BGP NEIGHBOR STATES
BGP forms unicast-based connection to each of its BGP-speaking peers. BGP it uses TCP port 179 as its underlying delivery mechanism. BGP establishes a neighbour adjacency with other BGP routers before they exchange any routing information.
Unlike other routing protocols, however, BGP does not use broadcast or multicast to “discover” other BGP neighbours.
Related Article – BGP Local Preference
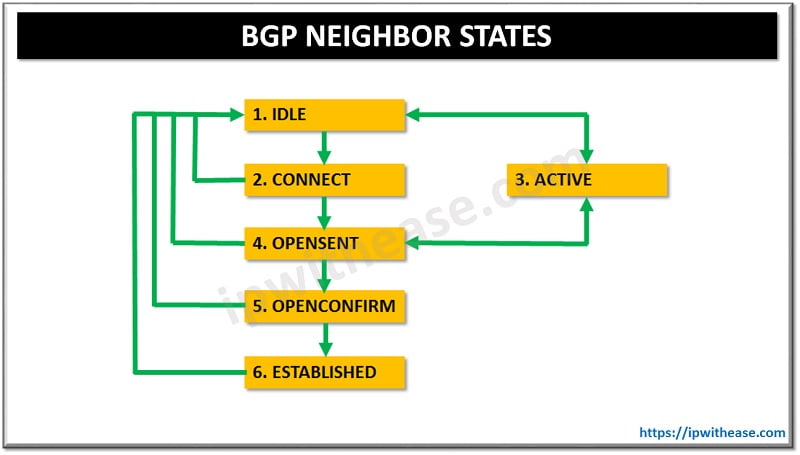
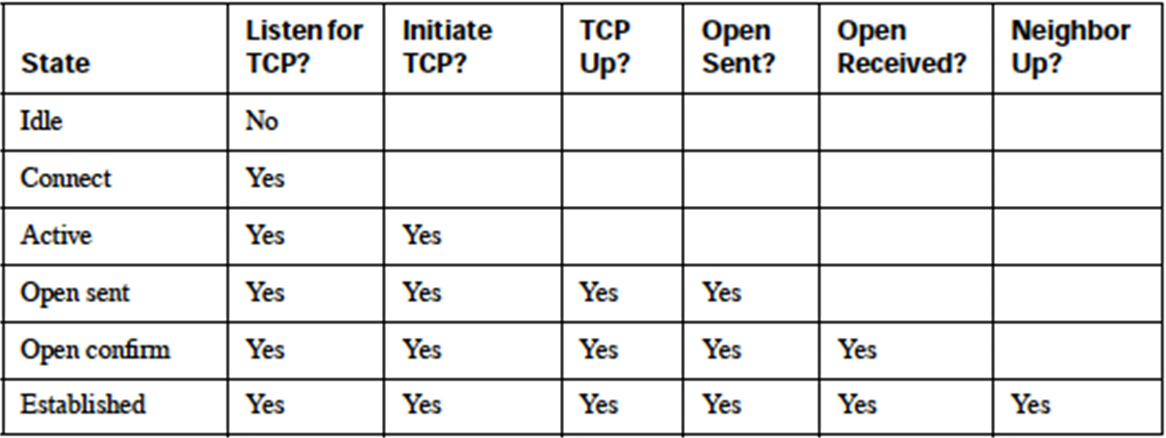
When BGP is configured with a neighbour IP address, it goes through a series of stages before it reaches the desired Established state. Per RFC 1771, BGP goes through the following stages of a neighbor relationship –
- IDLE State: verifying route to the neighbor
BGP refuses all incoming connections. No BGP resources are allocated in idle state, and no incoming BGP connections are allowed.
- Connect State:
BGP waits for a TCP connection to be completed. If successful, the BGP state machine moves into the OpenSent state after sending the OPEN message to the peer. Failure in this state could result in either going into Active state or Connect state, or reverting back to Idle state, depending on the failure reasons.
Related – BGP Interview Questions
- Active State: (Attempting connectivity to neighbor)
In this state, a TCP connection is initiated to establish a BGP peer relationship. If successful, BGP sends its OPEN message to the peer and moves to OpenSent state. Failure can result in going to the Active or Idle states.
- OpenSent State: (Open message sent to neighbor)
After sending an OPEN message to the peer, BGP waits in this state for the OPEN reply.
If a successful reply comes in, the BGP state moves to OpenConfirm and a keepalive is sent to the peer. Failure can result in sending the BGP state back to Idle or Active.
- OpenConfirm State: (Neighbor replied with open message)
The BGP state machine is one step away from reaching its final state (Established).BGP waits in this state for keepalives from the peer. If successful, the state moves to Established; otherwise, the state moves back to Idle based on the errors.
Related – BGP Confederation
- Established State: (Connection between neighbors established)
This is the state in which BGP can exchange information between the peers. The information can be updated, keepalives, or notification.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj

“Per RFC 1711, BGP goes through the following stages of neighbor relationship –” isn’t it rfc 1771 ?