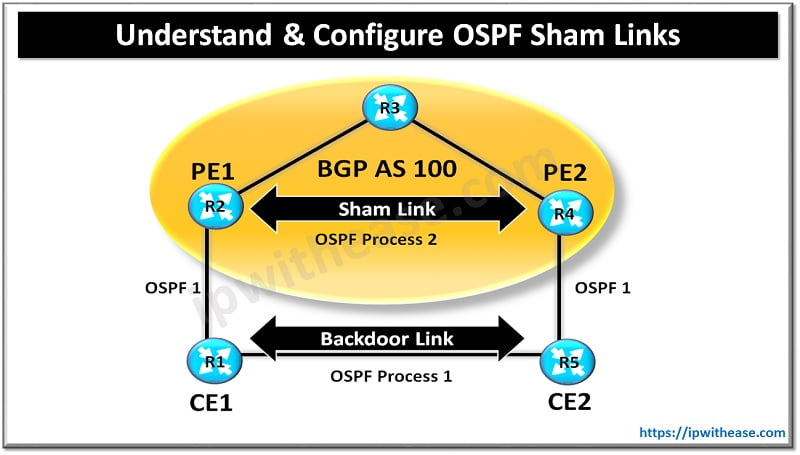
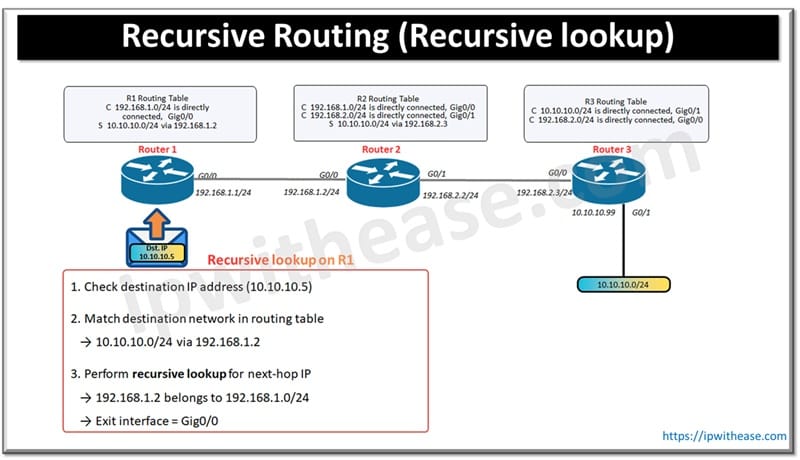
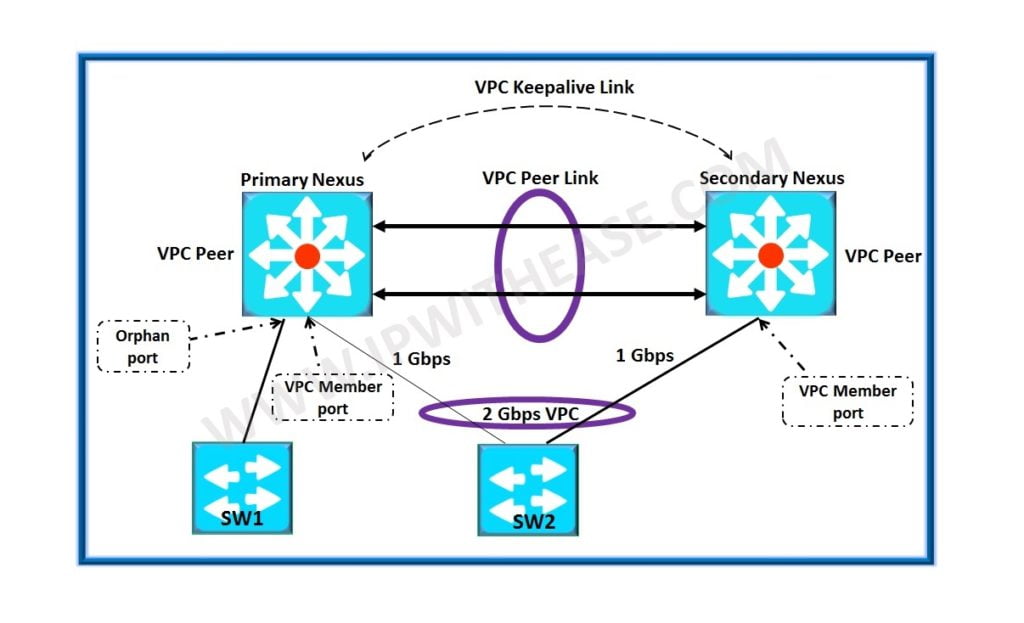
This post will enlist some of salient terms and components related to F5 LTM. These components are indispensable part and used frequenetly while working on F5 LTM system. Below is the list depicted through diagrams –
Nodes
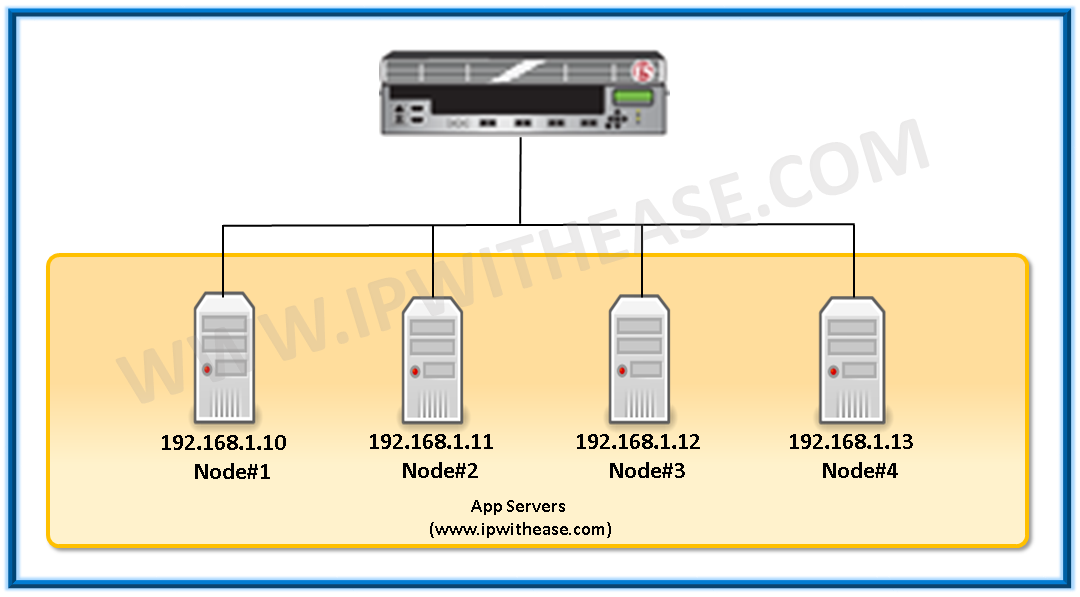
Nodes – A node is represented by the IP address of the Physical server on which application is hosted. It can be physical or logical (for example VMWare) server in the internal network. It can be called as a configuration object represented by the IP address of the server.
Pool Members
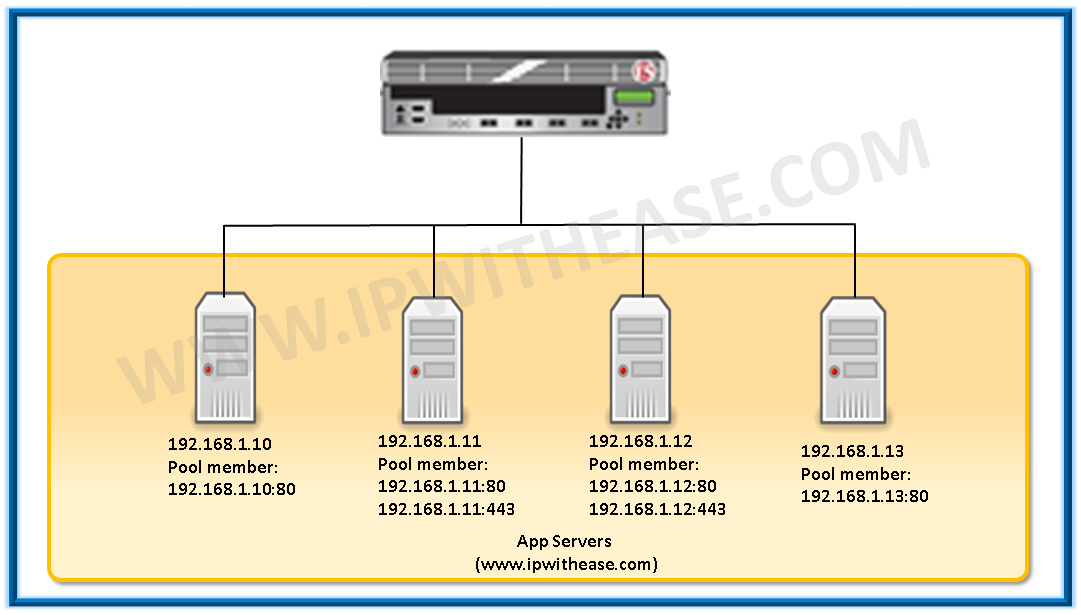
Pool Members: – A pool member is a service running on a node, represented by IP address of the node and service(port) number. For e.g. you have server 192.168.1.1 and application is listening on port 80, then pool member is 192.168.1.1:80. A Node can host multiple pool members like 192.168.1.1:80 and it can be 192.168.1.1:443. A node and service port to which BIG-IP LTM can load balance traffic.
