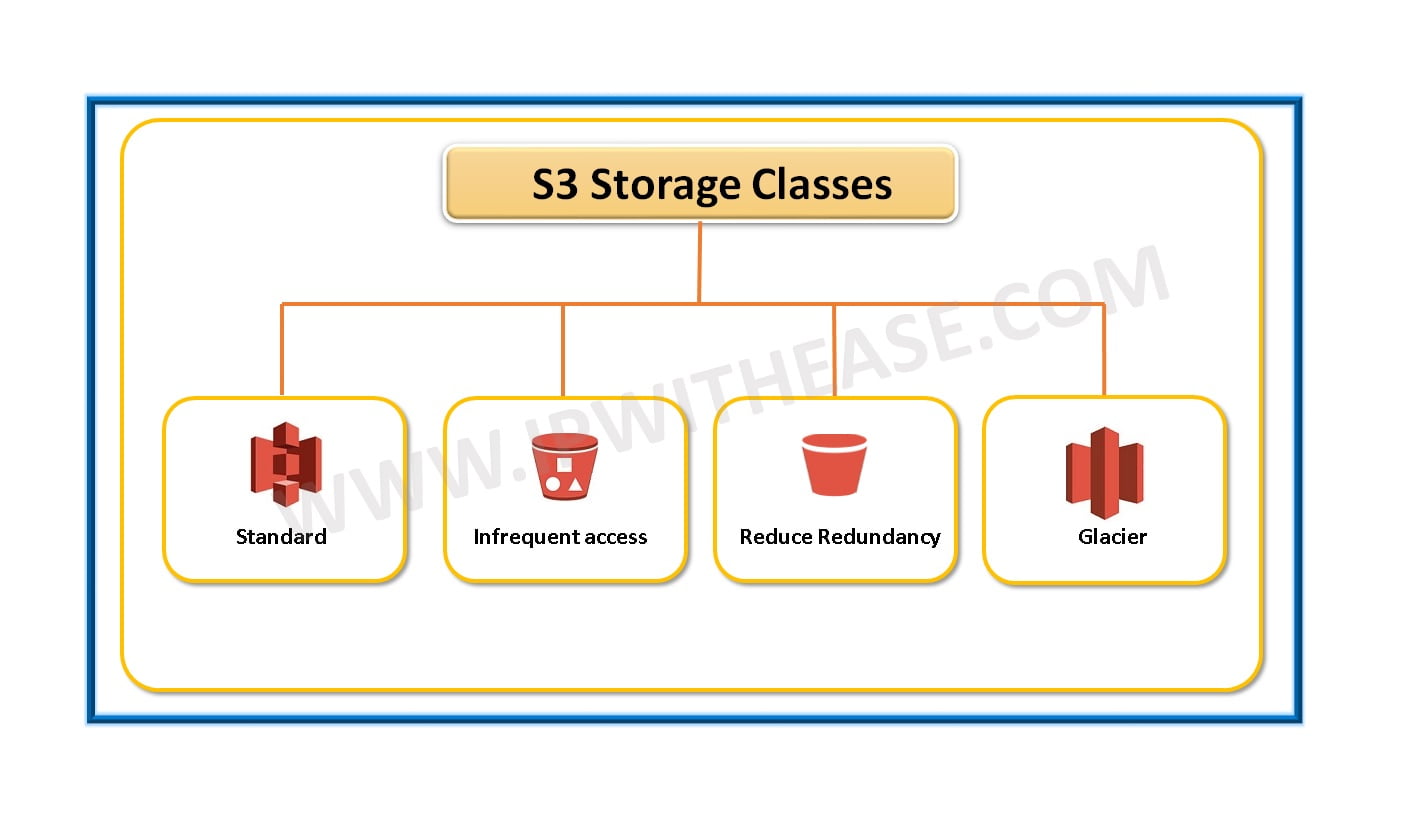
AWS – The organizational unit of Amazon that provides a variety of cloud services. AWS operates from 11 physical locations across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
Application Programming Interface (API) – An application programming interface (API) is an interface that allows the user to access information from another service and integrate this service into their own application. Through a set of defined requests, the asking application is allowed to access limited pieces of the called upon application’s functionality.
Big Data – Term that describes voluminous amount of structured and unstructured data that has the potential to be mined for information.
Cloud Backup – Cloud backup is the process of backing up data to a remote, cloud-based server
CDN – Content delivery network, CDN is A distributed system consisting of servers in discrete physical locations, configured in a way that clients can access the server closest to them on the network, thereby improving speeds.
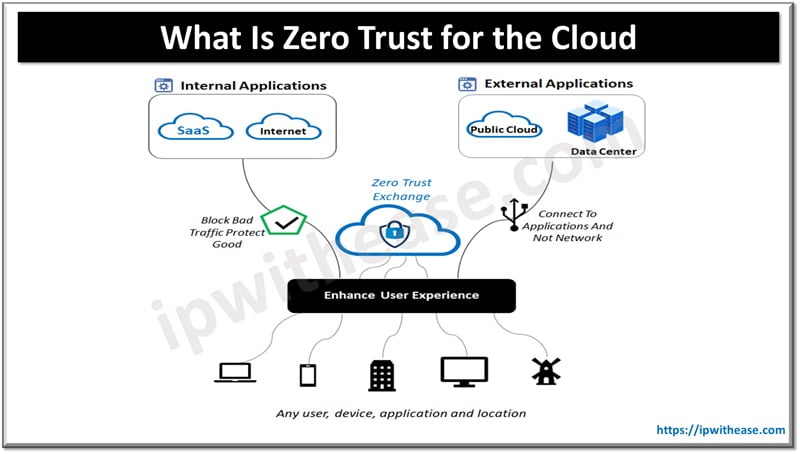
Cloud – A metaphor for a global network, first used in reference to the telephone network and now commonly used to represent the internet.
Cloud bursting – A configuration which is set up between a private cloud and a public cloud. If 100 percent of the resource capacity in a private cloud is used, then overflow traffic is directed to the public cloud using cloud bursting.
DevOps – An amalgamation of “development” and “operations,” DevOps is the combination of tasks performed by an organization’s applications development and systems operations teams. The DevOps software development method emphasizes collaboration, communication and integration between developers and other IT personnel with the goal of streamlining software development and quality assurance.
Docker – Open-source software that automates the deployment of applications inside virtualized software containers.
Elastic computing – The ability to dynamically provision and de-provision computer processing, memory and storage resources to meet changing demands without worrying about capacity planning and engineering for peak usage.
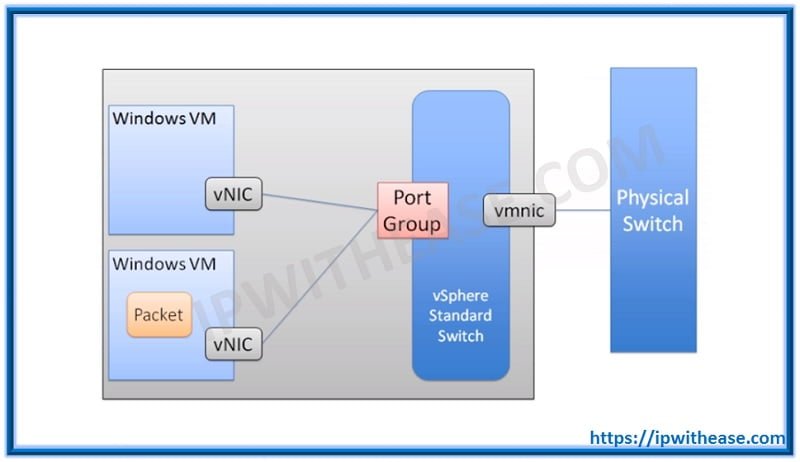
Hypervisor – A hypervisor is a hardware virtualization technique that allows multiple guest operating systems (OS) to run on a single host system at the same time.
Private Cloud – Private Cloud use services and infrastructure stored and maintained on a private network – whether physical or virtual – accessible for only one client. This provides improved level of security and control.
Public Cloud – A Public Cloud is one where services and infrastructure are hosted off-site by a cloud provider, shared across multiple clients and accessed by these clients via public networks such as the internet.
HaaS – Hardware as a service (HaaS) refers to managed services or grid computing, where there is a central computing center that leases computing power from a service provider rather than purchasing their own assets.
IaaS – Abbreviation for Infrastructure as a service, IaaS is a model of cloud computing that provides virtualized computing resources over cloud. In an IaaS model, the cloud provider hosts the infrastructure which was initially stationed at on-premises data center including servers, storage and networking hardware and virtualization or hypervisor layer.
Middleware – Middleware is software that connects software components or enterprise applications.
Open Stack – OpenStack is a free, open-source cloud platform that is primarily deployed as an infrastructure as a service offering.
PaaS – Abbreviation for Platform-as-a-service is a cloud model for building, testing, deploying and managing customized applications .With PaaS, there is no need to buy, configure, or manage the underlying infrastructure. Some examples of PaaS solutions are the “Google App Engine” system, “Heroku” which operates on top of the Amazon Web Services IaaS system, and “Force.com” built as part of the SalesForce.com Software as a Service offering.
Hybrid cloud – The combination of a public cloud provider (such as AWS) with a private cloud platform. The public and private cloud infrastructures operate independently of each other, and integrate using software and processes that allow for the portability of data and applications.
Multitenancy – The existence of multiple clients sharing resources (services or applications) on distinct physical hardware. Due to the on-demand nature of cloud, most services are multi tenant.
SDK – A software developer’s kit a programming package that enables a programmer to develop applications for a specific platform
SLA – A service level agreement (SLA) is a contractual agreement between a customer and a cloud service provider which outlines the level of service, availability and guaranteed performance.
UI – User interface is the way that the user and computer system interact.
Virtual Machine – Virtual Machine is a completely separate individual operating system installation on your usual operating system. It is implemented by software emulation and hardware virtualization.
Virtualisation – The act of creating a virtual rather than a physical version of a computing environment, including computer hardware, operating system, storage devices and so forth.
VDI – Virtual desktop infrastructure is a desktop operating system hosted within a virtual machine.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj