Table of Contents
Introduction to BGP FlowSpec
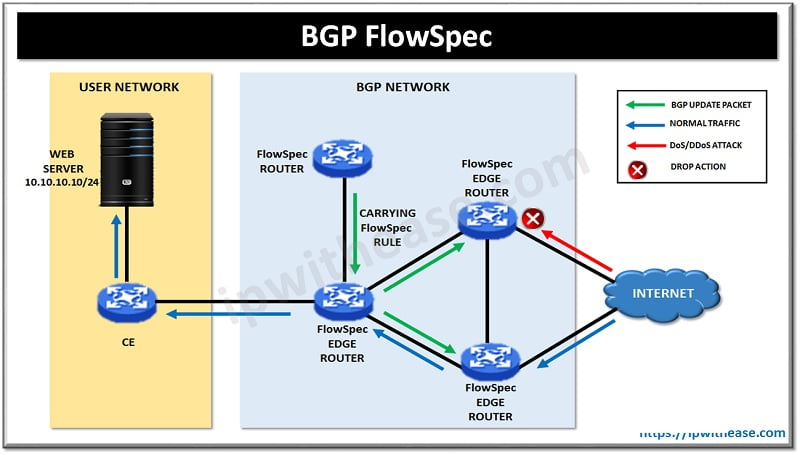
BGP FlowSpec feature permit implementation and propagation of filtering and policing configuration across the large number of BGP peer routers to mitigate the effects of a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack in the network from internet. Another method to mitigate from DDOS attack is Remotely triggered black hole (RTBH) filtering, a technique that provides the ability to drop undesirable traffic before it enters a protected network.
DDoS Overview
Distributed denial-of‐service (DDoS) attacks target network infrastructures or computer services by sending a number of service requests towards the server from many sources.
Addressing DDoS attacks
Detection: Detect incoming fake requests.
Mitigation: Forward traffic to a FlowSpec router that removes the UDP DDOS packets from the traffic stream while retaining the legitimate packets and send back the clean traffic to the server.
Goals of DDoS Mitigation
- Stop the attack.
- Drop only the DDoS traffic.
- Application aware filtering, redirection, mirroring.
- Dynamic and adaptive technology.
- Simple to configure.
- Easy to disseminate.
FlowSpec is used to mitigate the DDoS attack, but its use cases are expanding to other areas such as BGP unequal cost load balancing. With BGP flow specification, it’s possible to identify groups of users based on source address and then use FlowSpec to traffic on all core nodes. FlowSpec NLRI Types are as:
- Destination prefix: Destination address/Prefix of a packet.
- Destination port number: TCP/UDP port number.
- DSCP number: Quality of Service (QoS) packet.
- Fragment type: Flag bit of a fragment.
- ICMP Code: Code of an ICMP packet.
- ICMP number: ICMP traffic.
- Packet length: Total size/length of an IP packet.
- Port number: Port Number of a source or destination.
- Protocol number: Number of each protocol.
- Source prefix: Source subnet/prefix of a packet.
- Source port number: TCP/UDP port number.
- TCP flag: Flag bit in a TCP packet.
BGP FlowSpec Components
Controller: Injects rules remotely in the clients via control plane. BGP FlowSpec Controllers hardware are as: Router (ASR9K, CRS, NCS6000, XR12000), Server (Arbor Peak BGP flow specification Collector Platform), Virtual router (XRv).
Client: Receives rules from Controller(s) and programs the match/action in hardware at both Control Plane and Data Plane. Examples of BGP flow specification Clients: Router (ASR9K, ASR1K).
Route-Reflector (optional): Receives rules from Controller(s) and distributes them to Clients. Examples of BGP flow specification Route-Reflectors: ASR9K; CRS; NCS6000 or XRv.
