Table of Contents
Data security is of paramount importance for organizations. Enterprises employ various techniques and use a variety of tools to safeguard data. Cryptography is one such technique employed by organizations to ensure data security when data is transferred between communicating parties to ensure it is not modified by unauthorized parties and prevent hackers from gaining access to confidential information. The end objective of cryptography is to secure communication or set up a secure connection between two systems.
In today’s topic we will learn about cryptography, why it is used, various cryptographic techniques, its usage and advantages.
What is Cryptography?
The earliest known use of cryptography dates back to 2181 BCE when scribes were used for concealing messages. During the Han dynasty in China around 206 BCE – 220 CE) Chinese government officials used encryption for documents. The Caesar cipher is the most widely used cryptography technique to protect sensitive information invented by Julius Caesar in 44 BCE.
There is no single universal method to encrypt messages. There are several ways to do it, each having its own advantages and disadvantages. This uses a mathematical formula to convert plain text into cipher text and vice versa. The cryptography encryption algorithm or cipher used for data confidentiality and integrity in a computer system. Using an encryption key, it converts plaintext into ciphertext, and sent over communication channels such as the Internet, to a destination where the receiver will decrypt it.
Types of Cryptography Techniques
Simple code is a way to write alphabets in such a way that it makes messages difficult to read. Language can be used as a code such as Elvish and Esperanto. During the second world war Navajo language had been used as a code, if Navajo had no words for a particular notion, the code speakers chose a term instead such as Navajo word for ‘hummingbird’ meant fighter plane and ‘iron hat’ was Germany. Since the cryptography has evolved by a mile.
Let’s look at more in detail about cryptography techniques in the upcoming section.
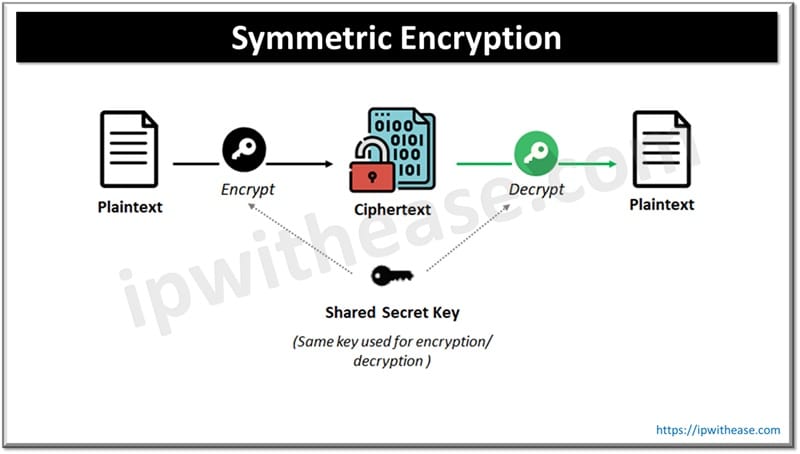
1. Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric Encryption is one of the most widely used encryption and decryption techniques using a secret key. Substitution ciphers are examples of symmetric encryption. A single key is used to encrypted data here.
Symmetric encryption algorithm is of two types:
- Block Cipher – A set of bits are coded with a specific secret key in data blocks. Kept in memory while waiting to get complete blocks
- Stream Cipher – pseudorandom cipher digit stream is used to combine plain text and characters.
Common Algorithms
| Algorithm | Key Size | Block Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AES | 128, 192, 256-bit | 128-bit | Most widely used; very secure |
| DES | 56-bit | 64-bit | Weak and outdated |
| 3DES | 112 or 168-bit | 64-bit | More secure than DES but slower |
| Blowfish | 32–448-bit | 64-bit | Fast and secure for many apps |
| Twofish | Up to 256-bit | 128-bit | Successor to Blowfish |
| RC4 | Variable | Stream cipher | Deprecated due to biases |
| ChaCha20 | 256-bit | Stream cipher | Fast, modern alternative to AES in mobile apps |
Use Cases
- File encryption
- VPNs (IPsec)
- Wireless security (WPA2, WPA3)
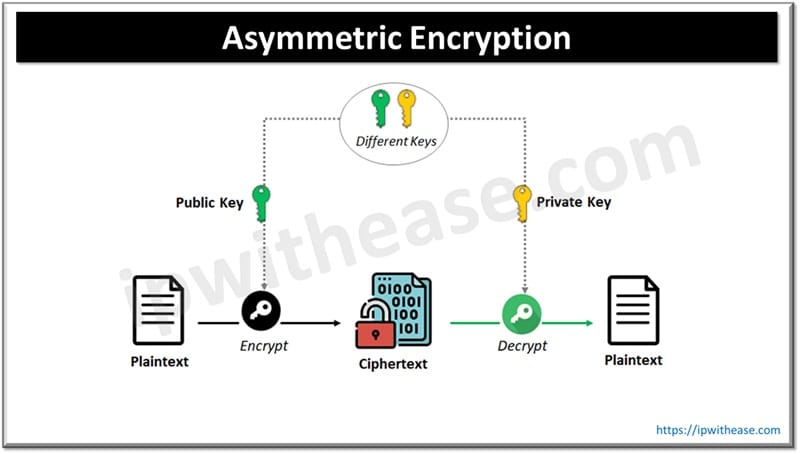
2. Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption or public key encryption as it is commonly known as. It helps to resolve key exchange problems. There are two keys used to encrypt plain text in this encryption technique. The secret keys are exchanged and whosoever has the secret key can decrypt the message hence asymmetric encryption uses two keys to increase safety. Anyone who wishes to send a message will have a public key but the secret key is held secret. A message encrypted with a public key can be decoded using a private or secret key. Message encrypted with private key can be decrypted using the public key.
Common Algorithms
| Algorithm | Key Size | Security Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSA | 1024–4096-bit | High | Widely used in SSL/TLS |
| ECC | 160–521-bit | High (shorter key) | Used in mobile, IoT |
| Diffie–Hellman | Variable | Medium–High | Key exchange only |
| ElGamal | Variable | High | Based on DH, used for encryption |
| DSA | 1024–3072-bit | Digital signatures only | US government standard |
Use Cases
- Secure email (PGP)
- HTTPS/SSL/TLS (web security)
- Blockchain and cryptocurrencies
- Digital signatures
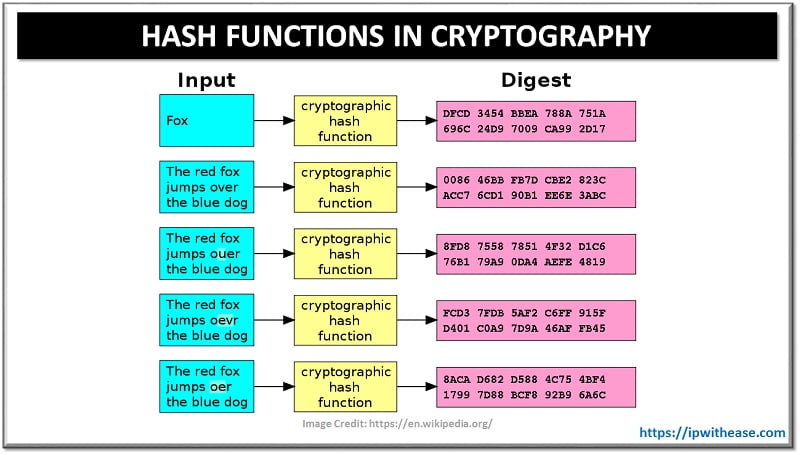
3. Hashing
Hashing is a technique which converts data that can be in any form into a unique string of data. Irrespective of size, type data can be hashed. Taking data of random length, it converts it into a fixed hash value. In hashing technique encryption is non reversable. Hashing is of two types – Static and dynamic hashing
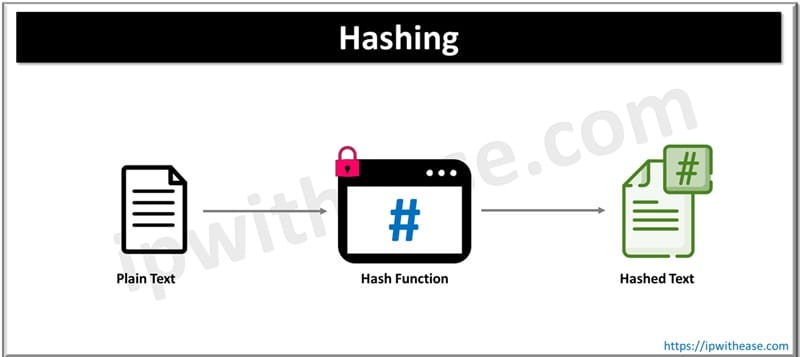
Common Algorithms
| Algorithm | Hash Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | 128-bit | Fast but insecure (collisions) |
| SHA-1 | 160-bit | Deprecated (collisions) |
| SHA-256/512 | 256/512-bit | Secure and widely used |
| SHA-3 | 224/256/384/512-bit | Newest SHA family |
| BLAKE2 | Variable | Fast and secure modern hash |
Use Cases
- Password hashing
- Digital signatures
- Data integrity verification (file checksums)
4. Message Authentication Code (MAC)
MAC combines a secret key and a message to produce a hash for authentication.
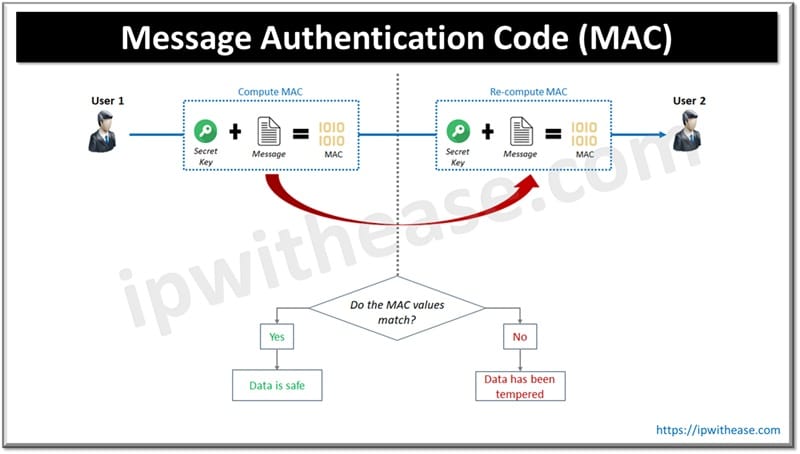
Common Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| HMAC | Hash-based MAC, e.g., HMAC-SHA256 |
| CMAC | Cipher-based MAC, e.g., AES-CMAC |
| GMAC | Based on Galois/Counter Mode with AES |
Use Cases
- Verifying data integrity in secure communication (TLS, IPsec)
- Ensuring message authenticity
5. Digital Signatures
Confirms the sender’s identity and ensures message integrity. The sender signs a hash of the message with the private key, and the receiver verifies using the sender’s public key.
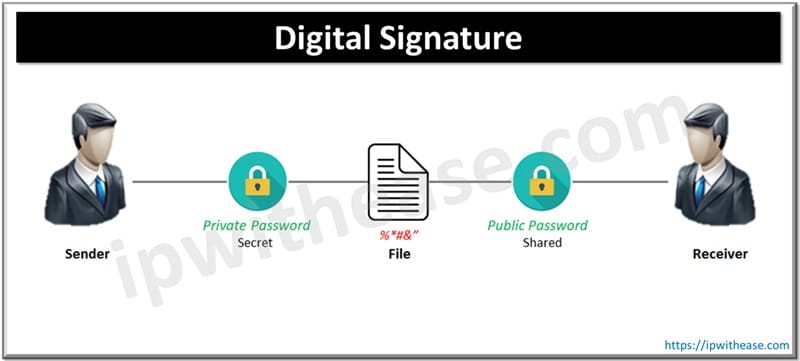
Common Algorithms
| Algorithm | Based On |
|---|---|
| RSA Signature | RSA |
| DSA | ElGamal |
| ECDSA | ECC |
| EdDSA | Ed25519 curves (fast & secure) |
Use Cases
- Software authenticity
- Electronic documents (e.g., PDFs)
- Blockchain transactions
6. Key Exchange Protocols
This is used to securely share secret keys over public networks.
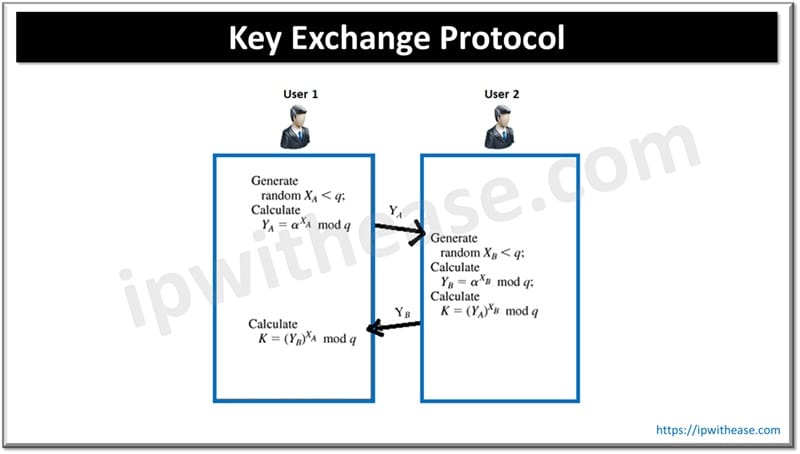
Techniques
| Method | Based On | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Diffie–Hellman (DH) | Discrete logs | Original protocol |
| Elliptic Curve DH (ECDH) | ECC | Faster and more secure |
| Post-quantum schemes | Lattices, etc. | Quantum-safe options |
Use Cases
- Initial key setup in TLS, VPNs, encrypted chat apps
7. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
It is designed to resist attacks by quantum computers.
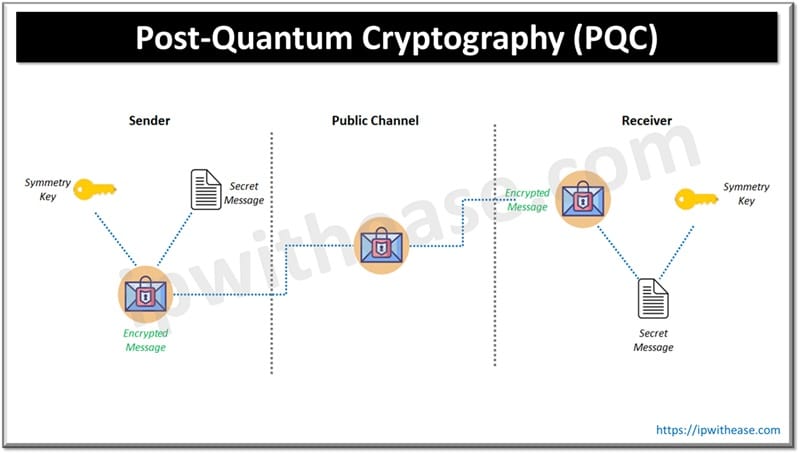
Categories
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Lattice-based | Kyber, NTRU |
| Code-based | McEliece |
| Multivariate | Rainbow (broken), HFEv- |
| Hash-based | XMSS, SPHINCS+ |
| Isogeny-based | SIDH (deprecated), CSIDH |
Use Cases
- Future-proofing secure communications
- NIST is standardizing PQC algorithms
8. Steganography (Data Hiding)
This method hides the existence of data within the media.
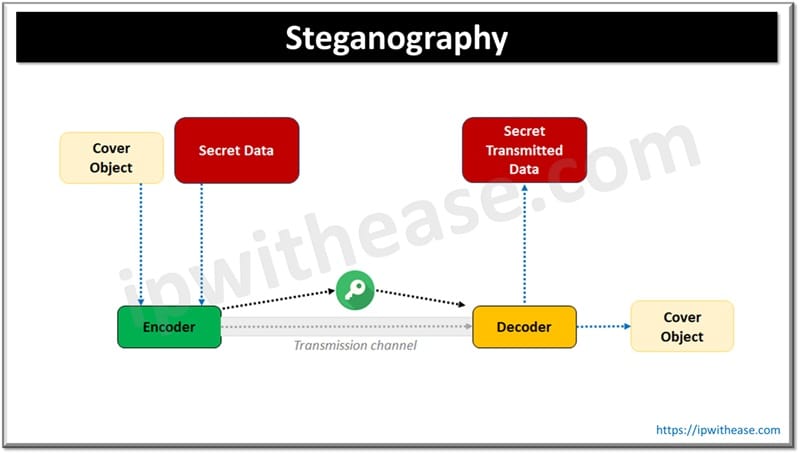
Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Image Steganography | Hide data in image pixels (e.g., LSB) |
| Audio Steganography | Embed data in audio signals |
| Text Steganography | Use invisible characters or patterns |
Use Cases
- Covert communication
- Watermarking
- Anti-piracy
To Summarize
| Type | Key Features | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetric Cryptography | Fast, same key | VPNs, file encryption |
| Asymmetric Cryptography | Secure key exchange | HTTPS, blockchain, digital signatures |
| Hashing | One-way, fixed output | Passwords, data integrity |
| MAC | Key + message hash | Secure message transmission |
| Digital Signatures | Non-repudiation + authenticity | Legal docs, code signing |
| Key Exchange | Secure secret key sharing | TLS handshake, encrypted messaging |
| Post-Quantum Crypto | Quantum-resistant algorithms | Next-gen secure systems |
| Steganography | Hidden communication | Secret data embedding |
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj