Table of Contents
When there are multiple software defined data centre solutions available in the market it is important to understand the underlying technology, functionality and features each one offers to choose a right mix of solution for your business; as digital transformation and rapidly changing technology, increased productivity, reduction in costs, and transformation in customer experience is the demand in current scenario and going ahead in future as well.
The traditional role of WANs to connect users to branch offices using dedicated MPLS circuits no longer works in the digital world where applications are moving out of the data centre into the cloud and users are consuming these applications on mobile devices using a diverse set of devices.
Today we look more in detail about Cisco ACI Multi-site release 3.0 fabric, its deployment and its features and limitations etc.
About Cisco ACI
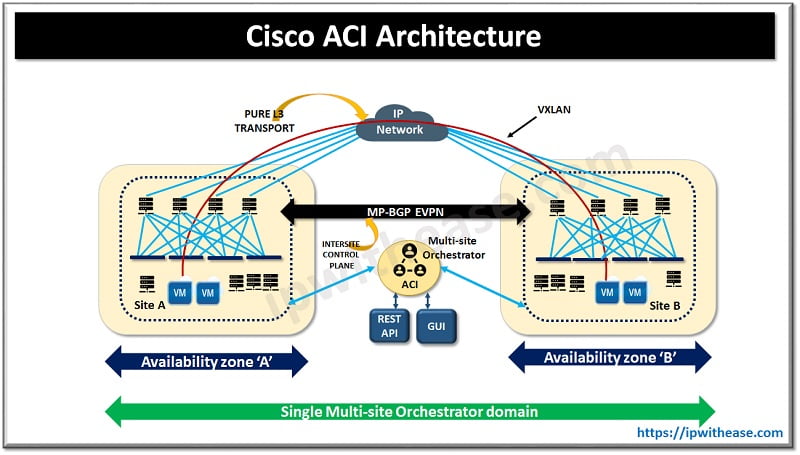
Cisco ACI or application centric infrastructure is a data center defined software solution. This helps to simplify, optimize and accelerate application deployment cycle by having a network which is defined based on network policies. Cisco ACI is a combination of hardware and software:
- Cisco Nexus 9000 family of switches act as hardware
- software and integration components included in Cisco ACI are Additional data centre Pod, Data centre policy engine and non-directly attached virtual and physical networks.
In Cisco ACI, end users can mention what application policy infrastructure outcome they are expecting, and network devices will interpret and act accordingly.
Features of Cisco ACI
- Simplify automation using an application driven policy model
- Application velocity, scalability
- Data centre application deployments acceleration
- Automated and unified data centre network policy for containers, virtual and physical systems
About Cisco Viptela SD-WAN
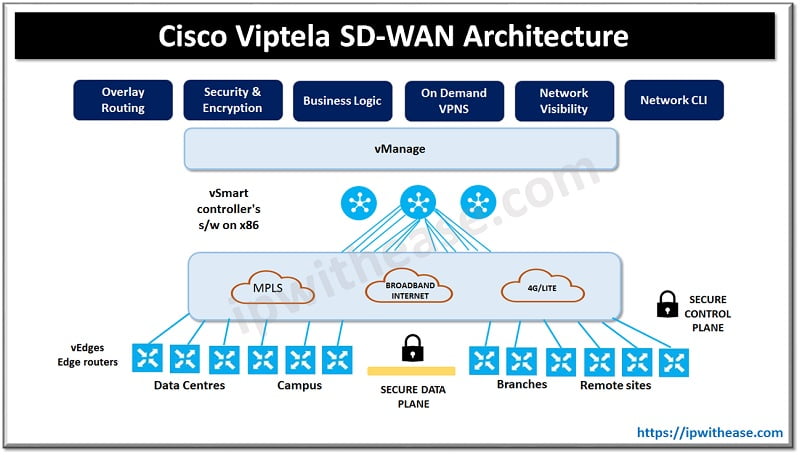
Cisco SD-WAN is a software defined WAN solution. The control plane and management plane are separated from physical devices. The security policy configurations are driven through cloud-based management vManage (management plane) solution. Control plane is managed by vSmart and vBond management tools.
All devices in SD-WAN architecture are based on a zero trust model and to maintain trust between the components they need to create the DTLS/TLS tunnels and exchange preloaded certificates. SD-WAN is an application aware network and choose path on the parameters such as SLA, Jitter etc.
We can use VRRP protocol to switch traffic flow from LAN to a different SD-WAN routers and the IPSEC/GRE tunnel will initiate from one SD-WAN to another SD-WAN router on the basis of traffic flow as instructed by controller. The controllers here are in a cluster and also carry zero trust policy. In the viptela SD-WAN controller, we have three types of controllers in the cluster :
- vBond
- vSmart
- vManage
Features of Cisco Viptela SD-WAN at data , control, management and orchestration plane
- vBond component operates at orchestration plane and it provides first point or initial authentications (White list model)
- Highly resilient
- vManage operates at management plane and it supports multi tenant with web scale
- it helps in software upgrades
- it has programming interfaces (REST, NETCONF)
- vSmart operates at control plane and it establishes secure connection to vEdge routers
- reduction in control plane complexity
- vEdge operates at data plane and provides secure data plane with remote vEdge routers
- Zero trust deployment support
- Traditional routing protocols are leveraged such as OSPF, BGP and VRRP
About Cisco SD-access
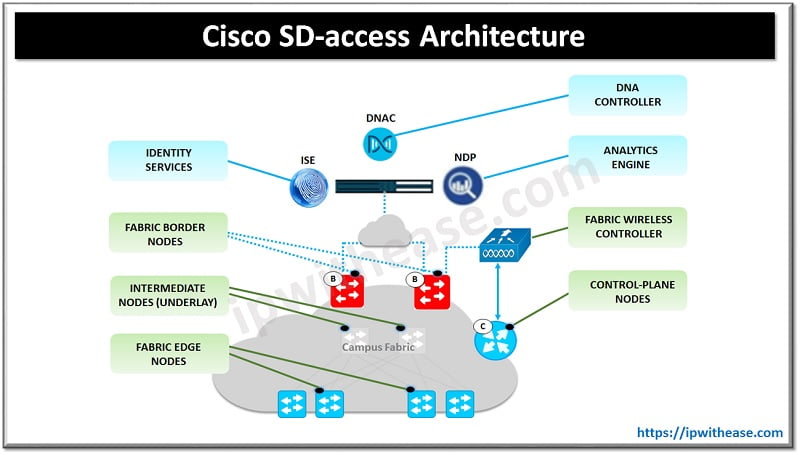
Cisco SD-access is software defined access in a campus based on intent-based networking. SD access clients will get a programmable network which can be revised as per customer requirements. It has a centralized management plane and policies which are driven through the management plane.
SD access has components such as a DNA center which acts as a controller for the control plane and while the data plane is still with devices in networks. DNA is an architecture and DNA Center is the architecture. The main component is Cisco ISE which is used for user authentication in the networks.
Features of Cisco SD-access
- Build standard based network fabric to convert high level business policy into network configuration
- It offers intuitive automation
- It offers contextual analytics and takes corrective actions when conflict arises
Cisco ACI vs Cisco Viptela SD-WAN vs Cisco SD-access
Below given table summarizes the differences between the three:
FEATURES | CISCO ACI | CISCO VIPTELA SD-WAN | CISCO SD-ACCESS |
| Definition | Software defined networking solution for simplification, management based on network policies | Software defined WAN offering from cisco for a segmented overlay which uses encryption for security, local policy enforcement etc. | Software defined access intent-based networking solution to implement business policies into network configurations |
| Solution | Meant for datacentres | Meant for Wide area networks | Meant for Local Area networks |
| Device architecture | Spine and leaf architecture | vEdges/ cEdges | Access / Border nodes |
| Routing | Supports transit routing to enable border routers to perform bidirectional redistribution with other routing domains | Routes traffic based on flow which allows multiple transports such as internet, MPLS and Cellular simultaneously | Routes are mutually redistributed between IS-IS and BGP and redistributed into EGIRP to allow end to end reachability of IP |
| Protocols supported | BGP, OSPF and EIGRP supported | Supports active WAN uplinks and uses a variety of transports such as Ethernet including PPP interfaces, GRE tunnels | EIGRP supported |
| IPv6 and multicast | Support to connect multicast applications using IPv6 | IPv6 and multicast supported | IPv6 clients are supported |
| Control Plane | BGP/COOP/IS-IS | OMP(Overlay management protocol) to establish and maintain viptela plane | LISP (Locator Identity Separator Protocol) based |
| Management Plane | APIC/NSO | vManage | Cisco DNA centre |
| Data plan (underlay) | Uses TEP Address pool | TLOC (transport location) defines specific interface on overlay network | RLOC (Routing locator) represent location of a computer on the network |
| Data plane (overlay) | VXLAN | IPSEC | VXLAN |
| Segmentation | VRF as in traditional routing | VPN | VN (a kind of macro segmentation) |
| End points | EPG | IP prefix | SGT (scalable group tag) |
| Communication | Contracts | Application aware routing and data policy | SGACLs (Security Group Access Control List) |
| Usage | Ideal for interoperability between physical and virtual workloads | Ideal for low-cost branch connectivity requirements | Ideal for policy-based automation from edge to cloud |
Download the comparison table.
Continue Reading:
Cisco SD Access Fabric in a box
Cisco ACI Multi-Tenant Environment: Datacentre basics
Top 100 Cisco SD WAN (Viptela) Interview Questions
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj