Table of Contents
Cyber hygiene is a constant process to secure use of IT assets and poorly maintained cyber hygiene could lead to breaches, malware infections, phishing attacks, compromises and financial losses.
Protection of digital assets is of paramount importance and it can’t be achieved only by implementing expensive security tools or hardware. It is more about practice, a reflex action which needs to be imbibed in organization culture.
Organizations can deploy world class IT security policies but users need to understand that sharing passwords is a big risk – here comes the human aspect of security. A missed patch, an unprotected system running with anti-virus software, an IT engineer left his system open with the admin console after the activity are some such examples.
In this article we will learn more in detail about Cyber hygiene, its importance in digital IT and what can be done to improve it.
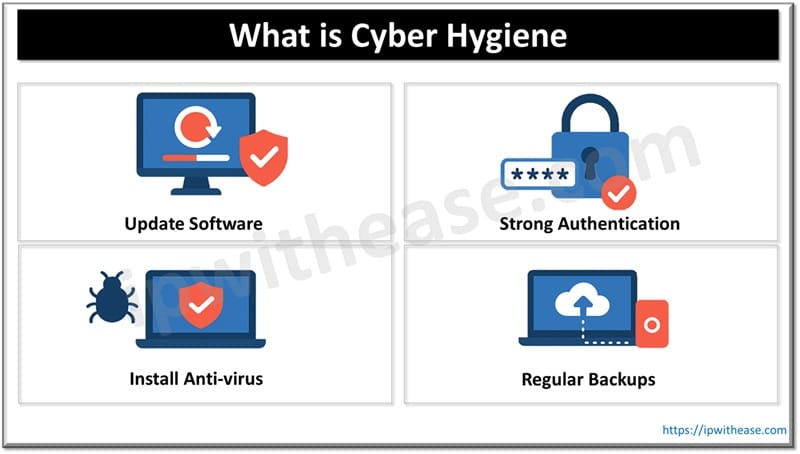
Understanding Cyber Hygiene
Cyber hygiene is collectively referred to as practises and behaviours which users and organizations adapt to ensure digital IT assets are healthy and operate and used in a secure manner. The aim is to prevent cyber threats such as ransomware, phishing attacks, malware infections, data breaches, unauthorized access etc.
It is not a tool or product to procure and deploy it is a discipline which combines ongoing commitment to security and best practices. Poor cyber hygiene leads to $4.4 billion losses in 2025 as reported by IBM in its cost of data breach report. The majority of such breaches were contributed due to human factors – reuse of passwords, not implementing security updates, or failing to recognize phishing emails which could lead to a door open for hackers to enter and breach organization systems.
Consequences of Poor Cyber Hygiene
- Financial losses – ransomware attacks are the most common cause of huge losses to businesses in ransom payments, reputation and brand image loss
- Reputational damage – a single breach can erode customer credibility and confidence in organization services
- Regulatory penalties – the data breach could lead to hefty penalties and fines
- Operational downtimes – cyberattacks can disrupt business operations and lead to downtimes and impact productivity
Poor cyber hygiene by users could lead to identity theft, credential theft, and financial raids.
Common Cyber Hygiene Practices
Good cyber hygiene is a collection of good practices. Let’s look at them more in detail.
- Strong Authentication – Use of complex and unique passwords with multifactor authentication enabled help in adding first layer of defence so even if the password is compromised the hacker cannot gain access to the account.
- Regular Software Updates – Periodic updates to all operating systems, firmware, applications are important aspects of cyber hygiene as it prevents attackers from exploiting systems which are vulnerable due to out of date patches.
- Phishing Awareness – regular awareness campaigns targeted around phishing attacks help in building a security aware users
- Regular Data Backups – are key to control and disarm the ransomware attackers
- Use of Standard Security Software – always install and maintain trusted antivirus or malware program preferable real time threat protection tools which help in effective containment of persistent threats.
- Secure Browsing – companies nowadays deploy web filtering software to ensure safe browsing experience as end users always ensure to verify open websites having HTTPS. Avoid downloading data from suspicious or unknown websites and be cautious while using public Wi-Fi networks and never share personal details such as bank information etc.
- Secure Devices – devices need to be secured with passkeys, or biometric authentication
- Identity Monitoring – Monitoring of tools and services indicates if personal information is being exposed and data breach has happened. Monitoring key security tools provide indicators of early breach signs and early detection help in containing the threat before being exploited by hackers.
Challenges to Cyber Hygiene
- Threat landscape – is consistently evolving as technologies like AI and ML are exploited by hackers which means organizations need to be always on the alert to identify and eradicate them
- User complacency – is another factor which is dangerous and majority of users underestimate the risks and their lax behavior impacts cyber hygiene effectiveness
- Resource constraints – small and medium businesses are often having urgency to delivery quickly, limited budget and low technical expertise which impacts cyber hygiene efforts
- Growing digital footprint – since systems are no longer confined to a physical space and users can operate from any locations or any devices. Each device or account becomes a potential source of vulnerability if not secured properly
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj