Table of Contents:
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is widely used. It is a process of sending data one bit at a time in sequential manner over a communication channel or medium. It is used for all long-haul communication and majorly used in computer networks where cabling costs and synchronization issues make it difficult to use parallel communication techniques. It takes less space as only one bit is transmitted at a time and is more resistant to crosstalk.
Today we look more in detail about comparison between serial communication protocols – RS -232 , RS-422 and RS-485, their features , how they operate and their key differences.
What is RS-232?
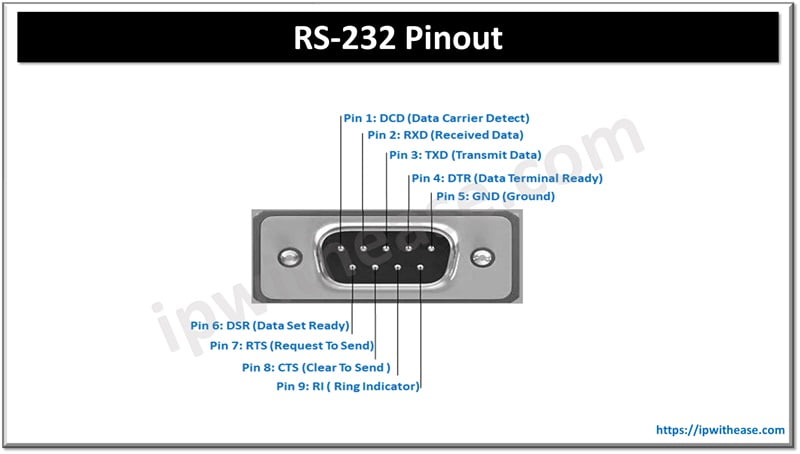
RS-232 is the first serial protocol to connect to a telephone modem. RS means recommended standard and now it is changed to EIA (Electronic Industries Alliance) / TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association). Serial interface peripherals such as modem, printer, mouse etc. use RS-232. We can only connect a single transmitter to a single receiver in RS-232. It supports full-duplex communication with baud rate up to 1 Mbps. The maximum cable length is 50 feet. RS-232 port has nine pins which are divided into male and female heads. The RS-232 C is the successor of RS-232 which supports data transmission rates of 50, 75,100, 150, 300, 600, 1200 ,2400, 4800, 9600 and 19200 baud per second.
Features of RS-232
- High interface signal level – its signal level is high
- The transmission rate is low, in asynchronous mode the bit rate s 20 Kbps
- Standard ground transmission is prone to interference having poor noise immunity
- The transmission rate is limited, and maximum it can go to 50 feet so it can reach only 15 meters
What is RS-422?
The RS-422 is ‘electrical characteristics of balanced voltage digital interface circuit’ to define circuit interface characteristics. It is a multiport serial interface. It can connect 10 transmitters to 10 receivers with a single bus. It uses two twisted pair cables to send data. The length of cable is 4000 feet with baud rate of 10 Mbps.
Features of RS-422
- Uses four wire interface for separate transmit and receive channel so there is no need for data control direction
- Signal exchange happens in software mode (XON/XOFF) or hardware mode
- Maximum transmission distance is 4000 feet about 1219 meters
- The highest transmission rate is only possible with short distance
- Requires terminating resistor which is connected to farthest end of cable
What is RS-485?
RS-485 is industry preferential protocol. It can connect 32-line receivers and drivers in differential connection. RS-485 is used when communication distance is several meters to several kilometers. It uses balanced transmit and differential receive to reject interference of common mode. It detects voltages as low as 200mV and can recover signals beyond a kilometer. It uses half-duplex mode and sends only one point at a time, thus the transmitting circuit is controlled by an enabled signal.
Features of RS-485
- Highest transmission rate is 10 Mbps
- Good anti-noise performance and capability towards common mode interference
- It has multi-station capability
Comparison: RS-232 vs RS-422 vs RS-485
| Function | RS-232 | RS-422 | RS-485 |
| Operation mode | It has Single ended mode of operation | It has differential mode of operation | It has differential mode of operation |
| Number of drivers and receivers on single line | It has one driver and one receiver | It has 1 driver and 10 receiver | It has 1 driver and 32 receiver |
| Maximum cable length | Can go up to 50 feet | Can go up to 4000 feet | Can go up to 4000 feet |
| Maximum data rate | Can go up to 460kb/s | Can go up to 10 Mb/s | Can go up to 30 Mb/s |
| Maximum driver output voltage | Can go up to +/-25V | Can go between -0.25V to +6V | Can go between –7V to +12V |
| Driver Output Signal Level (Loaded) | Can go between +/-5V to +/-15V | Can go up to +/-2.0V | Can go up to +/-1.5V |
| Driver Output Signal Level (Unloaded) | Can go up to +/-25V | Can go up to +/-6V | Can go up to +/-6V |
| Driver Load Impedance (Ohms) | Can go between 3k to 7k | Can go up to 100 ohms | Can go up to 54 ohms |
| Receiver Input Voltage Range | Can go up to +/-15V | Can go between -10V to +10V | Can go between -7V to +12V |
| Receiver Input Sensitivity | Can go up to +/-3V | Can go up to +/-200mV | Can go up to +/-200mV |
| Receiver Input Resistance (Ohms) | Can go between 3k to 7k | Can go up to 4k min. | Can go up to >=12k |
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj