Table of Contents
Transportation of datagrams happens at the transport layer in the OSI model. There are several protocols that operate at the transport layer in the OSI model. Transmission control protocol (TCP) and User datagram protocol (UDP) are two most popular and commonly used protocols of transport layer. But the need for a more secure protocol at the transport layer is the demand of recent times with increasing penetration of cloud computing. The explosion of internet telephony, streaming, online gaming and VPNs demand secure transport layer protocols.
Today we look more in detail about Datagram Transport layer security (DTLS) based on Transport layer security (TLS) as it is called, its features, use cases etc.
Introduction: Datagram Transport Layer security (DTLS)
Datagram transport layer security (DTLS) built on top of User datagram protocol (UDP) and protects the transportation of datagrams. While designing DTLS protocol security experts tried to adhere to TLS characteristics as much as possible resulting in DTLS which offers many security guarantees as TLS but also lessen the requirement to create a customer application layer protocol or use IPsec.
The most differentiating feature between DTLS and TLS is the underlying protocol being used. DTLS uses User Datagram protocol (UDP) whereas, TLS uses Transmission control protocol (TCP).
Telegram with digital data is what a datagram is; having enough information to get the correct route to its destination without the need for an existing connection between sender and receiver. The connection is unreliable and the sender cannot determine whether his message is delivered or not and packets arrive in correct order at the destination.
The User datagram protocol (UDP) has less overhead as messages are sent without a prior connection and mainly used for faster data transfers and short response times where reliability is not so critical. To overcome this challenge, DTLS lets packages not get lost or arrive in wrong order such as a live video streaming.
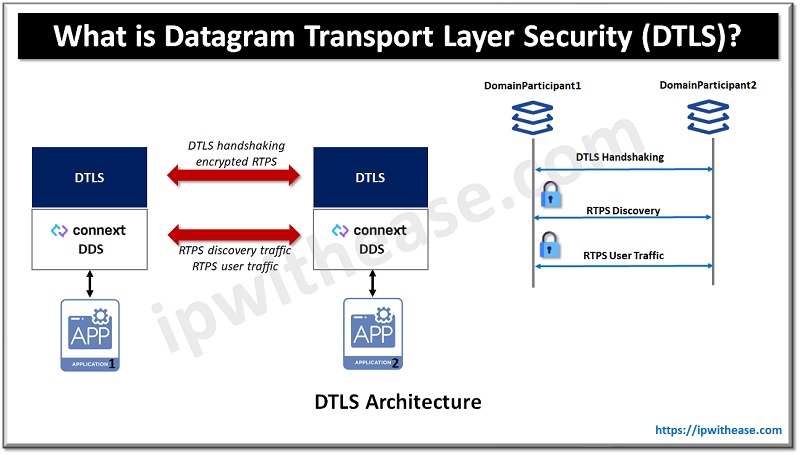
All Connext DDS network traffic with datagram transport layer security (DTLS) protocol (RFC 4347) is wrapped to provide data security. DTLS is a recent variant of the mature SSL/TLS family of protocols which adds the capability to secure communication over a connectionless network layer transport such as UDP.
UDP is preferred network layer transport for DDS wire protocol RTPS, as well as for NAT traversal. Authentication based certificates, encryption of data and message integrity is provided by DTLS protocol. Specification (RFC 4346) provides a number of cryptographic algorithms listed in TLS 1.1
Features of DTLS
- DTLS is secure protocol and provides privacy with datagrams.
- Addresses problems related to loss and reordering of packets.
- DTLS can improve VPN performance by setting up UDP based tunnel instead of TCP tunnel.
- Prevents tampering, eavesdropping and message forgery.
- Supports optionally record replay detection.
- DTLS delivers authenticated and encrypted application data but it enables lower latency.
- Handle unreliable transport layers and do not suffer from delays occur in streaming protocols.
- DTLS supports cipher suites including hash algorithms such as SHA-256, block cipher modes like AES-GCM and the RSA public key cryptosystem.
- Ideally suited for delay sensitive applications.
Use cases for DTLS
- Ideal to secure services and applications
- Real time applications such as IP telephony
- Online gaming
- Streaming audio and video content
Continue Reading:
SSL vs TLS: What is the difference?
Difference between TCP and UDP
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj