Q.1 Can we use OSPF without backbone area?
Yes, but it will be limited to intra-area (same area) communication. By default, Inter-area communication is not possible without backbone area
Q.2 What will be the status of Interface Fa0/2 of Catalyst Switch in the below 2 scenarios –
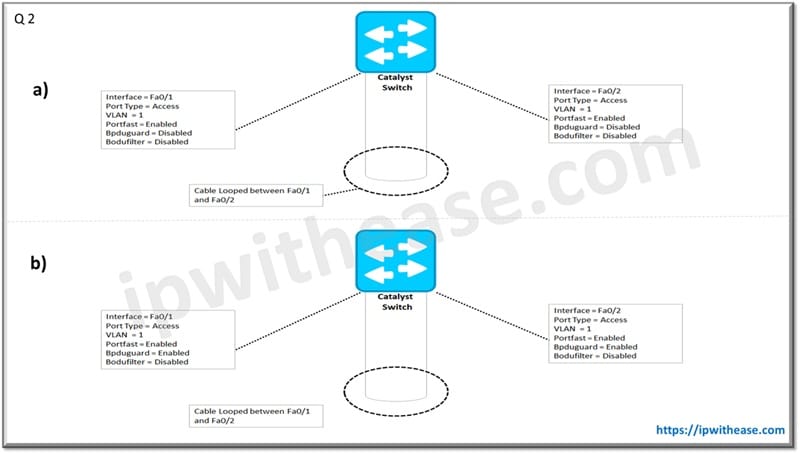
a) Blocked (Since Higher Port ID than fa0/1).
b) Err-disabled (due to bpduguard).
Q.3 A user accidentally connected the 2 port of the switch to each other. What will happen to the ports and network? The spanning parameters on vlan1 for both the ports have been shared in the below diagram –
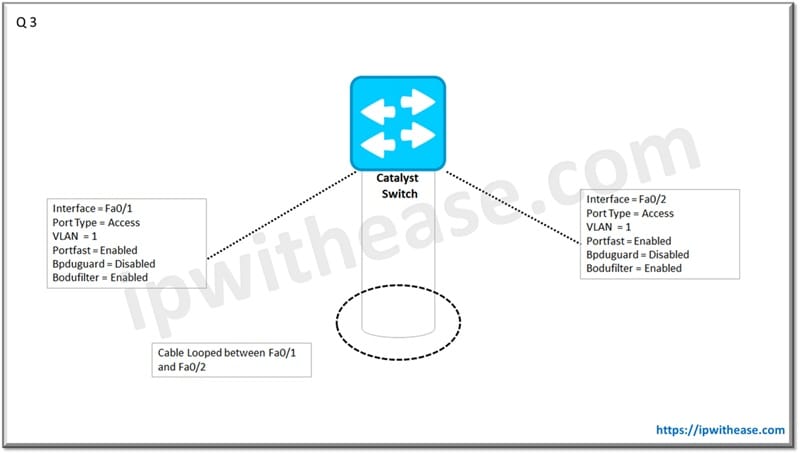
Loop in network since BPDU filter will filter the BPDUs and allow traffic to flow without blocking the… hence a loop in the network.
Q.4 Router A and Router B are running RIP V2. Router B is configured to advertise all connected interfaces via RIP v1. Which networks connected to Router B will be advertised to Router A ?
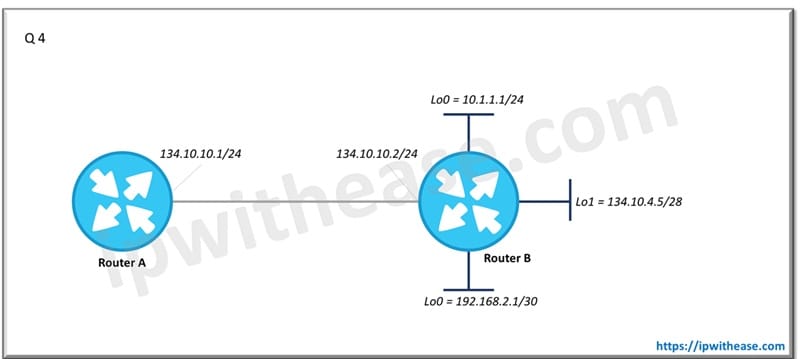
10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.2.0/24
Note – 192.168.2.1/30 is a subnet of /24 network. advertising any network prefix less than its classful major network is not allowed in RIP route summarization
Q.5 A new switch configured as a VTP client, and added to the existing VTP domain. Shortly after switch is connected, the whole network goes down. What could have caused this to happen?
The configuration revision of the switch inserted was higher than the configuration revision of the VTP domain.
Q.6 I want to use extended VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006-4094) on network switches. What should he VTP mode be set to before configuring extended-range VLANs?
Transparent mode
Explanation –
The switch must be in VTP transparent mode when you create extended-range VLANs. Only transparent mode support extended Vlans. Server and Client mode don’t allow to store in vlan database.
Q.7 How much data can be carried in a standard Ethernet frame?
1500 bytes or 1518 bytes
1518 bytes
Explanation –
A standard Ethernet frame MTU is 1500 bytes. The MTU size or packet size refers only to Ethernet payload. Ethernet frame size refers to the whole Ethernet frame, including the header and the trailer.
Preamble is not calculated in frame size so DA (6 bytes) SA (6 bytes) Type (2
bytes) data + pad (1500 bytes) FCS (4bytes) = a total of 1518
Note –
A standard Ethernet frame MTU is 1500 bytes. This does not include the Ethernet header and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) trailer, which is 18 bytes in length, to make the total Ethernet frame size of 1518. So the total size of an Ethernet packet can be as large as 1518 bytes, but the maximum payload is only 1500 bytes.
Q.8 802.1Q trunking uses which Ethertype to identify itself?
The IEEE 802.1Q specification defines the Ethertype field to be 8100 in the presence of a VLAN ID.
Q.9 What option is the best way to apply CIDR if a service provider wants to summarize the following addresses: 200.1.0.0/16, 200.2.0.0/16, 200.3.0.0/16, 200.5.0.0/16, 200.6.0.0/16, 200.7.0.0/16?
200.4.0.0/14, 200.2.0.0/15, 200.1.0.0/16
Explanation –
The Network 200.4.0.0/14 will encompass the 200.5.0.0, 200.6.0.0 and 200.7.0.0 networks. The second summarization, 200.2.0.0/15 will take care of both the 200.2.0.0 and 200.3.0.0 networks. Finally, the last network is needed in order to include the only remaining network, which is 200.1.0.0/16. This will summarize all 6 networks using only 3 statements.
Q.10 You are a network engineer for a company with three branch offices connected via routers using OSPF as the routing protocol. The network design is as follows:
- Router A (Head Office) is connected to Router B (Branch 1) and Router C (Branch 2).
- All routers are in OSPF Area 0.
- Each router has a loopback interface configured to simulate its router ID.
- Network engineers report that Router B is unable to reach a subnet connected to Router C (specifically, 192.168.30.0/24), although all OSPF neighbor relationships appear to be up, and pings to router loopbacks are successful.
Based on this scenario, what is the most likely cause of the issue preventing Router B from reaching 192.168.30.0/24?
A. Router B is not advertising its networks correctly.
B. Router C has not configured OSPF properly on the interface connected to the 192.168.30.0/24 subnet.
C. Router A is filtering LSAs using a type 3 LSA filter.
D. There is an MTU mismatch between Router A and Router B, preventing full LSA exchange.
Note: (Troubleshooting Steps)
- You check the routing table of Router B, and 192.168.30.0/24 is missing.
- On Router C, show ip ospf database lists the subnet 192.168.30.0/24.
- On Router A, show ip ospf database also lists 192.168.30.0/24.
- However, Router B does not show 192.168.30.0/24 in its OSPF database.
Q.11 Which 3 BGP attributes will be carried in every BGP update(both IBGP and EBGP)?
Origin, AS-Path, Next Hop
Q.12 Router A,B and C are running EIGRP and are EIGRP neighbors.
Router A configuration is shown below –
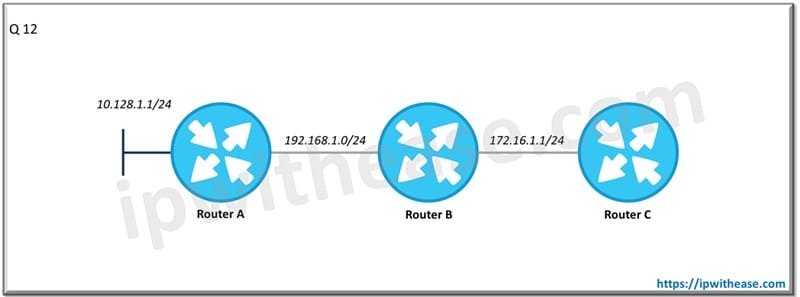
Router eigrp 1
Network 192.168.10.0
Redistribute connected
Which routes would show up in the routing table of Router B as EIGRP routes?
10.0.0.0/8 and 192.168.1.0/24
Q.13 From the perspective of below diagram, which routers will met he feasibility condition for network 192.168.1.0/24.
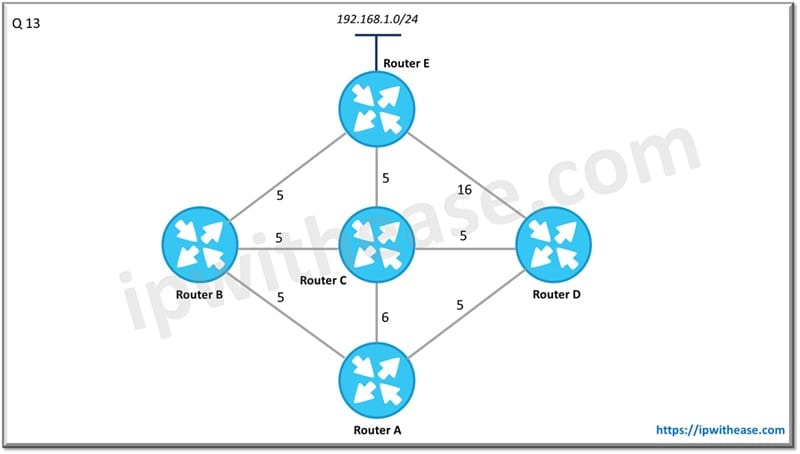
Router B and Router C.
Q.14 From the perspective of below diagram, which routers will be considered –
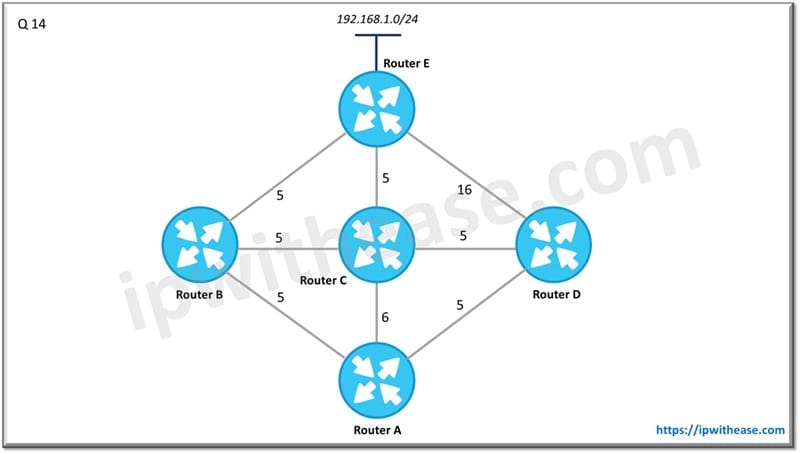
a) Successor
b) Feasible Successor
For network 192.168.1.0/24
Successor is Router B
Feasible Successor is Router C
Q.15 The “Show IP EIGRP neighbor” command is issued on the router A. Router A is configured with the default EIGRP settings. After issuing this command, which of the following RED value is incorrect ?

R1# show ip eigrp neighbors
IP-EIGRP neighbors for process 1
| H | Address | Interface | Hold (sec) | Uptime | SRTT (ms) | RTO | Q (Cnt) | Seq (Num) |
| 0 | 192.168.1.2 | Fa0/0 | 103 | 00:01:44 | 95 | 570 | 0 | 3 |
Hold Time should be between 10-15 and not 103 seconds.
Q.16 Which IP address maps to the Ethernet multicast MAC address of 01-00-5e-10-20-02 ?
239.144.32.2
224.16.32.2
Ethernet interfaces map the lower 23 bits of the IP multicast address to the lower 23 bits of the MAC 0100.5e00.0000. As an example, the IP multicast address 224.0.0.2 is Mapped to the MAC layer as 0100.5e00.0002. HEX 01 = 00-5e (all Multicast Addresses);HEX 10 = 00010000 – could be both 16 and 144 (decimal) due to the fact that we ignore the first bit of the second octet when converting to binary; HEX 20 = 00100000 = 32; HEX 02 = 00000010 = 2
Q.17 What is the primary purpose for the RPF check in IP multicast networks?
To prevent multicast traffic looping through the network.
Explanation – Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) provides loop avoidance. It is an algorithm used to forward multicast packets. The RPF rules are: If a router receives a datagram on an interface that it uses to send unicast packets to the source of that packet, then the packet has arrived on the RPF interface. If the packet arrives on the RPF interface, a router forwards the packet out the interfaces that are present in the outgoing interface list of a multicast routing table entry. If the packet does not arrive on the RPF interface, the packet is silently discarded.
Q.18 In an MPLS network, which protocol is used to distribute traffic engineering information?
OSPF Opaque LSAs or IS-IS TLVs
Explanation:
OSPF Opaque LSA provides a generalized mechanism for OSPF to carry additional information. The new information can be used directly by OSPF or indirectly by other applications, which use OSPF to distribute information.
Q.19 What is penultimate hop popping (PHP) and what is its use?
PHP is the technique for removing the (POP) MPLS label before the egress router. The MPLS label on a switched packet is popped by either the egress router or the penultimate router, depending on your configuration. If you decide to use penultimate hop popping, you essentially terminate the LSP one hop earlier. The MPLS labels are popped by the routers that connect to the egress router, rather than all of them being popped by the same egress router.
Q.20 Explain BGP “Site of Origin” Attribute?
Site of Origin BGP Community Attribute
The site-of-origin (SoO) extended community is a BGP extended community attribute that is used to identify routes that have originated from a site so that the advertisement of that prefix back to the source site can be prevented. The SoO extended community uniquely identifies the site from which a router has learned a route. BGP can use the SoO value associated with a route to prevent routing loops.
For More Interview Q&A Please visit:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj