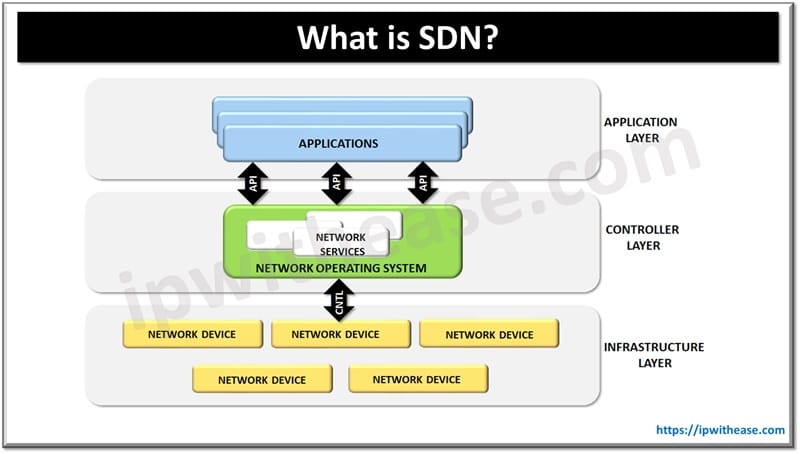
Introduction to Kubernetes
Kubernetes is an open-source software platform developed to manage services and workloads by containerizing applications within the system.
For a time-saving booster, you can automate the deployment of clusters, which are groups of containers in Kubernetes. While automating Kubernetes cluster deployments can be initially challenging, several tools make this process user-friendly and secure.
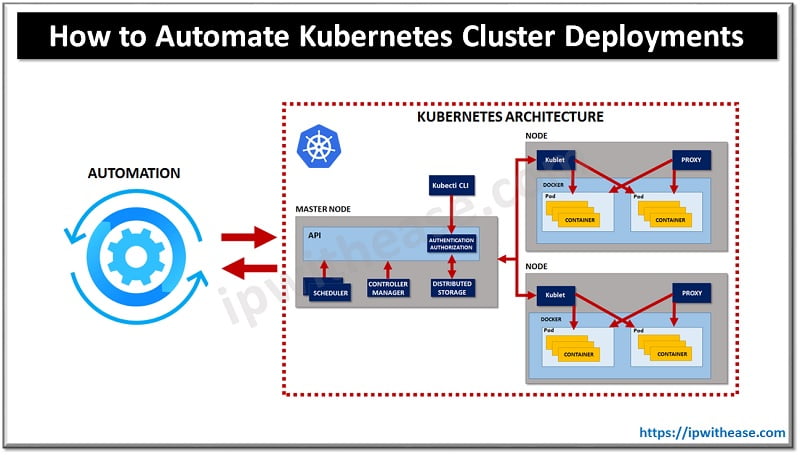
Explore the following six tools to assist in setting up automated cluster deployments.
Cluster deployment automation using Rancher Kubernetes Engine (RKE)
Rancher RKE is a Certified Kubernetes Conformance program (CNCF-certified) generic distributor. It is an ideal tool for automating cluster deployments thanks to its simplification of the installation process and automated operation and use of FIPS to improve security standards. You can use RKE-powered tools like these to automate your next cluster deployment.
RKE’s strength lies in the simplicity that it provides users, which is one of Kubernetes’ most significant weaknesses.
Cluster deployment automation using Ansible
Ansible is a tool that utilizes configuration management to help automate Kubernetes cluster deployments.
Ansible is an incredibly desirable platform in large part because it allows IT administrators the ability to automate repetitive duties from start to finish.
Cluster deployment automation using Kubernetes Operations (Kops)
Setting up automated kubernetes cluster deployments with Kops is significantly more accessible and streamlined than setting up deployments manually. It also reduces any friction when scaling up the cluster or any nodes.
Kops is an excellent tool for setting up automated deployments because it offers a high degree of customization.
Cluster deployment automation using Spellbook
Ubuntu developed Conjure-up, which gives users the ability to cast “spells” to “summon” large software stacks. Conjure-up is modeled after Juju’s framework from Canonical.
Using this framework, Conjure-up created “conjure-files,” which allow users the ability to cast “charms” that set specific parameters on the spells or software stacks before summoning or deploying them.
Cluster deployment automation using Playbook
Automated cluster deployment with Playbook utilizes Kubespray, built using Ansible’s deployment and provisioning capabilities. Because of this integration, Kubespray is a highly customizable amalgamation of Ansible’s Playbooks.
Kubespray abstracts and automates tasks such as creating and planning to deploy clusters. Furthermore, Kubespray supplies supplementary playbooks that assist in the automation of updating, scaling, and upgrading clusters.
Unfortunately, it cannot self-orchestrate or manage like Kops, but it somewhat remedies this weakness by offering Terraform support for public clouds.
Cluster deployment automation using Kube-AWS
Like Kops, Kube-AWS is a command-line automation tool that allows you to alter and deploy clusters in various ways.
Kube-AWS shines in its high level of customization, but you can only use it on AWS cloud-based systems. Of course, if you don’t use AWS, this option won’t be available to you.
However, Kube-AWS can be an invaluable tool for individuals and businesses that already use AWS systems.
Wrap up
Although complicated and time-consuming to become familiar with, Kubernetes offers a high degree of customization and scalability.
Consider any of the above tools or platforms to help streamline your automation process. If you’re not interested in using any of these tools, Google, who created Kubernetes, also offers a comprehensive guide on setting up automated deployments on Google Cloud.
Continue Reading:
Kubernetes vs Docker : Detailed Comparison
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.