Difference between BIOS and CMOS
Difference between BIOS and CMOS
In computer system, especially the motherboard, there are 2 key components –
- BIOS
- CMOS
In this article we will understand both the terminologies in detail. Also, how are they related and differences in their features/attributes.
What is BIOS?
BIOS implies to Basic Input Output System. It is a pre-installed program on windows based computer systems. BIOS is used to start the computers. BIOS is the first program installed in windows computers even before the operating system.
When we power on a computer, the CPU approaches the BIOS to find out all Input-Output devices and to look over if all hardware connections are properly functioning. BIOS is the one which loads the operating system in to the computer memory, thus completing the booting process.
BIOS is a part of the motherboard. It is stored in the permanent memory called non-volatile Read-only Memory or Erasable Programmable Read-only Memory (EPROM) chip or Flash Memory on the Motherboard of a computer. EPROM and Flash memory is used to upgrade the BIOS program as we can change the contents of EPROM and Flash memory.
Once the booting process is complete, the BIOS acts as an intercessor between the Input-Output devices and the CPU. All hardware details of the computer are known and managed by the BIOS. Whenever IO device changes, the information needs to be communicated to the BIOS.
Related – RAM vs ROM
Main Functions of BIOS
Power-On Self-test (POST): The primary function of BIOS is to check whether computer hardware is functioning properly and there is no issues with the hardware. It is done by POST. If POST fails, computer generates different beep sounds to indicate the error.
Bootstrap Loader: Once POST is done, BIOS looks for capable operating system. If found, it will pass control to the operating system. This is called Booting.
BIOS Drivers: BIOS drivers are low level drivers. Low level drivers are a collection of programs which are stored in non-volatile erasable memory chips. They give basic information about computer hardware and also give basic operational control over computer hardware.
BIOS setup or CMOS setup: BIOS setup is a configuration program that allows us to configure computer hardware settings like passwords, time and date.
When we switch on our computer, the sequence of things done by BIOS are as follows:
- Inspect the CMOS Setup for custom settings
- Freight the interrupt handlers and device drivers
- Boot the registers and power management
- conduct the power-on self-test (POST)
- show the system settings
- Identify which devices are bootable
- Start the bootstrap sequence
With the latest OS from Microsoft, you may want to set up your BIOS and enable Windows 11 Secure Boot to upgrade from Windows 10.
What is CMOS?
CMOS technically stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor. It is a physical portion of the motherboard. CMOS is a memory chip that holds configuration settings and is supported by the onboard battery called CMOS battery. CMOS battery is an associated component that offers power for Real Time Clock whether the computer is switched on or off. Whenever changes are made in BIOS configuration all the changes are stored to CMOS chip.
The lifetime of a CMOS battery is around 10 Years. When the battery drains out of energy, CMOS is reset, loses all the custom settings and system clock is also reset. The CMOS returns to factory settings when the power is not coming from the battery. It’s a regular practice to remove the battery to recall CMOS settings if there is a configuration problem.
CMOS stores a small amount of data, usually 256 bytes. The information on the CMOS chip contains different types of disk drives that are installed, the current date and time of the system clock, and the computer’s boot sequence.
Boot Device Selection
Boot Device Selection is one of the most important roles of CMOS. It can change the device boot process. This is the key for system restoration because the CMOS may need to alter boot priority from the hard drive to the optical drive or flash drive to initiate the operating system installer or alter which hard drive to load the operating system.
Motherboards embody a jumper which is used to clear CMOS settings if systems BIOS is not accessible. Jumper is useful especially in the cases like BIOS is password-protected and user don’t know the password.
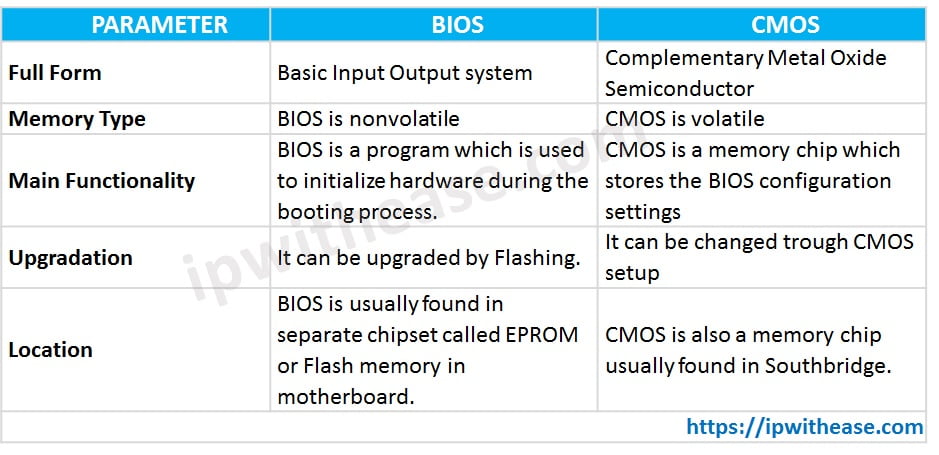
Comparison Table: Difference between BIOS and CMOS
The key difference between BIOS and CMOS are as follows
| PARAMETER | BIOS | CMOS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Basic Input Output system | Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor |
| Memory Type | BIOS is nonvolatile | CMOS is volatile |
| Main Functionality | BIOS is a program which is used to initialize hardware during the booting process. | CMOS is a memory chip which stores the BIOS configuration settings |
| Upgradation | It can be upgraded by Flashing. | It can be changed trough CMOS setup |
| Location | BIOS is usually found in separate chipset called EPROM or Flash memory in motherboard. | CMOS is also a memory chip usually found in Southbridge. |
![]()
Download the comparison table here.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

 Difference between BIOS and CMOS
Difference between BIOS and CMOS