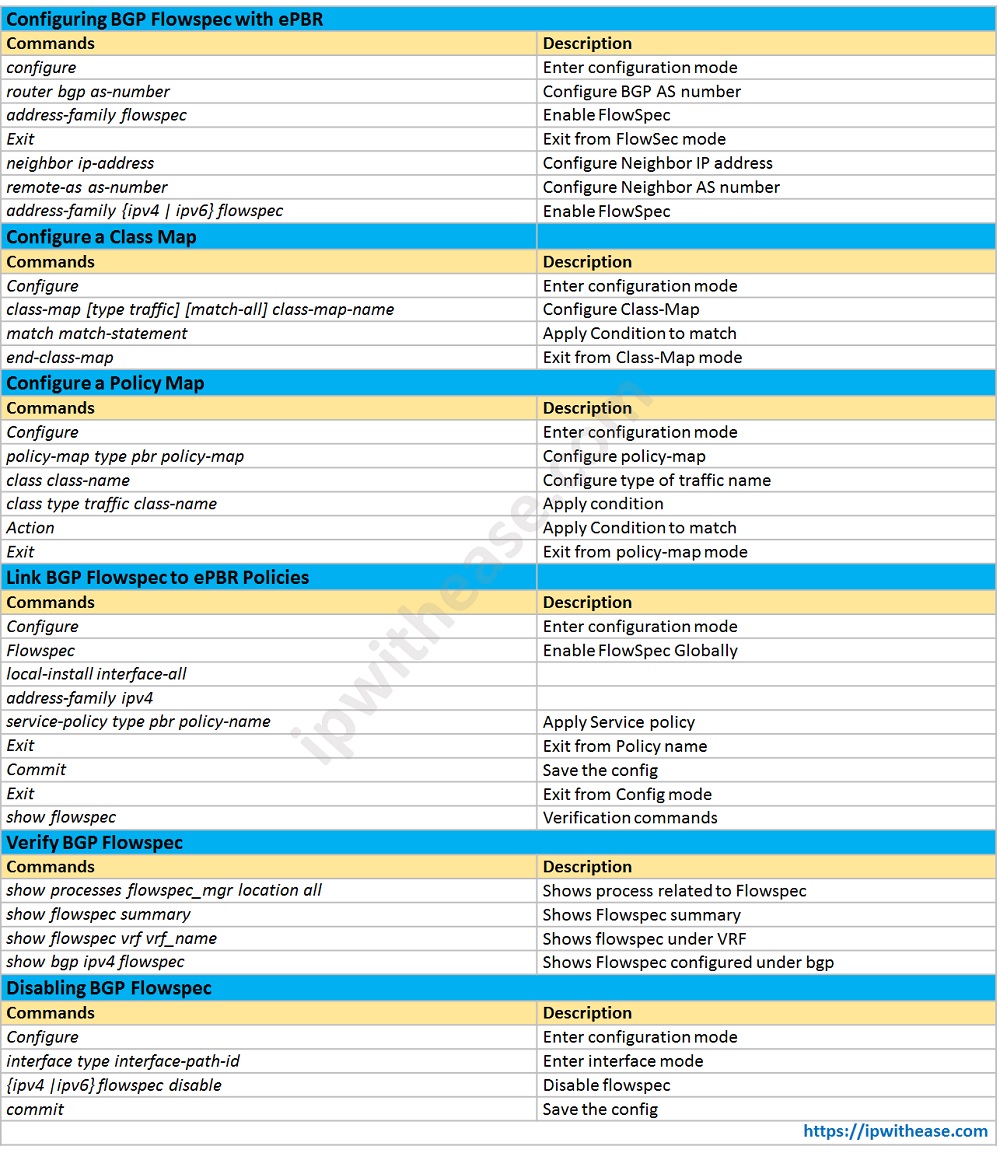
Download the command table here.
Conclusion
BGP Flow Specification is a new feature to assist in DDOS mitigation is a. Flowspec uses the BGP protocol extension to distribute flow specification filters to network routers. Expanding routing information with FlowSpec, the routing system can take advantage of class map and policy map filtering capabilities on the forwarding path to prevents from DDOS attack.
Continue Reading:
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj