Table of Contents
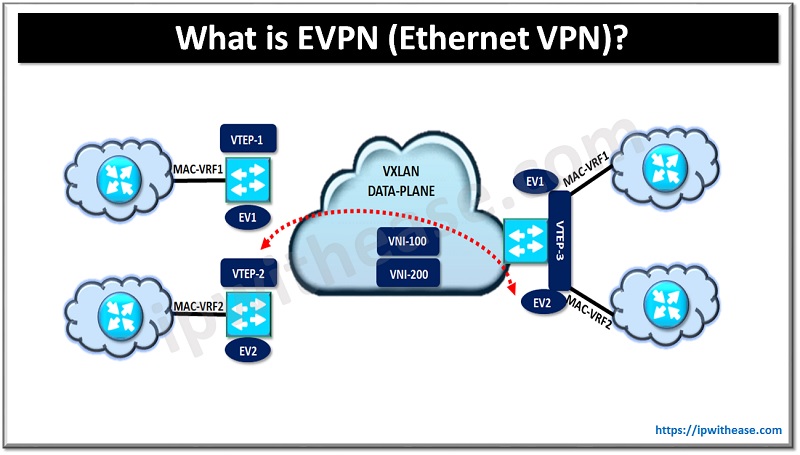
What is EVPN?
An EVPN or Ethernet VPN is a BGP based control plane mechanism for VXLAN to advertise the MAC addresses, MAC-IP bindings & IP Prefixes. Apart from EVPN, there are a variety of control plane mechanisms that exist today for VXLAN i.e. Multicast, Head End Replication & Controller-Based mechanisms.
Multicast & HER are the static control plane mechanism which operate on the flood and learn mechanism i.e. MACs are learnt via the flooding.
Related – What is VXLAN
Multicast
You will learn the MACs in underlay via the flooding to a Multicast group. With other control plane mechanisms available, this method today has become obsolete and is rarely used.
Head-End-Replication
In this method you will have to manually define the remote VTEPs under the VXLAN tunnel configuration. The BUM (Broadcast, Unknown Unicast and Multicast) traffic will only be sent to those VTEPs which are configured manually.
EVPN (Controller-Based mechanism)
In this control plane method, we use the MP-BGP to dynamically populate the flood-list for BUM traffic and post dynamic discovery then advertise the MAC addresses, MAC-IP bindings and IP prefixes. MAC addresses are not learnt via Flood and Learn mechanism and hence this method is less BW intensive but at the same time is complex to configure and troubleshoot.
Related – Top VXLAN Interview Questions
EVPN Terminologies
- Network Virtualization Overlay (NVO): Overlay network for delivering layer2 and layer 3 VPN services. Example: VXLAN domain having one or more VNIs to carry the application/user traffic over common underlay IP fabric.
- Network Virtualization End-Point: The nodes in NVO environment used to encapsulate the traffic in the overlay network. Analogous to VTEP in VXLAN domain.
- EVPN Instance: Logical Switch within the EVPN domain to connect multiple VTEPs providing the L2 and L3 connectivity.
- MAC-VRF: VRF aware MAC table to store the MAC addresses on a VTEP for a specific Tenant.
Understanding the Concept of Ethernet VPN
In EVPN environment a new BGP NLRI message is carried using MP-BGP using newly defined address family EVPN. AFI (25) & SAFI (70).
In DC environment we often need multi-tenancy support where traffic from multiple tenants will traverse the same NVEP, hence to keep traffic segregated from multiple tenants we use MAC VRF and IP VRFs. You can imagine it to be similar to service provider environment where multiple CEs connect to Service Provider PE routers and traffic for each customer is kept segregated with the help of VRFs on PE.
EVPN Route Types
Type 1
Ethernet A-D (Auto Discover) route is used to announce the reachability of the Multi-homes Ethernet Segment. For this to be advertised the ESI (Ethernet Segment Identifier needs to be the same). It is used for fast-convergence, advertises the Split Horizon Label and also is known as Mass Withdraw route.
Type 2
It is used to advertise the MAC addresses or MAC-IP bindings (optional). We can achieve ARP suppression when using the MAC-IP advertisement.
Type 3
This route allows for the dynamic discovery of the remote VTEPs for BUM traffic flooding.
Type 4
The route is used to discover VTEPs which are attached to the same shared Ethernet Segment. Additionally, this route type is used in the Designated Forwarder (DF) election process
Type 5
It is used to advertise the IP prefixes from the remote VTEPs and provide the L3 VPN topologies.
Advantages of EVPN
- Flexibility: Because EVPN-VXLAN is a multi-protocol technology, it is simple to integrate into existing networks. Additionally, EVPN-VXLAN shares common architectural components with other popular network services such as VPNs, making it easy to implement.
- Scalability: Enterprises may scale up their networks by adding new switches without any redesigning of the underlay network. Adding new switches without any redesigning of the underlay network is simpler because of the EVPN-VXLAN-based architecture.
- Enhanced Security: The fine segmentation of the network makes it more difficult for hackers to inflict damage. It also enhances security by restricting traffic flow between all connected devices in the network, as well as restricting the blast radius of assaults.
- Better Resilience: Spine-leaf architectures have less of an impact on fabric performance as a result of lower latencies between devices.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj