Table of Contents
What is SDN OpenDayLight Project?
The OpenDayLight Project is a collaborative open source project in a vendor-neutral environment. The goal of the project is to accelerate the adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) and create a solid foundation for Network Functions Virtualization (NFV). The software is written in Java.
OpenDayLight, the largest open source SDN controller, is helping lead the transition for building programmable networks that are flexible and responsive to organizations’ and users’ needs.
History
OpenDayLight Project is hosted by The Linux Foundation. It all started on April 8, 2013 when Linux Foundation announced the founding of the OpenDayLight Project as a community-led and industry-supported open source framework to accelerate adoption, foster new innovation and create a more open and transparent approach to Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV).The founding members of project were committed to donating software and resources for OpenDayLight’s open source framework, a platform for SDN. The member were –
- Arista Networks
- Big Switch Networks
- Brocade
- Cisco
- Citrix
- Ericsson
- HP
- IBM
- Juniper Networks
- Microsoft
- NEC
- Nuage Networks
- PLUMgrid
- Red Hat and
- VMware
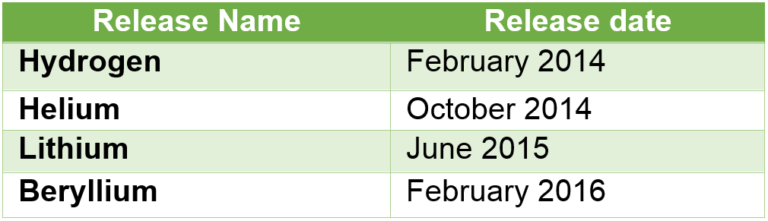
A lot of deliberations have been happening on OpenDayLight project and members working day and night to improve the framework capabilities and adjusting experience. Below are the OpenDayLight releases –
OpenDayLight Project Framework
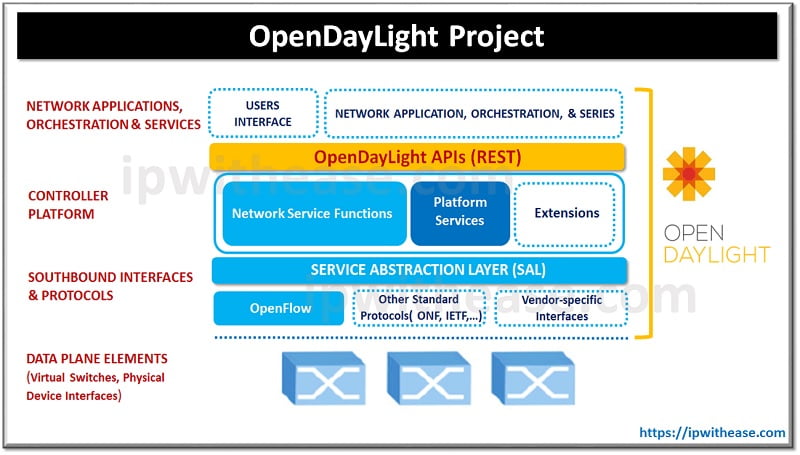
As shown in the above Project framework of OpenDayLight ,
Key Components of OpenDaylight
- Controller: The core of the OpenDaylight platform, it manages the network through SDN protocols such as OpenFlow, BGP, PCEP, and more. The controller is responsible for maintaining a global view of the network and applying policies that are defined by applications.
- Model-Driven Service Abstraction Layer (MD-SAL): This layer provides a common API framework that separates the business logic (applications) from the underlying data models. It supports both YANG (Yet Another Next Generation) models and REST APIs, allowing for dynamic configuration and management.
- Network Applications: Various applications can be built on top of the OpenDaylight platform to perform tasks such as routing, switching, firewalling, and network analytics. These applications interact with the controller through well-defined APIs.
- Plugins and Protocols: OpenDaylight supports a wide range of networking protocols and technologies, such as OpenFlow, NETCONF, OVSDB, BGP, and more.Plugins allow the platform to be extended and customized for different use cases.
- Southbound Interfaces: These are interfaces that communicate with the network devices (like switches, routers) to gather state information and implement the control policies decided by the controller. Protocols like OpenFlow and NETCONF are used for this purpose.
- Northbound APIs: APIs provided to applications running on top of the OpenDaylight platform to interact with the underlying network infrastructure. Typically, RESTful APIs are used to allow applications to retrieve data and execute operations.
- Clustering and High Availability: OpenDaylight can be deployed in a clustered environment to ensure high availability and scalability.
- The clustering mechanism allows for the distribution of workloads and state information across multiple instances.
To summarize, the open community is building following key elements:
- An evolvable SDN platform capable of handling diverse use cases and implementation approaches
- Common abstractions of capabilities Northbound for people to program
- Intermediation of those capabilities to multiple Southbound implementations
- Programmable network services
- Network applications
- Whatever else we need to make it work
Benefits of OpenDaylight
- Flexibility and Modularity: Allows customization and extension of the platform to suit specific needs.
- Open Source: Encourages collaboration and innovation through a community-driven approach.
- Vendor-Neutral: Supports a wide range of hardware and software from different vendors.
OpenDaylight serves as a powerful framework for organizations looking to adopt SDN and network automation, providing the tools and infrastructure needed to build and manage next-generation networks.
Continue Reading
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj