Table of Contents
Cisco ASIC or Application Specific Integrated Circuits are commonly used in networking. These can be compared to a CPU unit but not meant for general purposes but designed to operate for a specific purpose or application in network devices marketed by Cisco. They are usually tailored to handle a specific task or a set of related tasks. They enhance device performance as they are meant to efficiently perform a specific task with less power consumption.
ASIC are widely used but are bit expensive as they are designed for a specific function or task in networking equipment such as high-speed packet forwarding, deep packet inspection (DPI) usually used by firewalls, traffic management and QoS (Quality of service), data compression and data decompression capabilities for WAN traffic, Network address translation (NAT) in cisco devices.
Since these are customized for a specific task or set of tasks there is a lack of flexibility as once they are designed they can’t be reprogrammed for another task and if need be then a new ASIC design is to be made.
In this article we will learn about Cisco ASIC, its functioning, features and use cases.
Introduction to Cisco ASIC
Application specific integrated circuit as the name suggests meant to be implemented for a specific use case or scenario, functionality, a single function. Unlike CPUs which are meant for general purposes or GCPUs meant for graphic intensive functions. ASIC chips are custom designed keeping specific requirements or functionality in mind.
Some of the examples of ASIC functions are Google Tensor processing units (GPTU) which are designed for acceleration in machine learning functions or for orbit maneuvering where orbit maneuvers are used to move rockets and their payload to a new orbit.
ASIC is hyper-efficient and consumes less power but is a highly complex design. It has a long and slow development cycle using HDL (Hardware description language) e.g. Verilog.
Widely used in packet switching and routing, to provide stateless firewall functionality in networking hardware. ASICs use a special type of memory called TCAM (Ternary Content-Addressable Memory) to store lookup tables of all sorts – such as forwarding tables, Access control lists, class of service (CoS) etc.
ASIC has the capability to execute tasks with high precision and speed makes it an ideal choice for specific business usage which uses dedicated hardware and requires high performance.
Cisco ASIC Technologies
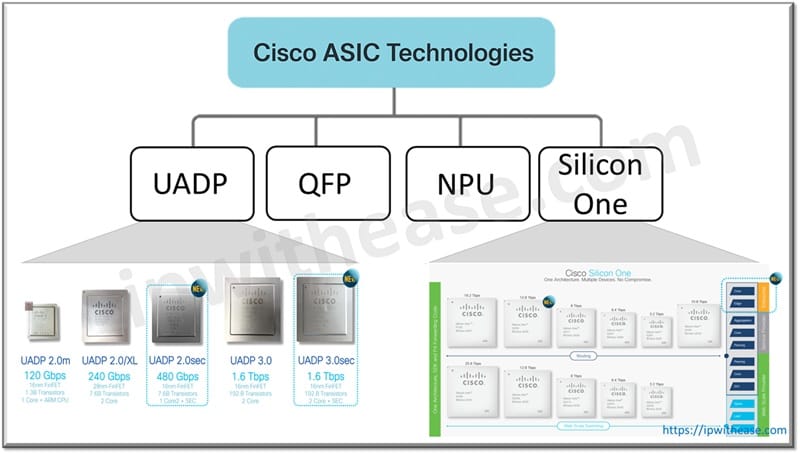
| ASIC | Platform | Description |
|---|---|---|
| UADP (Unified Access Data Plane) | Catalyst 9000 Series | Flexible, programmable ASIC designed for wired + wireless convergence, SD-Access, and segmentation. Enables real-time telemetry and security. |
| QFP (Quantum Flow Processor) | ISR, ASR routers | High-performance packet processing engine for deep packet inspection, routing, QoS, and security at scale. |
| NPU (Network Processing Unit) | Nexus switches, CloudScale platforms | Programmable chips used for custom packet forwarding, allowing support for evolving protocols and telemetry. |
| Silicon One | Cisco 8000, core routers | Cisco’s most advanced ASIC—high-speed, unified routing + switching silicon, supporting up to Tbps speeds. Suited for hyperscale and service provider networks. |
Key Characteristics of ASIC
- Custom design – ASIC are customized for a specific task or set of related tasks. It is tailored for a specific requirement
- Efficiency – efficient in terms of low power consumption and performance as they majorly handle a specific task.
- Developmental cost – process is slow, complex and definitely expensive as it means creating a chip for a specific purpose.
Use Cases of ASIC
- High speed Packet Forwarding – routing and switching in network equipment. Swift lookup of forwarding tables to make real-time decisions
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) – used in advanced network equipment such as firewalls to inspect data packets and make decisions to allow, block, drop traffic based on protocol, applications, specific content etc. and seamless inspection without any bottlenecks.
- Traffic Management and QoS (Quality of service) – traffic prioritization as per predefined policies, rules to ensure critical traffic moves fast such as like streaming etc
- Data Compression and Decompression – Traffic optimization over WAN links is achieved by data compression and decompression handled by ASIC to reduce volume of data that needs to be transmitted over the networks.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) – functionality allows conversion of private IP addresses to public IP addresses on routers or firewalls and that is achieved using ASIC to facilitate communication between public Internet and private networks.
- Consumer Electronics – image processing units in mobile phones, camera performance enhancements, real time facial recognition is handled with ASIC
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj