Table of Contents
The ability to store and access data from anywhere in the world offers a significant competitive advantage for any business in most industries. Hence, in the digital age, cloud services have become a practical necessity for businesses seeking cost savings, scalability, flexibility, and remote accessibility. They’re especially popular among companies looking to facilitate collaboration among large teams and those that hire remote employees from multiple different parts of the world.
If your business is looking to maximise the benefits of cloud systems, however, you’ll need to strengthen your cybersecurity posture. While cloud-based solutions have undoubtedly allowed modern businesses to unlock numerous—and in many cases unprecedented—advantages, they also give rise to their own unique set of security challenges. Addressing these difficulties is a must to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity. Fortunately, certain tools and best practices have historically proven effective at mitigating the security risks associated with deploying cloud solutions.
This article aims to provide expert tips for strengthening the security posture of your company’s cloud-based systems.
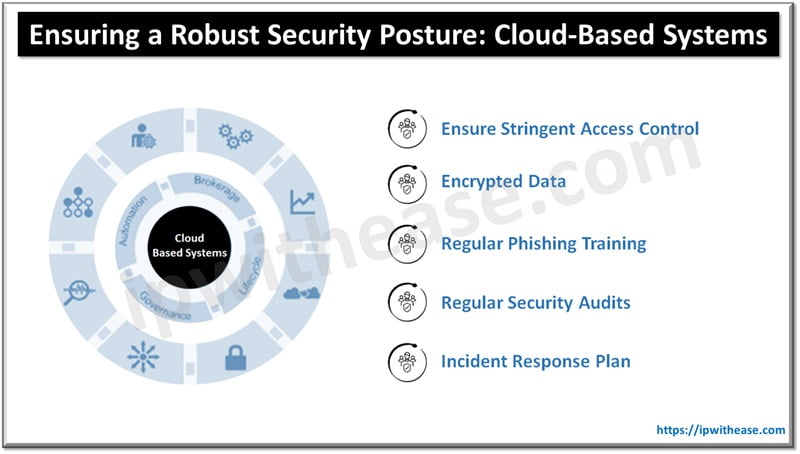
Strengthening the Security Posture: Cloud-based Systems
Implement the following practices to ensure comprehensive protection and maximise the benefits of your cloud investments:
1. Ensure That Access Control Is as Stringent as Possible
Cloud-based systems are designed to be accessible from anywhere, with almost any type of device. While this grants companies unprecedented flexibility, it also makes access control an even more urgent concern than it is for organisations using strictly on-premise systems. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of unauthorised access, as it requires users to provide additional information beyond just a password before they can log in. This makes it much more difficult for malicious actors from outside your organisation to breach your systems.
In addition to MFA, you may also find it helpful to implement role-based access control (RBAC), which limits data access based on user roles and responsibilities. This practice ensures that employees only have access to the information necessary for their job functions and thus minimises the risk of internal threats. Be careful about managing permissions and regularly review access rights; doing so will help you maintain tight control over who has the right to use critical company information and resources.
2. Make Sure to Encrypt All Data
Data encryption is recognised as the go-to measure for protecting sensitive information, both in transit and at rest. In-transit encryption involves using protocols like SSL/TLS to safeguard data being transferred over networks. This ensures that data remains invulnerable to interception during transmission, protecting it from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
At-rest encryption, on the other hand, involves securing data stored in the cloud. By encrypting data at rest, you protect it from unauthorised access even if physical security is compromised, such as in the event of device theft or a natural disaster. Using advanced encryption standards (AES) will keep your data unreadable without the proper encryption key, so you can rest assured that your data remains confidential and secure at all times.
3. Provide Employees with Regular Phishing Training
Phishing attacks often target employees by tricking them into revealing sensitive information or granting access to secure systems. Regular training sessions can help employees recognise these threats and respond appropriately. Effective training should include real-world examples and simulations to demonstrate how phishing attacks occur. You can also structure them as part of a larger cybersecurity awareness training initiative, which can also include best practices like making strong passwords and effective incident response.
In the long run, your efforts to educate your staff on how they might help strengthen your organisation’s cybersecurity posture will help foster a culture of awareness and vigilance companywide. If your entire team is committed to acting as a line of defence against potential cyber threat, you’ll see far fewer successful phishing attempts and other security incidents. Make sure to update and retrain your employees continuously over time, so they’re always informed about the latest tactics that cybercriminals use and are prepared to counter them.
4. Integrate Regular Security Audits into Your Overall Strategy
The purpose of security audits is to identify and address potential security weaknesses in your cloud-based systems. They typically involve comprehensive vulnerability assessments that can help you uncover any openings that malicious actors might exploit. Once you’ve gotten a clear perspective on your security landscape, you’ll then be able to implement any necessary improvements.
Penetration testing, a crucial aspect of security audits, involves simulating cyberattacks to evaluate your system’s defences. In a nutshell, pen tests mimic real-world attack scenarios to shed light on any vulnerabilities that might otherwise go unnoticed. Some common cyberattack scenarios pen tests can simulate include phishing attacks, SQL injection, brute force attacks, and zero-day exploits. Run these tests periodically to keep your cloud environment resilient and adaptable to emerging security challenges.
5. Develop a Strong and Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
No matter how proactive you try to be about strengthening cybersecurity at your organisation, there’s no way to completely eliminate the possibility of a breach. Alongside preemptive measures, a well-defined incident response plan is essential for quickly and effectively responding to security breaches. This plan should outline the key components of a successful response, including identifying potential threats, establishing response procedures, and defining roles and responsibilities. A clear plan will empower your team to act swiftly and decisively in the event of a security incident, minimising its overall impact.
Developing an incident response plan isn’t a one-and-done process, either. You’ll also have to test and update it regularly over time. Conduct frequent drills and learn as much as you can from real incidents, as these experiences will help you refine the plan and improve its effectiveness. Bear in mind that the threat landscape is continuously evolving, and your incident response strategy will have to follow suit in order to remain robust.
At the end of the day, it’s entirely possible to take advantage of the many conveniences that digital innovations like cloud systems offer without worrying about potential security risks. With the support of strong security systems and protocols, your organisation will be able to leverage the many benefits of cloud-based services without fear.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.