Table of Contents
As business grows organizations need to decide to continue sticking to the traditional IT landscape or move onto cloud infrastructure. Both have their own inherent advantages and limitations. Use of traditional IT would be a large capex budget, running operations costs, skilled resources of people with enhanced security and better control. Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, lower capex costs but less control and more concerns around data security and threats like shadow IT.
In today’s article we understand the difference between shadow IT and traditional IT, key features of both, risks of shadow IT.
What is Shadow IT
Any system or IT component, software or tool used in a business network without the knowledge of the IT department is known as shadow IT. It may include using Dropbox or thumb drives to store files, meetings organized on skype instead of WebEx (approved app), groups formed on slack without IT endorsement. Network authorized end user unofficial assets form the shadow IT.
Using shadow IT assets poses a threat to corporate networks as it is not secured or monitored by an IT team who is ignorant of its existence. Efficiency gains are prime motivators for the workforce to use shadow IT and especially cloud-based SaaS apps form the majority of this. It also includes BYOD devices which employees bring into work.
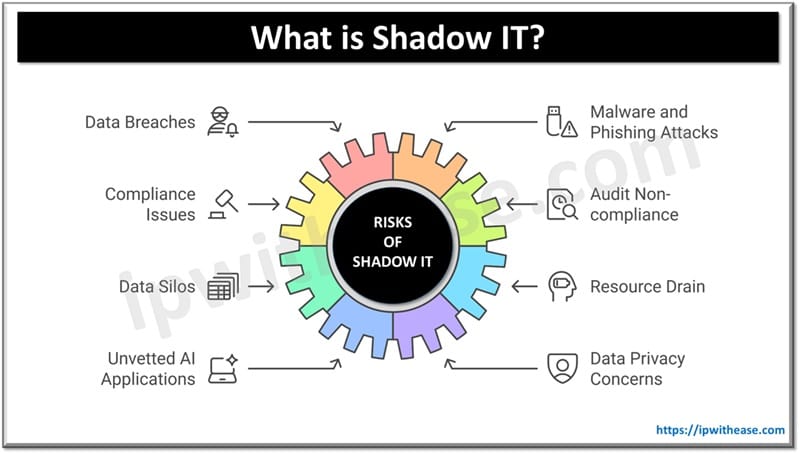
Risks of Shadow IT
- Observability and monitoring – what is not visible is not watched. The shadow IT assets or tools exist outside the preview of IT security – any misconfigurations, vulnerabilities or policy violations remain undiscovered and untreated
- Data corruption – Shadow IT assets are not governed by organization policies and procedures which means any data lying on these assets is not backed up or recovery strategy is not formulated
- Expansion of attack surface – each instance of shadow IT expands the security attack surface. As these assets are not protected by cybersecurity tools deployed by organizations such as endpoint detection and prevention tools , next generation antivirus solutions.
- Cost – business wide adoption in long term is not beneficial or cost effective as indirect costs related to fines and penalties , reputational damage from breaches could dent into business profits.
What is Traditional IT
Traditional IT relies on physical infrastructure and comprises physical data centres hosting various equipment to enable IT services for an organization. These data centres have hardware and software components such as servers, networking equipment – routers and switches, physical hardware appliance firewalls etc. which are owned by businesses who operate them.
A skilled inhouse team generally manages and maintains the components and business substantially relies on this infrastructure for running business operations. Usually this kind of setup requires huge investment in servers, storage, and networking equipment. For performance and scalability, they also maintain physical data centers for disaster recovery with hot/cold sites depending on business demand.
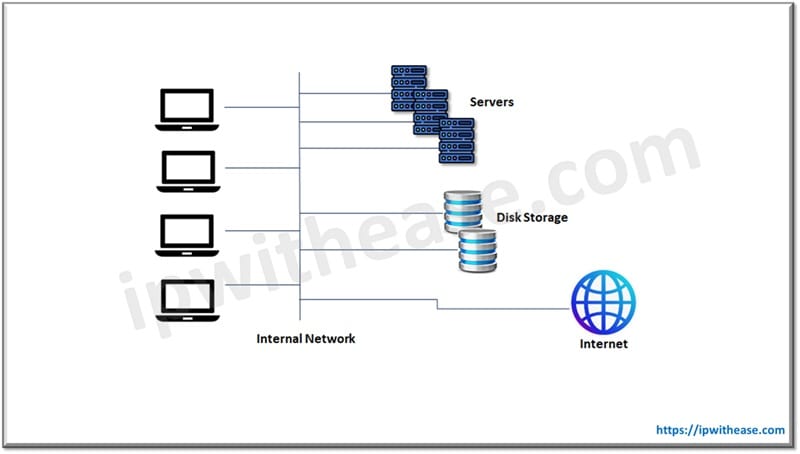
Key Features of Traditional IT
- Control – in traditional computing organization has full control over its infrastructure and they can customize it as per the need
- Security – organization is wholly and solely responsible for the security of systems and data. All security related stuff need to be handled by IT team itself
- Scalability – expansion of traditional IT systems require substantial investment in terms of time and money and requires to buy new equipment and software
Comparison: Shadow IT vs Traditional IT
| Features | Shadow IT | Traditional IT |
| Definition | Use of unauthorized or unapproved systems, tools or software in company network without the knowledge of IT department. | On premises or physical data center hosting where hardware, software, licenses everything is owned by the organization. |
| Purpose | Reduce time to market and improve productivity. | It is an approach towards setting up and building IT infrastructure to support business. |
| Security | Shadow IT leads to many risks to business – data corruption, data loss, elevated privileges, insecure systems and applications, non-compliance to regulations, laws etc. | Traditional IT ecosystem is secure and the organization hosting the hardware and software is responsible wholly and solely for its security. |
| Control | There is no control. It is about loss of control only as IT department is not aware who is hosting what and for what purposes? | There is complete control on what hardware and software or tools will be deployed the risk of unmanaged systems is reduced to a greater extent. |
| Examples | Using Dropbox or google drive to store finance data, analytics application used by marketing for which IT is not aware, using AI applications without proper approvals or sanctions. | Physical data centers hosted by organizations to run their business operations or data centers operated by cloud providers to provide IaaS as a service to its clients. |
Download the comparison table: shadow it vs traditional it
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj