Table of Contents
In MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), Route Distinguisher (RD) and Route Target (RT) refer to concepts used in the context of VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) and routing. In this article we will discuss the comparison RD vs RT in detail.
Route Distinguisher (RD)
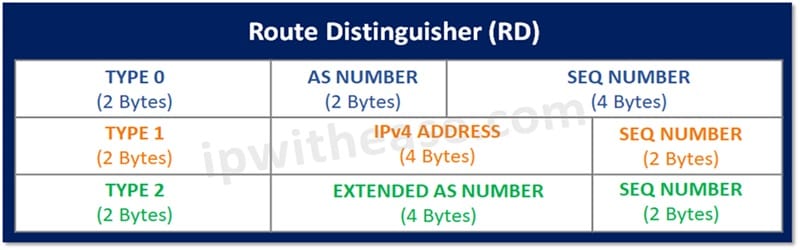
A Route Distinguisher (RD) separates routes (one VRF for each customer routing table) of one customer from another. RD is prepended to each route (64-bit identifier is prepended) within a VRF to identify which VPN the route belongs to. An RD is carried along with a route via MP-BGP when exchanging VPN routes with other PE routers.
Route Target (RT)
Route Target is a 64-bit identifier used as part of MP-BGP attribute (extended community) to identify which route should be exported or imported to specific VPN. Whereas route distinguishers are used to maintain uniqueness among identical routes in different VRFs, route targets can be used to share routes among them. We can apply route targets to a VRF to control the import and export of routes.
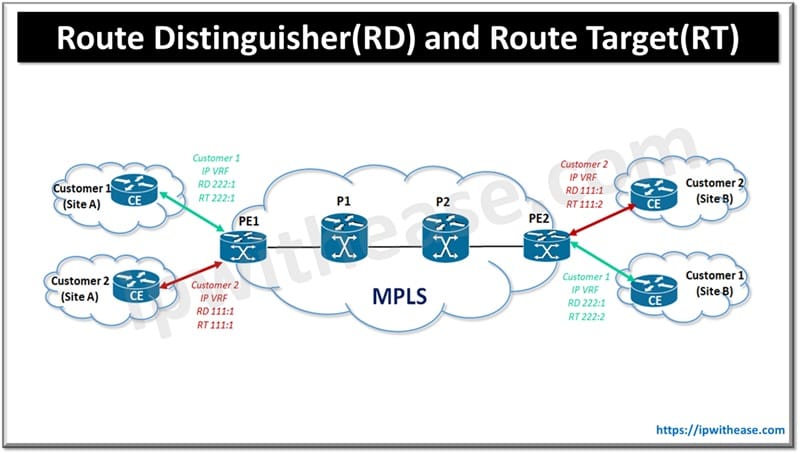
In case of configuring VRF lite, while RD is mandatory to be configured, RT configuration may not be required. Additionally, Route target may be categorized into 2 types –
- Export Route target
- Import Route target
Comparison Table: RD vs RT
Below table summarizes the differences between RD and RT –
| PARAMETER | RD | RT |
|---|---|---|
| Abbreviation for | Route Distinguisher | Route Target |
| Definition | 64-bit identifier prepended to IPv4 route used to identify VPN the route belongs to | 64-bit identifier used as part of MP-BGP attribute (extended community) to identify which route should be exported or imported to specific VPN. |
| Required in VRF Lite | Yes | Not required |
| Same value across different VPNs | No | May be same across multiple VPNs especially when using shared services. |
| Types | No further subtypes | 2 Types – •Export Route target •Import Route target |
| Configuration example | ip vrf <VRF name> rd 1:1 | ip vrf <VRF name> rd 1:1 route-target import 100:100 route-target export 100:100 |
Configuring RD and RT
Configuring Route Distinguishers (RDs) and Route Targets (RTs) in MPLS VPN involves setting up VRFs (Virtual Routing and Forwarding instances) and ensuring proper import and export of routes.
Example Configuration
Step 1: Define VRFs and Assign RDs and RTs
- The
rdcommand assigns a unique RD to each VRF. - The
route-target exportcommand sets the RT for exporting routes. - The
route-target importcommand sets the RT for importing routes.
Router(config)# ip vrf Customer_A
Router(config-vrf)# rd 65000:1
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 65000:1
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 65000:1
Router(config)# ip vrf Customer_B
Router(config-vrf)# rd 65000:2
Router(config-vrf)# route-target export 65000:2
Router(config-vrf)# route-target import 65000:2Step 2: Assign Interfaces to VRFs
- Each interface is assigned to a VRF using the
ip vrf forwardingcommand. - The
ip addresscommand assigns an IP address to the interface.
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding Customer_A
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/1
Router(config-if)# ip vrf forwarding Customer_B
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0Step 3: Configure BGP for VPNv4 Address Family
- BGP is configured to support the VPNv4 address family.
- Neighbors are activated and configured to send extended community attributes.
- Routes from connected interfaces are redistributed into the VRF-specific address families.
Router(config)# router bgp 65000
Router(config-router)# address-family vpnv4
Router(config-router-af)# neighbor 192.0.2.1 remote-as 65000
Router(config-router-af)# neighbor 192.0.2.1 activate
Router(config-router-af)# neighbor 192.0.2.1 send-community extended
Router(config-router-af)# exit-address-family
Router(config-router)# address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_A
Router(config-router-af)# redistribute connected
Router(config-router-af)# exit-address-family
Router(config-router)# address-family ipv4 vrf Customer_B
Router(config-router-af)# redistribute connected
Router(config-router-af)# exit-address-familyStep 4: Verify Configuration
- Use
showcommands to verify VRF configurations, route tables, and BGP VPNv4 routes.
Router# show ip vrf
Router# show ip route vrf Customer_A
Router# show ip route vrf Customer_B
Router# show bgp vpnv4 unicast allBy following these steps, you can configure RDs and RTs in an MPLS VPN environment, ensuring proper route differentiation and distribution across multiple VRFs.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj