HUB –
A hub is the least expensive, least intelligent and least complicated. Its job is very simple – anything that comes in one port is sent out to the others. If a message comes in for computer “A”, that message is sent out all the other ports, regardless of which one computer “A” is on.

And when computer “A” responds, its response also goes out to every other port on the hub.
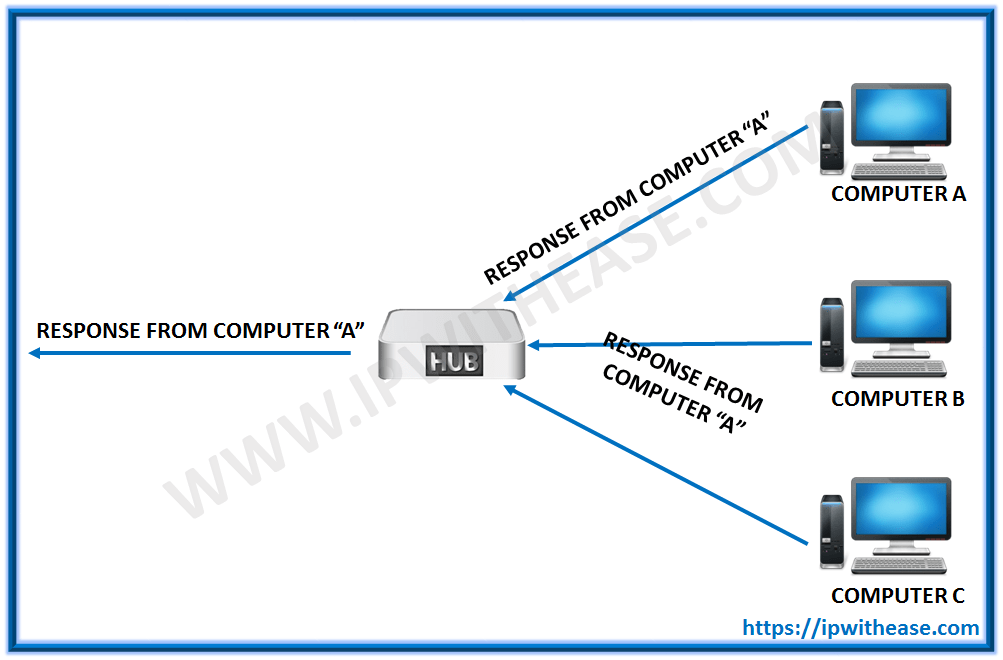
Every computer connected to the hub “sees” everything that every other computer on the hub sees. The computers themselves decide if they are the targeted recipient of the message and when a message should be paid attention to or not.
The hub itself is blissfully ignorant of the data being transmitted. For years, simple hubs have been quick and easy ways to connect computers in small networks.
SWITCH –
A switch does essentially what a hub does, but more efficiently. By paying attention to the traffic that comes across it, it can “learn” where particular addresses are. Initially, a switch knows nothing and simply sends on incoming messages to all ports:

Even accepting that first message, however, the switch has learned something – it knows on which connection the sender of the message is located.
Related Blog – Functions of Network Switch
Thus, when machine “A” responds to the message, the switches only need to send that message out to the one connection:
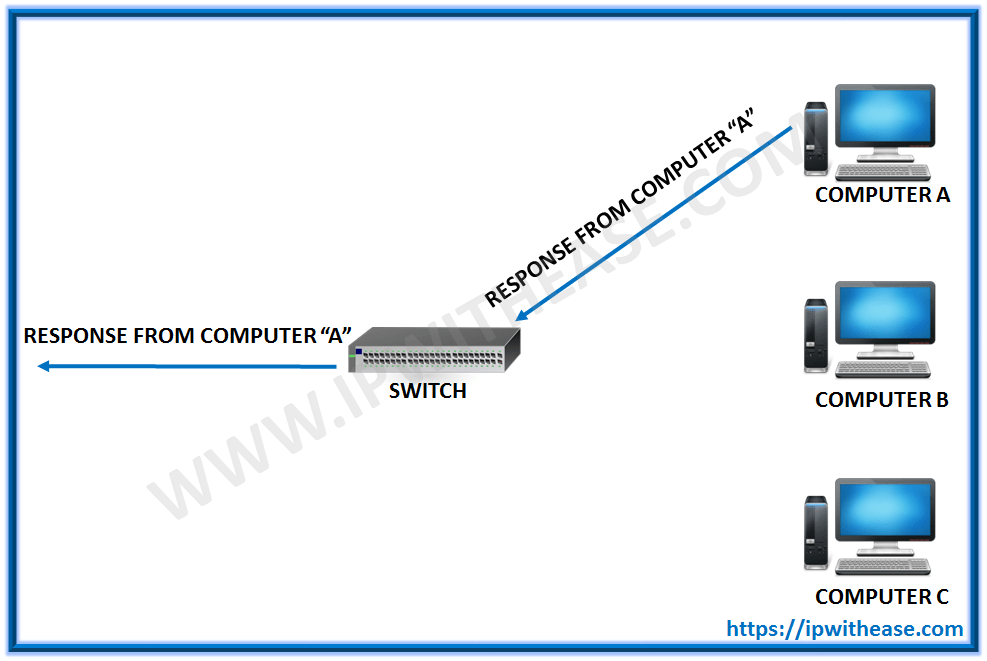
In addition to sending the response through to the originator, the switch has now learned something else – it now knows on which connection machine “A” is located. That means that subsequent messages destined for machine “A” need only be sent to that one port:
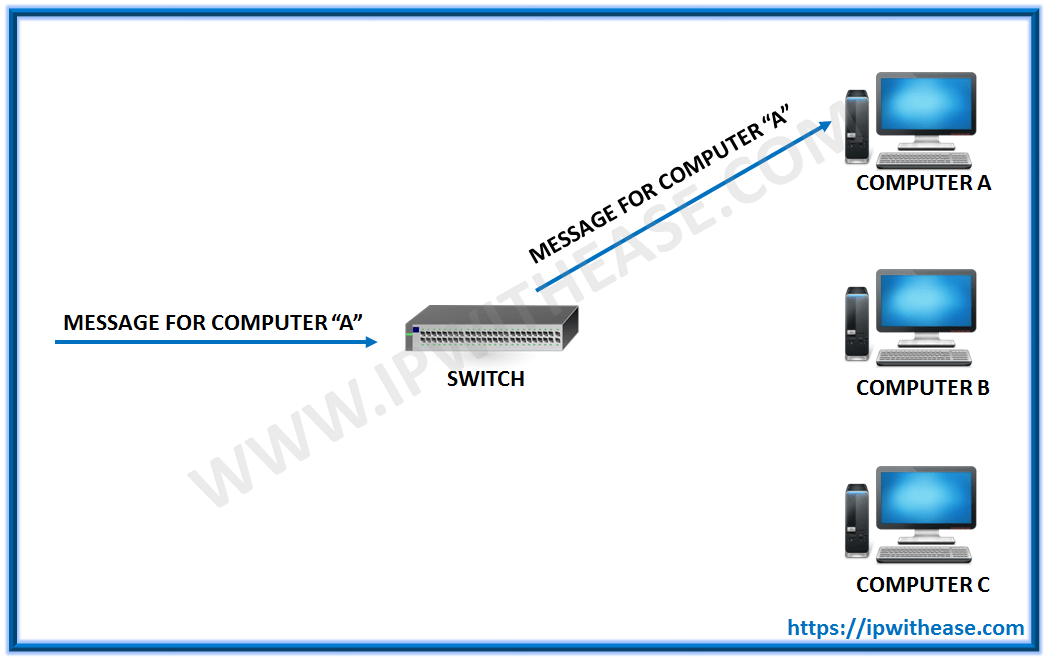
Switches learn the location of the devices that they are connected to almost instantaneously. The net result is that most network traffic only goes where it needs to rather than to every port. On busy networks, this can make the network significantly faster.
Comparison Table: Switch and Hub
A detailed comparison and difference in Network Switch & Hub is given below –
PARAMETER | HUB | SWITCH |
| LAYER | Physical layer. Hubs are classified as Layer 1 devices per the OSI model. | Data Link Layer. Network switches operate at Layer 2 of the OSI model. |
| PORTS | 4/12 ports | Switch is multi port Bridge. 24/48 ports |
| DEVICE TYPE | Passive Device (Without Software) | Active Device (With Software) & Networking device |
| TRANSMISSION TYPE | Hubs always perform frame flooding; may be unicast, multicast or broadcast. | First broadcast; then unicast & multicast as needed. |
| TABLE | A network hub cannot learn or store MAC address. | A network switch stores MAC addresses in a lookup table. |
| DATA TRANSMISSION FORM | Electrical signal or bits | Frame (L2 Switch) Frame & Packet (L3 switch) |
| TRANMISSION MODE | Half duplex | Full duplex |
| FUNCTION | To connect a network of personal computers together, they can be joined through a central hub. | Allow to connect multiple device and port can be manage, Vlan can create security also can apply |
| BROADCAST DOMAIN | Hub has one Broadcast Domain. | Switch has one broadcast domain [unless VLAN implemented] |
| DEFINITION | An electronic device that connects many network device together so that devices can exchange data | A network switch is a computer networking device that is used to connect many devices together on a computer network. A switch is considered more advanced than a hub because a switch will on send message to device that needs or request it. |
| COLLISIONS | Collisions occur commonly in setups using hubs. | No collisions occur in a full-duplex switch. |
| SPANNING TREE | No Spanning-Tree | Many Spanning-tree Possible |
Download the comparison table: Switch vs Hub
Know more about Switch vs Hub in this video:
Continue Reading:
What are Functions of Network Switch?
SWITCHING TOP 50 INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj