Use of physically separate infrastructure like Fibre Channel (FC) for Enterprise application traffic and storage increases Capex and Opex, makes data center management more difficult, and decreases business flexibility.
A unified fabric can meet these challenges faced by consolidating I/O in the data center and allowing Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks to share a single, integrated infrastructure. Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is one of the major components of a Unified Fabric. iSCSI and FCoE are two important technologies that vendors support to provide Unified Fabric solutions.
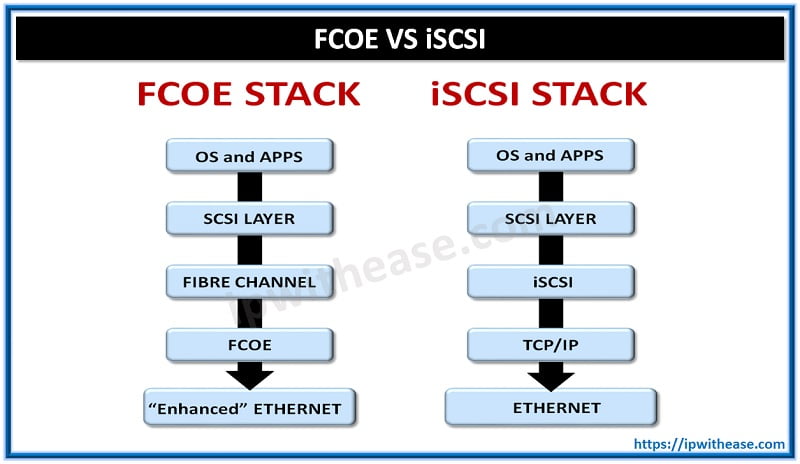
FCoE supports standard Ethernet cards, cables and switches to handle Fibre Channel traffic at the data link layer, using Ethernet frames to encapsulate, route, and transport FC frames across an Ethernet network from one switch with Fibre Channel ports and attached devices to another, similarly equipped switch.
Small Computer System Interface over IP (iSCSI) is a mature technology created by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It is based on the IP protocol stacks, it assumes an underlying unpredictable network and gives to TCP the recovery of lost packets.
Let’s further deep dive and understand the difference between both FCOE and iSCSI technologies.
FCoE vs iSCSI
| PARAMETER | FCoE | iSCSI |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation for | Fibre Channel over Ethernet | Internet Small Computer System Interface |
| Protocol Mapping | Mapping of Fibre Channel over Ethernet | Mapping of SCSI over TCP |
| Skillset | Ethernet FC expertise required to implement/manage FCOE | Skill set required to implement iSCSI is similar in many ways to general network operation |
| Configuration steps | Configuring FCoE requires - More network configuration steps Fewer configuration steps on each individual host when compared with iSCSI | Configuring iSCSI requires Fewer configuration steps in the network when compared with FCoE. More work on each individual host |
| Network / end node centric control | FCoE control is Network-centric i.e. FCOE relies on fact that the network will control what each end device has access to. This control is centrally managed and requires a special set of FC skills to administer properly | iSCSI is End-Node-centric. iSCSI relies on the fact that the network will allow communication between the iSCSI Initiator and what iSCSI Target the Server Admin directs the Initiator at. control is managed at each individual end point |
| Target customer | Large Enterprise | SMB |
| Performance | High | Lower than FCOE |
| Tolerance | High | Lower than FCOE |
| Distance Supported | Required FCIP for Supporting long distance | Supports long distance |
| Cost | Higher than iSCSI | Lower than FCOE |
| Platforms | Nexus 7K , 6k and 5K and Cisco MDS9700 ,9200 etc. | All network switching platforms like Cisco catalyst 3800,2900 etc. |
| Layer 3 Routing | FCoE is not routable at the IP layer, and will not work across routed IP networks | Routable across networks |
| Standard | Standard published in 2009 | iSCSI was ratified as a standard in 2004 |
![]()
Download the difference table here.
Watch the video –
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj