Table of Contents
Have you wondered how your mobile device switches between different network providers? Or how did your uk eSIM work during your last vacation? The answer lies in two tiny technologies: eUICC and eSIM. While they both relate to the way connections to cellular networks are enabled, they have different functions.
Confusion in the usage of these two terms often arises because eSIM technology relies on eUICC functionality. When you hear about eSIM-capable devices, they’re usually also eUICC compatible. This means they can store multiple SIM profiles. But what does all this tech-speak mean? Let’s go into the fine details below:
Origin of eUICC and eSIM
Traditionally, SIM cards were physical chips and used to be bigger. They enabled a device to be recognized on a carrier network by the profile ID associated with it. To switch a carrier network, you’d have to manually swap the SIMs.
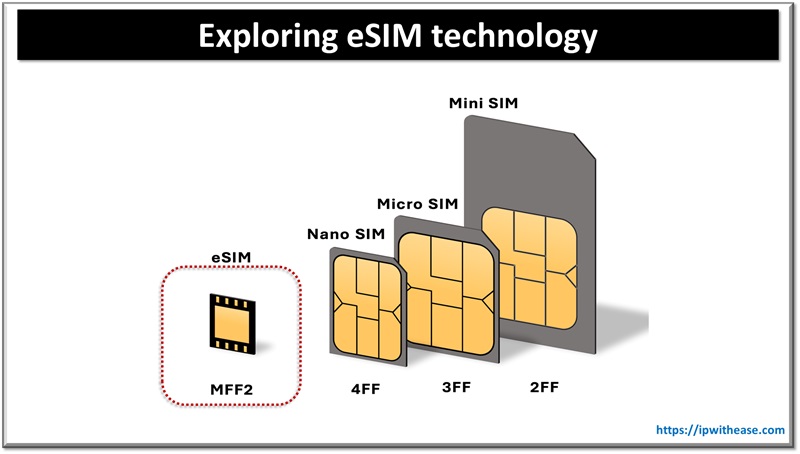
However, over time technology evolved as devices became more portable. The first bulky SIMs, referred to as the first form factor of SIM (1FF), became smaller with time. The evolution progressed as follows:
1FF >> 2FF (mini-SIM) >> 3FF (micro-SIM) >> 4FF (nano-SIM) >> eSIM
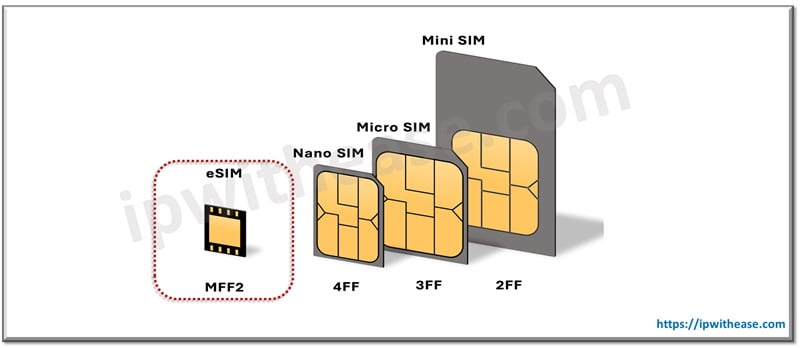
When eUICC (Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card) technology was introduced, it allowed devices to store multiple SIM profiles digitally. This new capability presented opportunities to explore the technology for eliminating physical cards.
Thus, the eSIM was born. Instead of physically inserting a SIM in a device, the eSIM came already embedded in the device. This freed up space in gadgets and made them more durable.
What is eUICC?
eUICC stands for Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card. Remember, the eUICC is the technology that manages and/or stores SIM profiles from different carrier networks. Simply put, the functionality of the eSIM ecosystem depends on the eUICC.
The eUICC is made for remote management and is rewritable. It is responsible for:
- Remote reconfiguration that allows users to switch between carrier networks wirelessly without physically swapping SIMs.
- Storing information from different mobile network operators.
What about eSIM?
The eSIM stands for embedded SIM. This is the technology that encompasses:
- the eSIM chip
- the SIM profile
- the remote provisioning environment.
The eSIM serves as a digital option to the traditional and physical SIM cards. It allows devices to have a SIM card embedded directly into them without the need for a physical card. The eSIM is soldered into the device (the motherboard) and can store multiple network carriers’ profiles in a single device!
Understanding the Difference
So far, you have seen there are considerable differences between the eUICC and the eSIM. Yet, many people use the terms interchangeably. The key difference is in their functionalities.
Basically, the eSIM is the physical SIM chip that is embedded in the device. Although it is a physical or hardware component, it cannot be removed without physical distortion of the device. It enables devices to connect to different cellular networks. This is without needing a physical SIM card and is made possible through a remote provisioning platform.
The eUICC, on the other hand, is a feature component that determines how multiple SIM profiles are managed. It also carries out this function using a remote positioning platform.
Benefits of the eUICC and eSIM Technologies
Convenience
With eUICC, you can switch carriers without needing to physically swap SIM cards. This is great for travelers or people who frequently change their network plans.
Flexibility
eUICC-enabled devices offer more flexibility in choosing your network provider. You can easily switch to one with better coverage or pricing.
Space Saving
eSIM removes the need for a physical SIM card. This frees up space in devices for other components.
Remote Provisioning
Both eUICC and eSIM technology allow for remote provisioning of SIM profiles. This makes it easier for carriers to change network plans without requiring a physical visit.
Conclusion
eUICC and eSIM are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of SIM technology. eUICC is about the capability to store multiple SIM profiles, while eSIM is the physical chip that enables devices to connect to cellular networks remotely. Understanding this difference can help users make informed choices when selecting devices and plans.
Continue Reading:
Exploring eSIM technology: How it works, benefits, and impact on telecom
The Estimated Annual Growth Rate of AI In Telecommunications Industry
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.