Table of Contents
Cookie poisoning is a technique where cookie information is modified by the hacker with its own malicious code to trick the website into believing that the threat actor is a legitimate user and once the threat actor gains unauthorized access to system it can access user credentials, sensitive information and do unauthorized transactions on website on behalf of actual user.
Cookies are a widely used term and very popular on the Internet. We all encounter cookies while browsing websites but do we know what purpose these cookies serve and why we need them?
Cookies are transmitted by web server to web browsers comprising small messages used in monitoring user activity while they are visiting the webpage. It is stored on your computer and used at the time of iteration during web browsing. Information is transmitted back to the web server when the user revisits the website or webpage. The purpose of cookies is to improve user experience by session management; however, hackers or cyber attackers can temper with website cookies to gain unauthorized access to user accounts information, sensitive data or to control over web applications.
In this article we will learn more in detail about Cookie poisoning, how it works, what we can do to prevent cookie poisoning attacks.
Cookies and Their Purpose
Cookies are small text files stored on your system while you are browsing websites.
Cookies are used for a wide range of activities starting from session management to record user login details or establish user behavior preferences during navigating web sites. Personalization is another aspect which is dealt with using the cookies as they track individual browsing behavior and trailer the website content accordingly. Apart from these two functions cookies are also meant for tracking and analysis and collecting data on how the end user navigates the website and uses it. This tracking is required to improve website performance and end user experience. Cookies are stored either on your computer or web browser folder.
What is Cookie Poisoning?
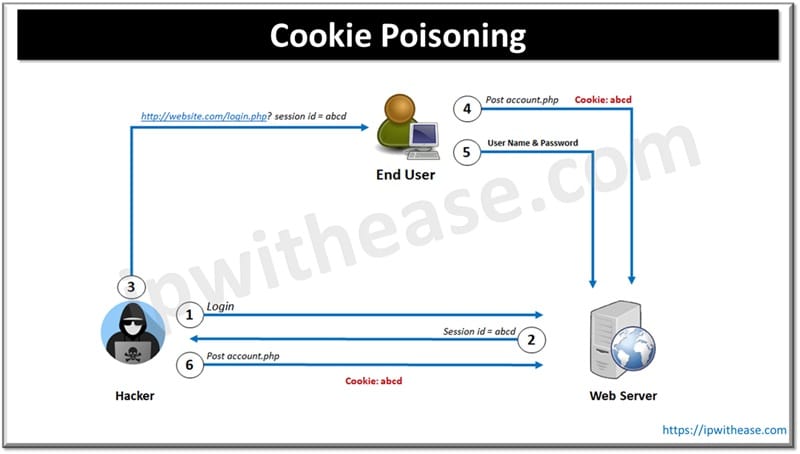
A type of cyberattack where a threat actor tampers with website cookies and tries to get unauthorized access to the end user system by gaining control over their credentials, sensitive data, and control the web applications. Cookies store information which could aid in identifying users, tracking sessions or remember end user browsing preferences. Hackers manipulate cookies to steal data, impersonate legitimate end users and gain access to systems and applications, perform transactions by impersonating legitimate users. Cookie poisoning is a serious threat to web security.
Causes of Cookie Poisoning
Malicious code is inserted by hackers into legitimate user website by
- Existing vulnerabilities exploitation for end of life or end of support software’s such as Java
- Using SQL injection and cross-site-scripting to inject malicious code into database queries on web server
- Modifying specific data in cookies such as product price during checkout process
- When cookie transmission happens over insecure protocols attackers can intercept traffic and change cookie contents during the transit
- Poor set cookie security without secure flags or HTTP Only make cookies vulnerable for client-side-attack
- Weak encryption is also one of the leading causes for cookie poisoning
- Lack of validation of data stored in cookies lead to hackers injecting malicious data which would go unnoticed
How Cookie Poisoning works
- Hacker takes the advantage to gain access to a website by utilizing cookie poisoning technique basis typical behavior of the website on how the user is logged in or not by using the cookie.
- Attacker can modify the login cookie and redirect user to a fake website which is similar to legit website
- At times applications use multiple URLs for a single website, in such scenario attacker can poison cookie of one website and gain access to multiple websites
Cookies can be poisoned from the client side by cookies modification happens directly on the web browser. Session tokens stored in cookies on many website hackers can use sophisticated tools or JavaScript to modify values stored in cookies and impersonate as legitimate users.
Man-in-the-middle attacks are done by hackers by intercepting data when it travels between web browser to web server. This kind of attack is quite common on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks where traffic flows unencrypted.
If cookies are captured during the transmission hackers can alter them and send them back to web servers.
Cookie Poisoning Detection and Prevention
- Vulnerability scans periodically can flag issues
- Periodic penetration testing helps in identifying cookie management weaknesses in the system or website
- Checking server logs for any unusual activity, suspicious session data or tempered cookies
- Cookie settings inspection to ensure they are set to HTTPOnly and secure flags
- Rotation of session cookies and setting them to expire reduces changes of misuse
- All cookie inputs are validated properly for blocking harmful content
- Using secure VPN over Wi-Fi networks
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj