Table of Contents
As more and more organizations are adopting cloud computing there are growing concerns around data security and safety. Businesses need to understand what is the cloud security architecture of provider organizations more in depth to assess exposure to security of their data in third party hands. How provider organizations have deployed security measures to protect cloud-based systems, data and infrastructure. What security measures are implemented to safeguard cloud resources against unauthorized access, data breaches and cyber threats.
In today’s topic we will learn about Cloud computing security architecture and its five key components.
Introduction
Cloud computing security architecture is a framework of policies, procedures, controls and technologies to safeguard cloud-based systems data and infrastructure. Under its umbrella, there are security measures implemented to protect cloud resources against access violations, data breaches, cyber attacks and violations related to compliance. It is a holistic approach towards securing the cloud ecosystem with technical, operational, process-based compliance measures to protect against ever evolving cyber threats.
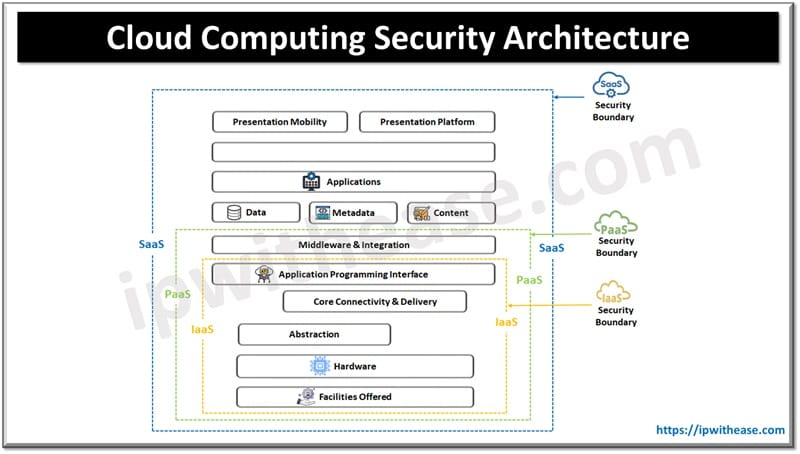
5 Key Components: Cloud Computing Security Architecture
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and access management (IAM) is all about management of access to cloud resources and what actions can be taken on those resources and by whom. IAM systems enforce policies, perform management of user identifies, provide audit trails of access and so on. IAM plays a crucial role to mitigate insider threats and this is achieved by implementation of ‘least privilege’ principle and segregation of duties (SOD). Organizations can limit potential damage caused by malicious insiders by following these two IAM practices and IAM also help in detection of unusual user behaviour, early warning signs of potential security breaches.
Network Security
Network security involves protection of data when it traverses within the network and is responsible to maintain its confidentiality, integrity and availability. Network security measures encompass firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/ IPS), virtual private networks (VPN) etc. All cloud providers offer a VNET or VPC feature to allow enterprises run private, secure and segregated private networks for each customer within cloud data centers.
Robust security measures related to the network are required especially in cloud computing environments where data travels over the Internet to reach its destination.
Data Security
Data security involves protection of data during REST, during TRANSIT or when it is in USE. It encompasses measures such as encryption, tokenization, randomization, pseudonymization, data loss prevention (DLP) solution implementation, secure key management practices etc. a critical aspect of data security in cloud is applying access controls and secure configuration to cloud storage accounts and cloud hosted databases. With propagation of data breaches and regulatory laws such as California privacy act (CCPA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) etc. data security has become top priority of organizations from compliance perspective as failing to comply with cloud regulation could result in heavy penalties and fines.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security focus is securing the endpoints or user devices connecting to access cloud resources, such as laptops, mobile phones, tablets etc. remote working has brought along with it the concept of BYOD – bring your own devices at work security is becoming a more critical aspect in cloud computing. Organizations need to ensure only secured devices are connecting to their cloud networks. Endpoint security measures include – antivirus, firewalls, device management solutions, web filtering controls etc. Endpoint security also involves user security awareness and training components to help end users to identify potential threats such as phishing etc.
Application Security
Application security is a vital aspect of cloud security as it involves security applications hosted on cloud and which require protection against cyber threats such as SQL injection attacks, Man in the middle attacks, cross site scripting (XSS), etc.
Application security is achieved via various means such as ensuring adoption of securing coding practices, vulnerability scans, container scans, and infrastructure as a code scan, penetration testing, runtime application protection (RASP) and web application firewalls (WAF) to provide additional layers of security to cloud based applications.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj