Table of Contents
The cyber threat landscape is changing very fast and making organizations vulnerable to subtler cyber-attacks, the conventional methods of threat detection proving to be futile. As attackers are launching sophisticated cyber-attacks to avoid disclosure of their identity. The solution to this problem requires a preventive mind-set rather than a detective mind-set so as to neutralize threats before they reach us.
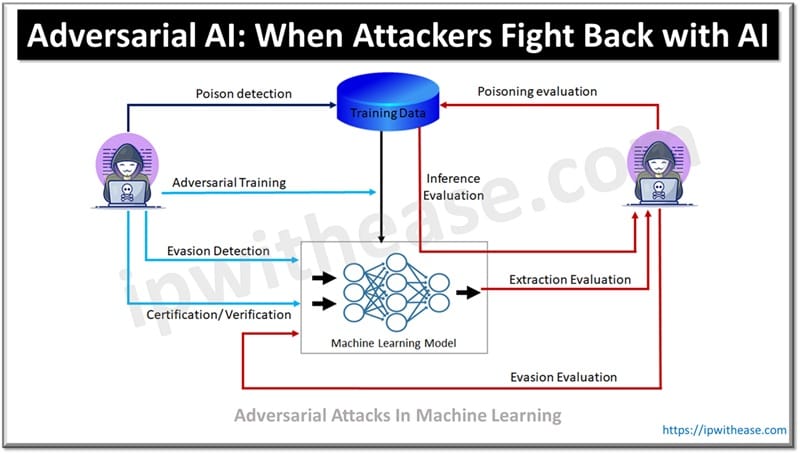
Artificial intelligence is a transformation agent in threat hunting as it automates detection, analyses massive data sets and does threat identification in real-time. Traditional security measures fail against advanced cyber threats making AI an ideal candidate in the modern cybersecurity landscape. AI-powered machine learning models, real-time anomaly detections and behavioral analytics can detect zero-day attacks, insider attacks, and sophisticated malware and ransomware. However, AI is not untouched by its own concerns related to False+ves, adversarial attacks and data privacy issues still AI powered SIEM solutions, NDR and EDR are providing valuable contributions in neutralizing cybersecurity threats.
In this article we will learn more in detail about the role of artificial intelligence in threat hunting.
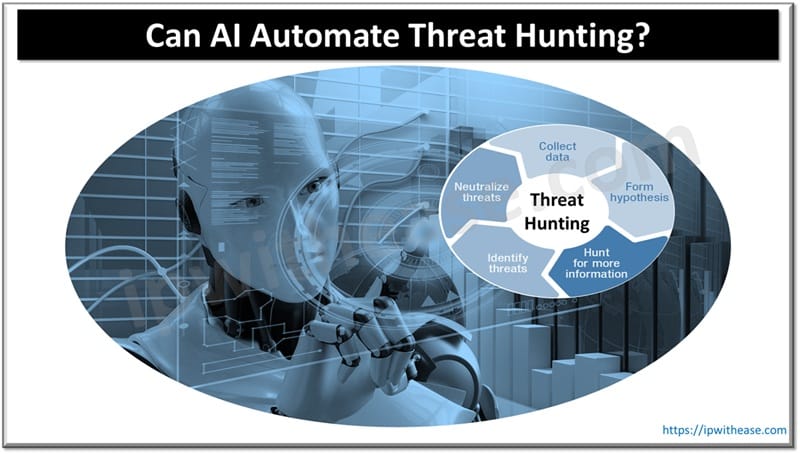
What is Threat Hunting
Threat hunting is discipline in cyber security that looks for or rather searches for advanced threats that have been there and evaded traditional security solutions such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems and malware programs. Threat hunters do behavioral analysis, use forensic techniques, and monitoring of networks to identify malicious activities and perform log analysis. Manual threat hunting is a daunting task as it involves human expertise, looking into massive logs, using static rule based detections often resulting in delays in detection, high False+ves and missing alerts.
AI in Threat Hunting
- Real-time data analysis – AI enabled threat hunting tools can analyse vast amounts of security logs, network traffic and analyse system behavior in real-time. Machine learning (ML) models detect anomalies and patterns which may indicate a potential attack happening.
- Anomaly detection and behavioural analytics – AI can detect deviation from normal behavior in user activities, system interactions and network traffic flows. For example, user is accessing important files at odd hours
- Integration of threat intelligence – threat intelligence databases are constantly updated from various sources such as dark web monitoring, past attack patterns. This helps in proactive identification of attacks to prevent potential breaches
- Threat prioritization automation – AI can filter thousands of security alerts and can prioritize threats based on its severity, risk exposure and potential impact. This helps security teams to only work on actual threats which need attention.
- AI driven threat attribution – AI can be used to correlate attack indicators with already known threat actors to provide valuable insight into understanding attacker identity, its motivation, tactics and technique used to infiltrate networks.
- Improved Incident response – Advanced AI threat hunting tools can be integrated with organization Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to correlate, detect, automated incident response. Isolation of compromised endpoints, blocking of malicious IP addresses and triggering remedial actions without needed humans.
Challenges of AI in Threat Hunting
Though AI is a powerful medium which bought significant improvement in threat hunting however it is not without challenges:
- High number of False Positives – AI models at times flag normal behavior suspicious and marked it as suspicious activity leading to false positive scenarios
- Adversarial attacks – cyber attackers are also utilizing AI to create AI resistant malware which can bypass machine learning based detections
- Data privacy issues – AI driven threat hunting tools process vast amount of enterprise data which is questionable under privacy and compliance
- Need for human expertise – AI can assist in detections but can’t replace qualified and skilled cyber specialists which can interpret complex cyber threats with human reasoning capabilities to make critical decisions
Use Cases of AI Powered Threat Hunting
- AI powered endpoint threat detection and response tools such as Microsoft defender, Crowdstrike Falcon and Sentinel One are some examples here
- AI powered network threat detection and response tools such as Darktrace and Cisco Secure Network Analytics
- Google AWS GuardDuty and Google chronicle use AI to continuous monitoring cloud security posture landscape
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj