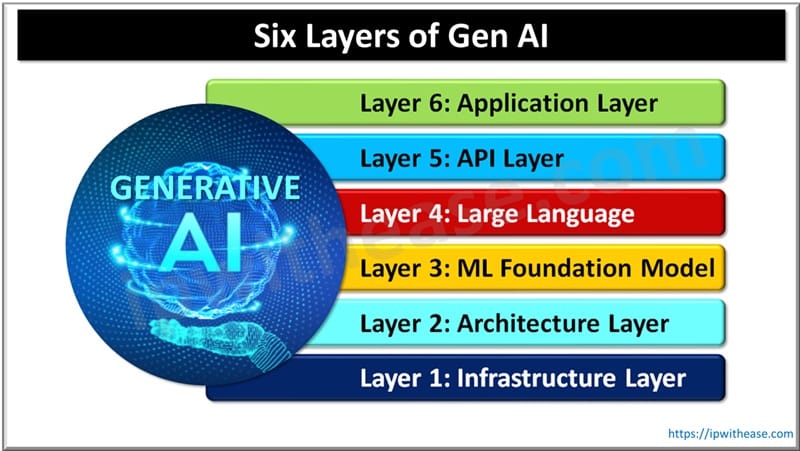
GenAI Architecture: Layers of Gen AI
GenAI architecture operates with a layered approach and each layer is dedicated to a specific set of functionalities. This layered approach helps in building robust GenAI based solutions and applications. Let’s look at each layer and its functions more in detail.
Layer 1: Infrastructure Layer
It is the basis of all GenAI models. It comprises hardware and software required for GenAI development, implementation and training of the model. Lack of a robust model will create a bottleneck in GenAI computational demands. Its key components are high performance computing resources (HPC) and Graphic processing unit (GPU), Tensor processing units (TPU) central processing unit (CPU) are specialized in parallel processing to train large-set of neural networks.
Distributed computing systems facilitate computation across multiple nodes, data lakes, databases, Datawarehouse are centralized data repositories to store vast amount of structure / unstructured/ semi-structured data, high speed networks are required for rapid transfer of data between storage and AI model and cloud infrastructure for scalability and availability of on-demand resources to support AI workloads.
Layer 2: Architecture Layer
It is responsible for the structural design of the GenAI model. It is meant to configure neural network architectures based on tasks. Key components of this layer are data transformers for natural language processing (NLP), translation and text generation, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for creation of highly synthetic data for augmentation and image creation.
Layer 3: ML Foundation Model Layer
This layer is responsible for developing ML models on vast datasets for pattern recognition. Key components of this layer are trainings for accessing high quality and diverse data sets for robust model training, pre-processing to normalize, clean and augment data to enhance the model, training algorithms, (supervised or unsupervised, self-supervised, semi-supervised), Model evaluations and validation techniques (Cross validation and hold-out validation).
Layer 4: LLM (Large Language Model)
This layer deals in LLM deployments such as GPT. Its key components are model architecture, transformer-based models, variants (GPT, BERT etc.), training data (large scale data sets Wikipedia and common crawl), representation and diversity, fine-tuning and transfer learning.
Layer 5: API Layer
This layer is for accessing and utilization of GenAI via standard interface. It is particularly useful for integration into applications and services. Key components are RESTful APIs, HTTP, endpoints, GraphQL APIs (Flexi queries and single endpoint) and SDKs (Software deployment kits) for various programming languages such as Java, C++, Python for integration of AI capabilities.
Layer 6: Application Layer
This layer is implementation of GenAI in real-world scenarios to resolve issues and productivity enhancements. Key components of this layer are content creation (text, image and video) generation, healthcare applications (drug discovery and medical imaging), customer service applications (voice assistants and chat bots).
Comparison of Gen AI Layers
| Layer | Purpose | Components | Primary Users | Examples | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6. Application Layer | User-facing products built using LLMs or foundation models | Agents, Copilots, chatbots, analytics tools, automation systems, domain-specific apps | End users, enterprises, SaaS providers | ChatGPT apps, GitHub Copilot, Notion AI, AI customer-service bots | Reliability, UX alignment, Guardrails, Real-world safety |
| 5. API Layer | Exposes model capabilities through accessible, scalable interfaces for developers | REST APIs, SDKs, model endpoints, vector search APIs, RAG endpoints | Software developers, integrators, product teams | OpenAI API, Anthropic API, Vertex AI Endpoints, Azure OpenAI, Pinecone/Weaviate APIs | Rate limits, Latency, Security, Integration complexity |
| 4. LLM (Large Language Model) Layer | Specialized subset of foundation models focused purely on natural language and reasoning | Text-based generative models, instruction-tuned models, fine-tuned LLM variants | AI engineers building text/agent systems | GPT-5.1, Claude Opus, Llama-3-Instruct, Mistral | Hallucinations, Context limitations, Prompt fragility, Compliance |
| 3. ML Foundation Model Layer | Houses general-purpose pretrained models capable of multimodal or single-modality reasoning | Base models (vision, text, audio, multimodal), embeddings, pretrained checkpoints | Model builders, AI research teams, enterprises customizing models | GPT-base models, Llama-3 base, Stable Diffusion, Whisper, CLIP | Training cost, Bias, Data quality, Alignment before fine-tuning |
| 2. Architecture Layer | Defines the structural design of how models are created, trained, connected, and optimized | Neural network architectures, transformer variants, parallelization strategies, attention mechanisms | AI researchers, model architects | Transformer, DeepSpeed ZeRO, MoE architectures, LoRA, RLHF pipelines | Designing efficient architectures, Managing huge parameter counts, Memory optimization |
| 1. Infrastructure Layer | Provides the physical and cloud-based computing backbone required to train and run generative AI systems | GPUs/TPUs, cloud compute, distributed systems, networking, storage hardware | Cloud providers, infra-architects, ML engineers | NVIDIA H100, Google TPU, AWS EC2 P5, Kubernetes, high-speed networks | High cost, Resource scarcity, Scalability limits, Power consumption |
Download: Layers of GenAI comparison table
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj