Table of Contents
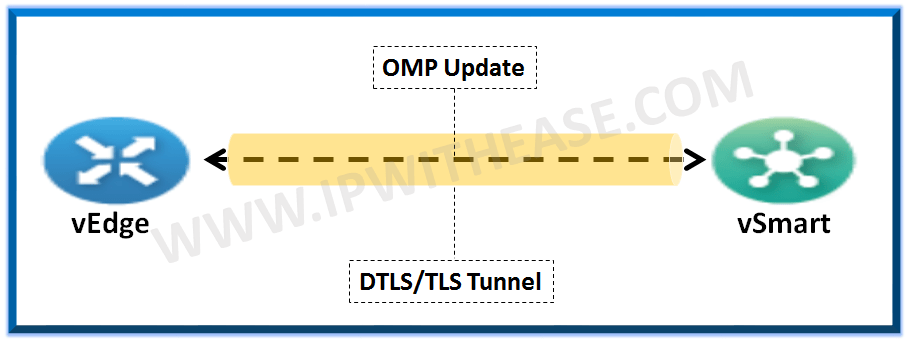
In Cisco’s Viptela SDWAN OMP is a new protocol introduced which forms the heart of the overlay network. OMP is a protocol that runs inside the TLS or DTLS tunnels formed between the vEdge router and vSmart controller. OMP is a control protocol that is used to exchange the routing, policy, and management information between the vSmart controllers and vEdge routers in the overlay network.
Related – Underlay vs Overlay Network
OMP protocol or Overlay Management Protocol is enabled by default so you needn’t explicitly enable the protocol on vEdge and vSmart. As soon as both the devices authenticate and build DTLS or TLS tunnels across them the OMP protocol peering is established on system IPs of the two devices and exchange of routing information takes place.
OMP Advertises three types of routes as below –
OMP Routes or vRoutes
OMP collects the routes from the site-local network via connected, static, OSPF or BGP running on the sites local network. These routes are then advertised to the vSmart controller along with the following attributes:
- TLOC: It identifies the next-hop of the vRoute. It is similar to the BGP Next_Hop attribute. TLOC is a 3 tuple value {System IP, Color, Encapsulation}
- System IP is the address of the OMP speaker that originates the OMP route
- Color to identify the link type
- Encapsulation type on the transport tunnel
- Origin: It identifies the origin of the vRoute i.e. whether route originated from BGP, OSPF, Connected or Static etc. along with the metric of the original route.
- Originator: IP address from which the route has propagated.
- Preference: If two similar OMP protocol routes exist the one with higher preference is preferred. Default is 0.
- Service: Network service associated with the OMP protocol route.
- Site-ID: Identifier of the site from which the OMP route is propagated.
- Tag: Optional which can be used to match a specific route and then take necessary action on that.
- VPN: VPN-ID in which the route has been propagated.
TLOCs (Transport Location)
TLOC routes identify a transport location. These are the points at which the WAN interface connects to a carrier/provider. Each TLOC is a 3 tuple value consisting of a System IP, Color and Encapsulation.
- System IP: It is an IP assigned to a device as a whole which is much similar like a router ID and isn’t tied to any interface.
- Color: It represents the type of WAN interface on the router.
- Encapsulation: Can be either IPsec or GRE.
Attributes advertised along with TLOC route are –
- TLOC private address: Private IP address of the interface associated with the TLOC.
- TLOC public address: NAT-translated address of the TLOC.
- Carrier: An identifier of the carrier type, which is generally used to indicate whether the transport is public or private.
- Color: Identifies the link type.
- Encapsulation type: Tunnel encapsulation type.
- Preference: Degree of preference that is used to differentiate between TLOCs that advertise the same OMP route. Default is 0.
- Site-ID: Identifier of site from which the OMP protocol route is propagated.
- Tag: Optional which can be used to match a specific route and then take necessary action on that.
- Weight: Value that is used to discriminate among multiple entry points if an OMP route is reachable through two or more TLOCs. For example, if TLOC A has weight 10, and TLOC B has weight 1, and both TLOCs have the same preference value, then roughly 10 flows are sent out TLOC A for every 1 flow sent out TLOC B. Default is 0.
Service Routes
Service routes represent services that are connected to a vEdge router or to the local-site network in which the vEdge router resides. The vEdge router advertises these routes to vSmart controllers using service address family NLRI.
Overlay Management Protocol automatically redistributes the following route types:
- Connected, Static, OSPF interarea and OSPF intra-area.
- For BGP and OSPF external routes we need to explicitly configure the redistribution in OMP.
Similarly, the Overlay Management Protocol routes aren’t by default propagated in Site local IGP routing hence need to be configured explicitly. AD value for an OMP route is 250.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj