Table of Contents
Introduction to ‘Multi-tenant’ environments
The exponential growth of data across industry has pushed providers to move from advancing technologies related to traditional data centres instead more towards building more agile and intuitive infrastructures based on cloud. Organizations are moving their in-house traditional data centres and its services to cloud computing and it is very common for a cloud provider to provide applications and services over a centralized network infrastructure platform. This has given rise to a new term called ‘multi-tenant’ environments.
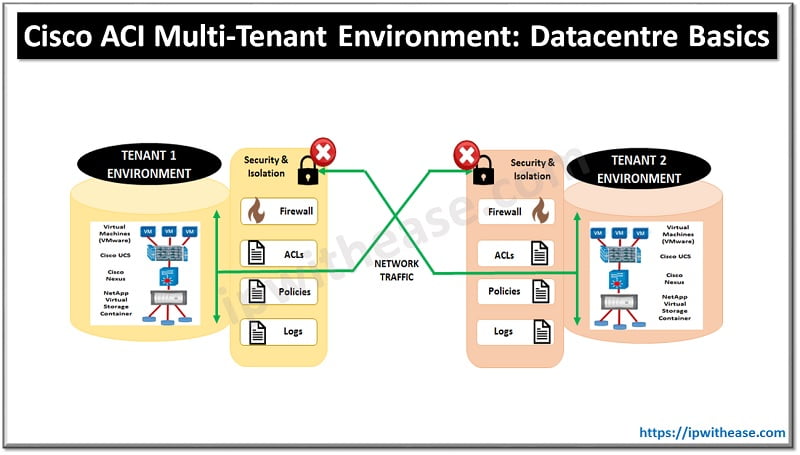
‘Multi-tenant’ environment or multi-tenancy data centres handle segregation of traffic between multiple tenants and ensure privacy and security between tenant data. VLANs have been deployed in data centres to isolate systems of different tenants on a single layer 2 network.
Today we look more in detail about Cisco ACI Multi-tenant environment w.r.t. data center, understand its deployment architecture, its features and use cases etc.
What is Cisco ACI Multi-Tenant environment
In a traditional service providers deployed a dedicated infrastructure for each hosted tenant. This approach will not be viable as it won’t scale up due to its cost, complexity and management perspective. Deployment of multiple tenants in a common infrastructure brings more efficient usage of resources with lower costs.
- Application centric architecture of ACI from Cisco is a holistic architecture with centralized automation and policy driven application profiles management. It delivers flexibility in software delivery with scalability of hardware and provides a robust transport network for managing dynamic workloads. It is built on a network fabric which has on the base the time-tested protocols which delivers a highly scalable, resilient , flexible architecture of low latency, high bandwidth links.
- As compared to traditional data centres where there was a logical separation via VDC (Virtual data centre) in Cisco ACI, tenants subscribed to virtual data centres (VDC) and based on the services hosted by the tenants within the virtual data centre , each virtual data centre can have multiple VN-segments. This could be extended to the virtualized data centres using hypervisor encapsulation VM packets with a VLAN tag related to the VM owner. This achieves Layer 2 abstraction to tenants this gives complete virtualization of layer 2 and layer 3 address spaces.
- Multi-tenant data centres are required to support mobility of VMs within and across SPDC, and into enterprise data centres also in order to achieve dynamic tenant growth and maximize resources utilization and sharing. If a new VM is added to an existing SPDC POD which is already full and all servers are overloaded then the VM tenant will be accommodated in another SPDC POD having sufficient capacity and a server is available. VN segmentation must be extended virtually to anywhere within or across multi-tenant data centres.
- Cisco ACI is delivered as a virtual appliance hosting standard COTS server. There would be a single policy domain and single instance namespace which will stretch across individual data centre fabrics.
- Administrators can configure how services and resources interact with each other.
- ACI multi-tenant environments support live and cold VM migrations and provide DR/BC use cases
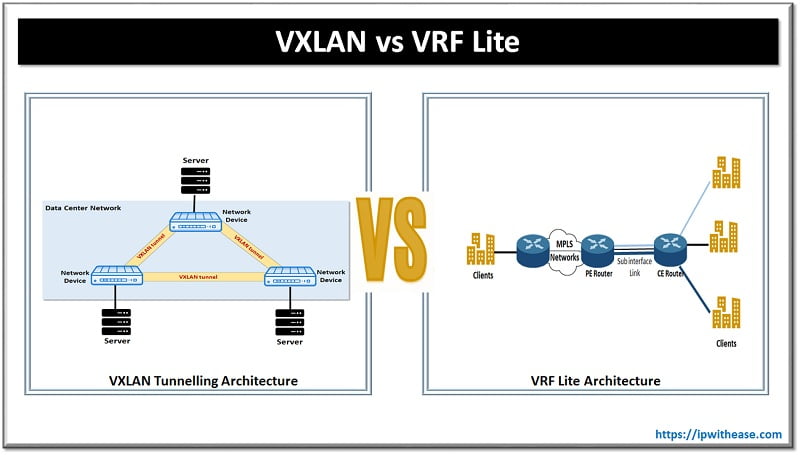
- Layer 3 separation is done using VRF lite which is a hop-by-hop virtualization technique. Each network device and all its physical interconnections are virtualized. VLAN tags can provide logical isolation on each point-to-point Ethernet link.
Features of Cisco ACI Multi-Tenant environment
- Each virtual network represents exact replica of underlying physical infrastructure
- Provides additional level of segregation and security as no communication allowed between devices belonging to different VRFs provided they are configured explicitly
- Simplifies automation by application driven policy model
- Any workload, anywhere , application velocity
- Centralized management , visibility and real time application health monitoring
- Flexibility for DevOps teams and ecosystem partner integration with open software
- Multi-tenancy at hardware level and scalability in performance
- Protection of investment by integration with existing fabric infrastructure e.g., Nexus 7000, ASR 9000 routers
- Integration gateway for VLAN, VxLAN and NVGRE networks from physical to virtual networks
- Open choice for hypervisor and customer is not restricted to hypervisor
- Tracking of network policy as per virtual machine mobility
Conclusion
Cisco ACI offers different multi-fabric options for deployment along with migration path. Cisco ACI multi-tenant data centres offer functions such as isolation, segmentation, and secure individual applications, services to its customers.
Continue Reading:
Cisco ACI Multi-Pod vs Multi-Site: Detailed Comparison
Cisco ACI Network Centric vs Application Centric approach
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj