Table of Contents
ARP is quite an essential protocol in LAN Networking. Computer systems will be unable to communicate with each other in LAN if ARP is not present. Just to refresh our understanding of ARP, when an end host or computer in LAN environment wants to transfer data to another host (like computer etc.) it must first know the MAC Address of the destination.
If the destination host MAC address entry is not there, in this case, ARP protocol sends a broadcast out to the LAN network asking for the MAC address of the destination host IP address. The machine with the IP address will respond with its MAC address. There are other scenarios also where ARP is used, however, we’ll now move our attention further to ARP timeouts and related flags.
Related – TYPES OF ARP
ARP Flag Types (Linux)
ARP flags are used in ARP messages to indicate the purpose or status of an ARP request/reply. These flags help network devices interpret ARP communication correctly.
Next let’s look at the ARP flags types especially in Linux system. ARP flags in Linux are the ones that will help us understand what type of entry is being placed in the memory as seen in the ARP table flags. Below is the output from “ARP –n” command statement where Flags are highlighted in RED circle –
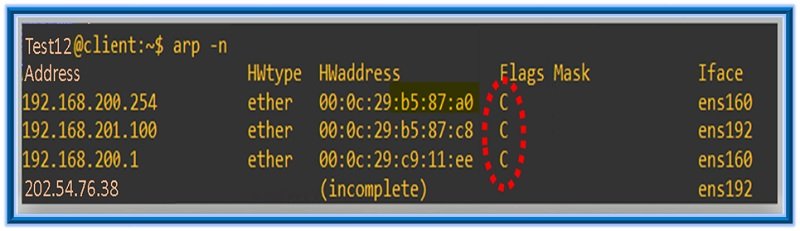
Based on the above output, 3 of the entries are showing Flag Type as “C”. Further, lets understand other flag types. There are 3 type of Flags in Linux
- C = This type of entry is seen when entries are dynamically learned by ARP protocol.
- M = This flag tells that entries have been manually entered/added in the memory instead of dynamically learned from ARP protocol.
- P = P here means Publish. It tells the host to respond to packets which are ARP request and ARP response.
Common ARP Flags in Linux
These flags are seen when managing the ARP table using ip neigh:
| Flag | Meaning |
| PERMANENT | A static (manually configured) ARP entry that never expires. |
| REACHABLE | The MAC address is known and recently used. |
| STALE | The entry exists but hasn’t been used recently. A new ARP request will be triggered when needed. |
| DELAY | The entry is waiting for a reply to an ARP probe. |
| PROBE | The entry is being validated by sending an ARP request. |
| FAILED | The ARP resolution failed (no response received). |
| INCOMPLETE | An ARP request has been sent, but no reply has been received yet. |
| NOARP | The interface does not use ARP (e.g., point-to-point links). |
How to view ARP Flags in Linux
To check ARP flags, use:
ip neigh showExample output:
192.168.1.1 dev eth0 lladdr 00:1a:2b:3c:4d:5e REACHABLE
192.168.1.2 dev eth0 STALE
192.168.1.3 dev eth0 INCOMPLETEARP Timers
ARP Timers manage the ARP Entries from a device’s ARP cache. They manage the how the entries are updated, stored or deleted. There are different ART Timer types depending upon the OS and different network devices.
Types of ART Timers
Some of the commonly used ARP Timers are:
Timeout Timer (Aging Timer)
ARP timeout means how much time the system will keep the dynamic leaned MAC address on its memory before flushing it if it’s not reused. Many of the networking systems have a timeout of 20 minutes for a completed entry and 3 minutes for an incomplete entry. However, there are an array of vendors in networking markets who have created their own standard timeout values for Address Resolution protocol. Below are the default ARP cache timeout of few vendors:
ARP Timeout values:
| VENDOR | Timeout Value |
| Cisco | 4 hrs |
| Juniper | 6 hours |
| Netscreen firewall | 20 min |
| Palo Alto | 30 min |
| Huawei | 20 min |
| Netgear | 20 min |
| Nexus 7000 | 25 min |
| Arista | 24 min |
Download the table: Vendor ARP Timeout values
Retry Timer
It determines how often the request is resent or retried in case of no response. Thus helps ensure connectivity by attempting to resolve the address multiple times before failing. The default retry timer value ranges from 1-5 seconds per entry.
Reachability Timer
It is used in advanced ARP implementations or in the Neighbor Discovery Protocol for IPv6. It is used to find out how long a resolved entry is considered reachable before revalidation is required. The value ranges from 30 seconds to a few minutes.
Delay Timer
It defines a short delay before an ARP entry is added to prevent ARP poisoning attacks. Thus, used in security implementations to validate a response before caching.
Dynamic Entry Timeout
It expires based on the timeout timer.
Static Entry Timeout
It remains permanent/static until removed manually.
Gratuitous Timer
It controls how often Gratuitous ARP or GARP messages are sent to detect duplicate IPs and update switches’ MAC tables.
Hope this article helped our viewers with concepts of –
- ARP Timeouts with different vendor devices
- ARP Flag types in Linus Operating System
Related – ARP VS RARP
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj