ATA – Abbreviation for Analog Telephone Adaptor, an ATA is a hardware device that connects analog telephones, PBX systems, fax machines, door alarms and similar devices to digital systems or an internet or IP based telephony network.
Codec – A codec is short for of coder-decoder. Codec converts an audio signal i.e. voice into compressed digital form for transmission and then back into an uncompressed audio signal for replay.Codecs generally provide a compression capability to save network bandwidth. They are especially useful for VoIP communication, video streaming and video conferencing.
DID – Abbreviation for Direct Inward Dialing , DID is method of directly dialing the number of a IP Phone or a telephone attached to a PBX without routing calls through an attendant or an automated attendant console.
PBX (Private Branch Exchange) – A PBX is the hardware and software that comprise a business telephone system. Internet enabled PBX technology is called IP PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange).
FXS stands for Foreign Exchange Subscriber and at times also called Foreign Exchange Station. FXS interface delivers POTS service from Phone Company’s Central Office (CO) and connects to subscriber equipment (telephones, modems, and fax machines). FXS interface points to the subscriber and provides the following primary services to a subscriber device:
- Dial tone
- Battery current
- Ring voltage
FXO – FXO stands for Foreign exchange Office. FXO interface receives POTS service from Central Office of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) An FXO interface provides the following primary service to the Telco network device:
- On-hook/off-hook indication (loop closure)
Related- FXS vs FXO
AAR – The Automated Alternate Routing feature enables Cisco Unified Communications Manager to establish an alternate path for the voice media when the preferred path between two endpoints is out of available bandwidth.
SRST – Stands for Survivable Remote Site Telephony. SRST provides remote site survivability in the event of WAN outage. SRST is an IOS router feature for supporting branch end locations.
ISDN – Integrated Services Digital Network – ISDN is a circuit switched telephone network system, designed to allow digital and not analog transmission of voice and data over ordinary telephone copper wires, resulting in better quality and higher speeds.
POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) – A single phone line and a single phone number. Home phones and dedicated fax lines are good examples of POTS.
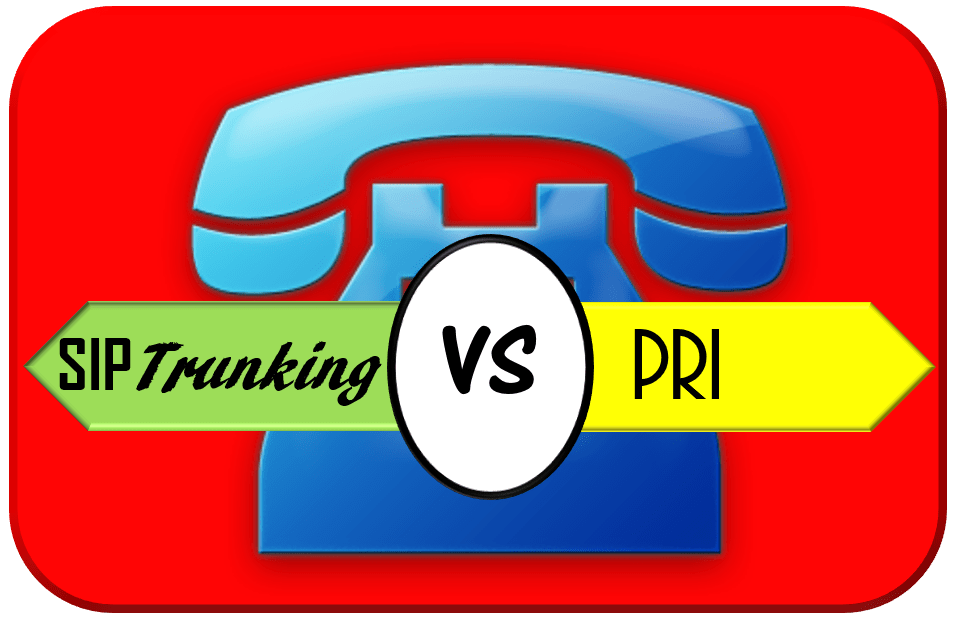
PRI (Primary Rate Interface) – PRI is a physical connection to the PSTN over a dedicated line that only serves voice transmission. Traditional business telephone systems leverage PRI.
SIP Session Initiation Protocol is a signaling protocol for Internet conferencing, telephony, and instant messaging. It is a request-response protocol, dealing with requests from clients and responses from servers.
IVR is abbreviation for Interactive Voice Response. It is a computerized system that allows a person, typically a telephone caller, to select an option from a voice menu and otherwise interface with a computer system.
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. DHCP is used to control the network configuration of a host through a remote server. DHCP is an excellent alternative to the time-consuming manual configuration of network settings on a host or a network device. DHCP works on a client-server model.
QoS stands for Quality of Service and refers to a network that guarantees a certain level of performance and quality. QoS is based on standard metrics and involves prioritizing traffic. Voice data packets are extremely sensitive to time delays in reaching their destination. By implementing certain QoS rules, you can instruct the network to give priority to voice packets while other types of data are queued for their turn.
Jitter – VoIP technology works by converting sound into digital packets that are sent over an active internet connection. When data packets arrive out of order, you experience audio jitter which sounds like a stutter.
ACD – Automatic Call Distribution. A feature/service used to distribute calls to call center agents.
Automated Attendant – An automated answering point for incoming calls to a company. Usually this is included as a feature in the voice mail system.
BHCA – Busy Hour Call Attempts. A measure of the maximum number of call attempts the system can support. Generally, BHCA and BHCC are considered to be the same.
IPCC – Cisco IP Contact Centre (IPCC) is an IP application that delivers intelligent call routing, network-to-desktop CTI, and multimedia contact management to contact centre agents over an IP network.
IP phone – A phone that transports voice over an IP network using IP data packets instead of circuit-switched connections over voice-only networks.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj