Whether you’re a company trying to safely store your data, or you run a business handling private information, at some point, you’ll need to decide whether to back up your data locally or opt for cloud backup. While both options have their advantages and disadvantages, depending on the data you store, one option may be more appropriate than the other. If you’re looking for all the details on whether to back up in the cloud or locally, we’ve got you covered.
What is Local Backup?
Backing up your data locally refers to the practice of storing your data back ups on an on-site physical storage device as your network. With local back ups, you make companies of your most important files, documents, databases, and systems and save them onto a device. These devices can include external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), or tape drives that are physically connected to your local network or computer.
Advantages
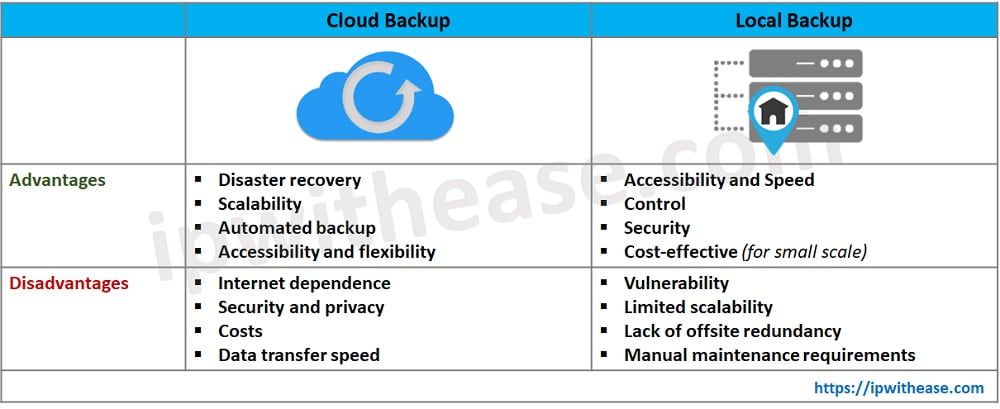
- Accessibility and Speed: Local back up options provide fast and efficient access to your data because your storage is physically present within your premises or network. This allows for quick data restoration, especially if you store large volumes of data.
- Control: With local back up storage, you have complete control over your data. With total control, you can customize your back up settings, schedule back ups according to specific requirements, and manage your back up process entirely.
- Security: Local backup options also offer an extra layer of precaution. Since your data remains on-premises, you reduce the risk of unauthorized users accessing your data or exposure to potential security breaches that are more common with cloud-based backups. Some also include password generators or password protection tools to improve the security.
- Cost-effective: Local backup is often to more cost-effective data storage option, especially for small-scale or personal backup needs. With local backup, you make a one-time initial investment in a storage device without a monthly recurring fee.
Disadvantages
- Vulnerability : While local backup is an excellent option for many reasons, it is more vulnerable to local disasters. In the event of natural disasters, fire, theft, or physical damage, both your original data and local backups may be lost. Because of this, if you decide to go the local backup route, consider investing in an additional offsite backup solution for recovery.
- Limited scalability : While you make one initial upfront investment with local backup storage, you are limited to a finite capacity. As your data grows, you may need to upgrade or replace your backup devices to accommodate your increasing storage needs, resulting in additional costs and maintenance efforts. This is an especially important consideration if you run a business or work with large amounts of data.
- Lack of offsite redundancy: As mentioned above, having a single on-site backup solution leaves you vulnerable in the event of some kind of disaster. Since local backups are stored in the same location as your original data, having an offsite backup solution ensures data redundancy and improves your overall disaster recovery capabilities.
- Manual maintenance requirements: With local backups, you must complete regular intervention and maintenance to ensure your backup protocols are performed correctly, storage devices are functioning properly, and your backups are regularly tested for data integrity. This process requires a human pair of eyes, which increases your margin of error while being a time-consuming monotonous process.
What is Cloud Backup?
On the flip side of local backup is cloud backup. Unlike local backup, a backup in the cloud refers to the practice of storing your data backups in a remote, cloud-based infrastructure. Cloud backup involves sending copies of your data over a network to be stored on servers hosted by a cloud storage provider. You can access and restore these backups from anywhere, so long as you have the encryption key and an internet connection.
Advantages
- Disaster recovery: A backup in the cloud provides offsite storage, which ensures your backups are stored away from your primary data source. This option protects you from localized disasters that could impact your original data. Should a major catastrophe affecting your original data source occur, you’ll easily be able to access and recover your lost data backups.
- Scalability: Cloud backup solutions also are typically more scalable than local storage solutions. As your data grows, you can easily allocate additional storage space without needing to physically upgrade or replace your hardware. With this flexible option, you can efficiently adjust your storage capacity based on your needs.
- Automated backup: Cloud back up services often offer automated back up schedules and continuous data protection features. These systems can perform automatic back ups without the need for manual intervention, ensuring regular and consistent back ups. Automated back ups also minimize your risk of human error and ensure your data is backed up promptly.
- Accessibility and flexibility: If you choose to back up in the cloud, you’ll be able to easily access and restore your data from anywhere with an internet connection. This provides flexibility and convenience, allowing users to retrieve their backed-up data from various devices and locations. This may be particularly useful if you operate a remote business or for businesses with multiple branches.
Disadvantages
- Internet dependence: While the cloud allows you to access your data from anywhere, they do rely on an internet connection to transfer data. If your internet connection is slow or unreliable, the back up and restoration process can be delayed or interrupted, affecting the speed and accessibility of data recovery.
- Security and privacy: If you go the back up in the cloud route, you have to be careful about selecting a reputable and trustworthy provider with robust security measures and encryption protocols. While many providers prioritize data security, there can still be concerns about breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Costs: Cloud backup services as Dropbox or AWS typically involve subscription costs based on storage usage, features, and service levels. While these can be cost-effective compared to upfront hardware investments, the cumulative cost over time should be considered to ensure they align with your budget.
- Data transfer speed: Another cost of a back up in the cloud is the data transfer speed. Uploading large volumes of data to the cloud for your initial back up process can be time-consuming depending on upload and download speed limitations. This is another factor to consider when planning back up and recovery timeframes.
Picking the right back up solution for your data
Overall, deciding between back up in the cloud or locally depends on your specific needs and priorities. While both options include distinct advantages and disadvantages, by weighing the pros and cons of each option, you make the best decision for your business or personal data. When deciding between the two, assess your needs, risk tolerance, budget, and any regulatory requirements to select the best solution for you.
Continue Reading:
What is object storage and its benefits?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.