Table of Contents
Since the trend for adoption of internet and online services increased exponentially over a few years; it changed the way people work, socialize and communicate. The primary goal of the internet is data transmission from one node to another node in a network; however, this vast ocean of data and information is haunted by security and privacy issues. It has become a playground for cybercriminals who are always on the lookout for security loopholes and vulnerabilities that exist in a network.
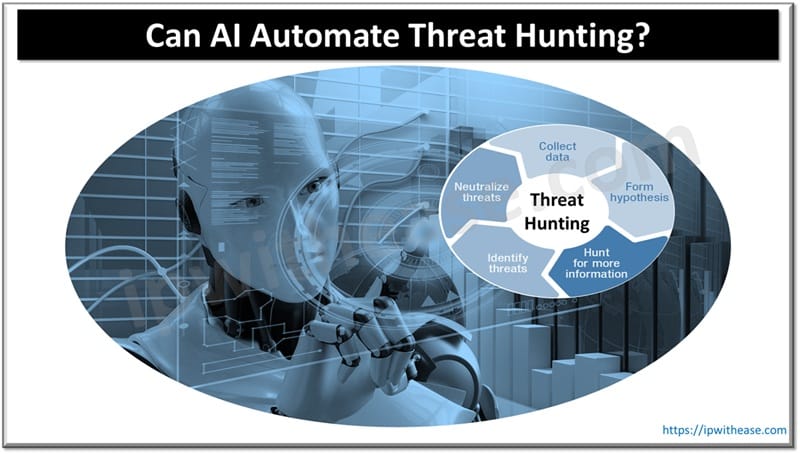
Intrusion detection and prevention systems play a key role in the cyber security landscape. However, these robust security solutions can’t catch zero day vulnerabilities deployed by hackers using more advanced cyberattacks. These zero day vulnerabilities remain hidden from intrusion detection/prevention systems in most of the cases.
Signature based and rule based algorithms are used in intrusion detection / prevention systems which provide an effective guard against traditional security threats but not that capable when it comes to advanced persistent threats.
Many researchers did try to propose using different artificial intelligence-based techniques to detect, respond and prevent advanced threats. AI and MI can help in building accurate and more precise prediction systems which can deal and act intelligently in persistent threat scenarios.
In this article we will learn more in detail about the role of AI in detecting zero-day exploits.
What is Zero-Day Exploit
A zero-day exploit is an undetected or new vulnerability in hardware, firmware and software. There are no fix / patch available which attackers can exploit which poses a security risk. A zero day is one of the most dangerous kinds of cyber-attacks as its target is an undisclosed or undiscovered vulnerability which leaves legacy systems highly susceptible to compromise.
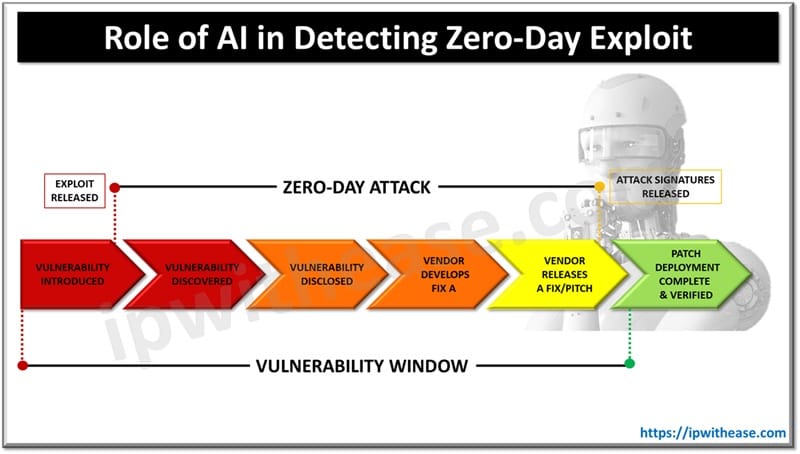
Role of AI in Zero-Day Exploit Detection
Traditional threat detection and prevention systems work on signature or pattern based methodology which are not enough to handle modern day advanced and persistent cyber-attacks which can change memory, interact between components, communicate with command and control, open files and activate threads and perform packet routing. To cope with such advanced threats machine learning algorithms can help in developing something more accurate and precise to predict future events.
A zero-day exploit looks for ‘traffic pattern of interest’ and it has no matching pattern in malware in networks. Zero-day attacks are unknown in nature and used to launch complex attacks which are tough to detect by intrusion systems. Zero-day attacks can come in various forms such as worm (polymorphic) virus, Trojans, network attacks or any other type of malware which are not detectable sometimes. They use various exploitation techniques such as dropping shells for compromised hosts for connections in future, evasion of target defenses etc.
Deep learning (DL) is part of ML which comprises multiple hidden artificial neural networks (ANNs). This applies model non-linear transformation and high-level model abstraction on databases and DL learning algorithms have computational models made up of multiple processing layers to learn data representation using abstraction at several layers. DL can find complex structures in large and complex datasets and this technique can be used for technical predicament.
Key Benefits
- Real-time detection: for quick identification of new threats
- Faster response: reduces time in detection and mitigation
- Scalability: can handle massive volumes of data and complex modern day cyber threats
AI Based Solutions for Exploit Detection
This section introduces various AI models, datasets, evaluation metrics used in zero-day exploit detections.
- Decision Trees – An ML approach which is a supervised and non-parametric learning technique which is based on recursive tree structure which is used in classification and regression. The end goal is to determine the value of the target variable with learning basic decision rules abstracted from data attributes using a tree like model. Also, it does not require extensive processing.
- Random forests are a simple supervised learning algorithm which is applied to both classification and regression and produces a forest via collection of decision trees trained frequency using a ‘bagging’ model.
- Multi-layer perception technique is used to deal with non-linear separable situations. It does pattern classification, approximation, recognition and predictions.
- Bloom filter model used to check whether an object belongs to specific data sets.
- Long short term memory – is a DL model based on artificial RNNs to handle whole data sequences such as voice recognition and handwriting identification.
Hybrid multilevel anomaly detection-IDS – it stores signatures from network traffic to identify malicious traffic.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj