Table of Contents
If you do not know what BIOS is, its functions, and their types, then worry not. After reading this article, you will know everything about Computer BIOS: its function and types.
Is your computer having a problem booting up? The first thing you should do is check your BIOS setup. Most times, a successful BIOS setup will fix the issue. However, most people are unaware of what BIOS is.
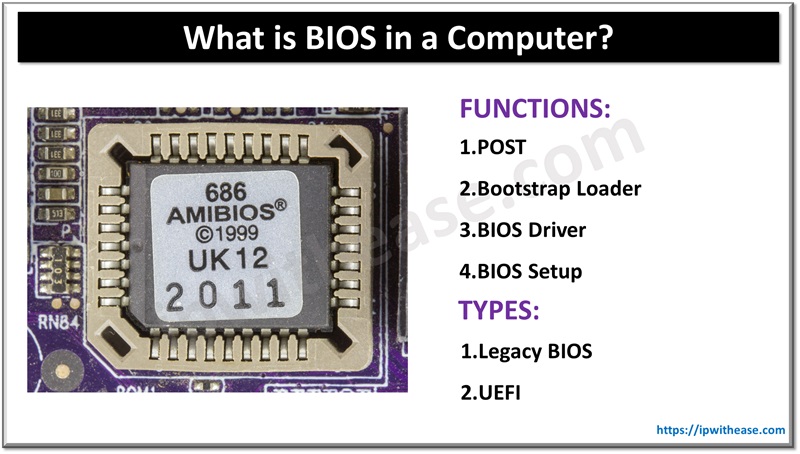
What is Computer BIOS?
BIOS was invented by Gary Kildall in 1975. The full form of BIOS is the Basic Input Output System. It is a chip programmed on the motherboard of a computer. BIOS is the first device that starts when you start the computer. After starting, BIOS then checks if all the hardware like the Keyboard, Mouse, RAM, Hard Drive, etc. is working fine. If any of them is not working fine, they won’t be started and you won’t be able to use them. You will also hear a beep sound if something is not working.
BIOS then checks for the OS file in the Hard Drive and loads it into the processor and your computer starts.
In simpler words, BIOS is essentially responsible for the flow of data between hardware and processor and also responsible for the correct bootup of your device.
BIOS is a primary non-volatile memory that does not erase after the power is off.
Also Check – Difference Between BIOS and CMOS
Function of BIOS
Now that we know what BIOS is, let’s understand why all computers use BIOS.
A BIOS has 4 functions:
- POST
- Bootstrap Loader
- BIOS Driver
- BIOS Setup
Let’s have a look at each BIOS function now.
POST
POST stands for Power On Self Test. As you start your computer, the first function of BIOS is to check whether all the hardware is working fine and properly connected for the computer to boot up properly.
If all the hardware like ROM, RAM, Hard Drive, Keyboard, Mouse, etc. are working fine, you will hear a beep and the computer will start. However, if the hardware is broken or has a connection problem, you will hear multiple beeps.
You can listen to the number of beeps to figure out which hardware has a problem.
| Beep Code | Problem |
| 1 short beep | DRAM refresh failure |
| 2 short beeps | Parity circuit failure. |
| 3 short beep | Base 64 K RAM failure. |
| 4 short beep | System time failure. |
| 5 short beep | Processor failure. |
| 6 short beep | Keyboard controller failure |
| 7 short beep | Virtual mode exception failure |
| 8 short beep | Display failure |
| 9 short beep | ROM BIOS failure. |
| 10 short beep | CMOS shutdown failure. |
| 11 short beep | Check failure |
Bootstrap Loader
The second function of BIOS is to load the OS for the computer to BOOT.
After the POST is completed and all the devices are checked, BIOS looks for the OS in the Hard Drive and loads it into the memory of your computer using Bootstrap Loader.
BIOS Driver
Along with the loading of the operating system in memory, BIOS also loads drivers in your computer memory.
Drivers are software that is used to control your hardware like mouse, keyboard, sound card, graphic cards, etc.
If the drivers are not loaded properly, you won’t be able to use that hardware.
BIOS Setup
The last function of BIOS is to set your hardware settings like Time, Date, Boot Order, change fan speed, boot option, etc.
You can enter BIOS setup mode by pressing buttons like F10, F8, or ESC when your computer starts based on your motherboard.
What are the Different Types of BIOS?
With time, BIOS has evolved. As of now, there are 2 types of BIOS.
- Legacy BIOS
- UEFI
The older one is Legacy BIOS and the updated one is UEFI. Now let’s have a look at how they both are different in brief.
Legacy BIOS
Legacy Basic Input Output Systems are the ones that were used with older computers before 2017.
They did not support Graphical User Interface and needed a keyboard to interact. Also, Legacy BIOS can not support drives larger than 2.1 TB and is slower compared to UEFI.
UEFI
UEFI was developed in 2002. It stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. It was developed to address the problems faced by Legacy BIOS.
- It works on the GUID Partition Table approach which means that it can support drives larger than 2TB.
- It is also more easy to use because it supports Graphical User Interface. UEFI is also more secure than Legacy BIOS because it only loads trusted software during bootup process.
- Most computers have shifted to UEFI and left Legacy BIOS now because of the features UEFI has.
Difference: UEFI vs Legacy BIOS
| Feature | Legacy BIOS | UEFI |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Basic Input/Output System | Unified Extensible Firmware Interface |
| Introduced | 1975 (IBM PCs) | 2005 (by Intel as EFI, then standardized as UEFI) |
| Boot Mode | MBR (Master Boot Record) | GPT (GUID Partition Table) |
| Storage Support | Up to 2.2 TB drives | Supports drives >2.2 TB (up to 9.4 ZB theoretically) |
| Interface | Text-based interface | Graphical and mouse-supported interface (optional) |
| Speed | Slower boot time | Faster boot time and resume from hibernation |
| Security Features | No Secure Boot | Supports Secure Boot (prevents unauthorized OS loading) |
| Compatibility | Compatible with older hardware/software | Modern systems, backward compatible with Legacy BIOS |
| Driver Support | Limited to BIOS-specific drivers | Uses UEFI drivers, better device support |
| Programmability | Hard to modify | Easier to customize and update |
| Location on Disk | Stored in the first sector (MBR) | Stored in the EFI System Partition (ESP) |
| Boot File | BIOS loads bootloader from MBR | UEFI loads .efi files from ESP |
Conclusion
In conclusion, BIOS standing for Basic Input Output System is a chip placed on the motherboard that helps start the computer and manages the flow of data from hardware to processor. BIOS is of two types, UEFI and Legacy. Legacy BIOS is outdated and replaced by UEFI in modern PCs.
We hope that after reading this article, you understand what a BIOS in a computer is along with its functions and types. If you have any questions, feel free to ask in the comment section.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.