Pool
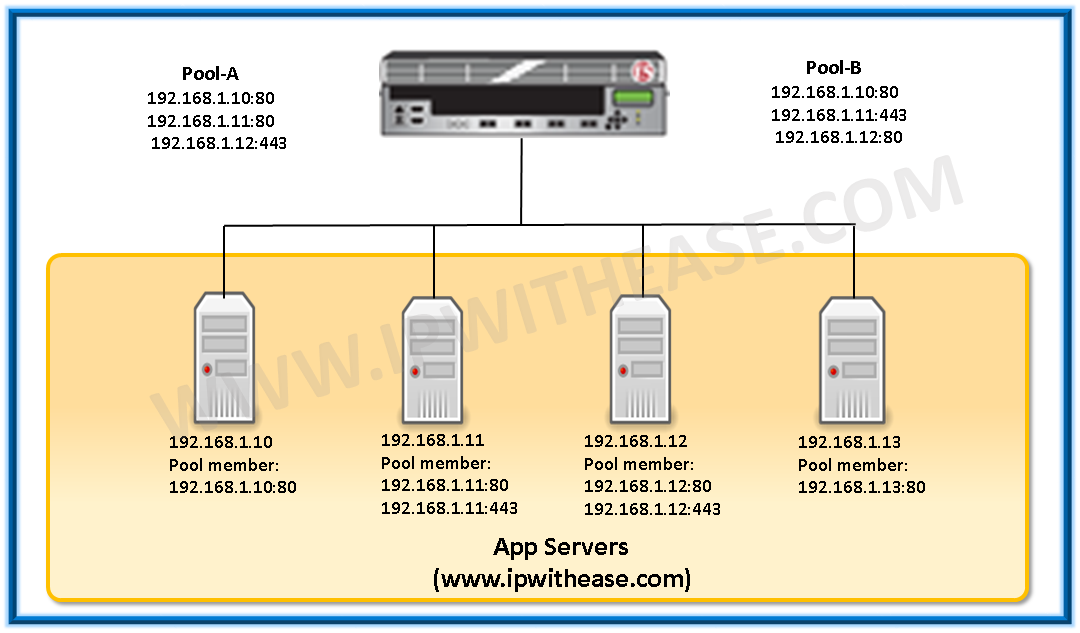
Pool: – A pool is logical grouping of pool members that represents an application. Each pool can have different load balancing method. A pool groups pool member together to receive and progress network traffic in a fashion determined by a specific load balancing algorithm.
Monitor
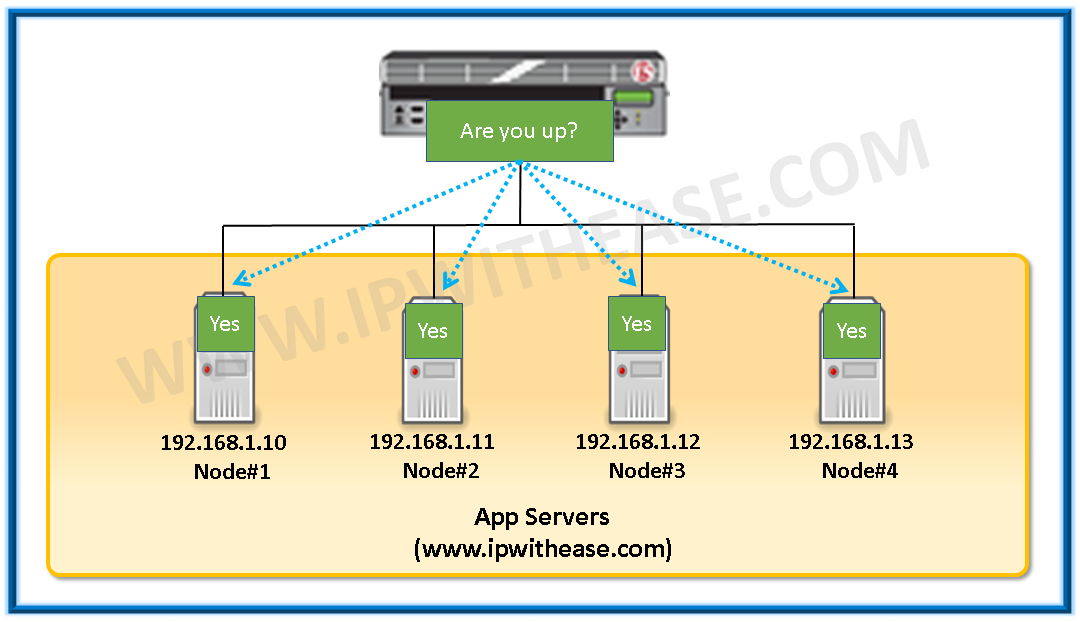
Monitor: – A configuration object that checks the availability or performance of network resources such as pool members and nodes. Monitors check the status of a pool member or node on an ongoing basis, if a pool member or node being monitored does not responded within the set interval, BIG-IP LTM marks it offline, but continues to monitor. BIG-IP LTM continues to direct traffic to the remaining pool members while continuing to monitor the offline pool member or node. When a pool member or node responds, BIG-IP LTM marks it available and starts directing traffic to the pool member.
Virtual Server
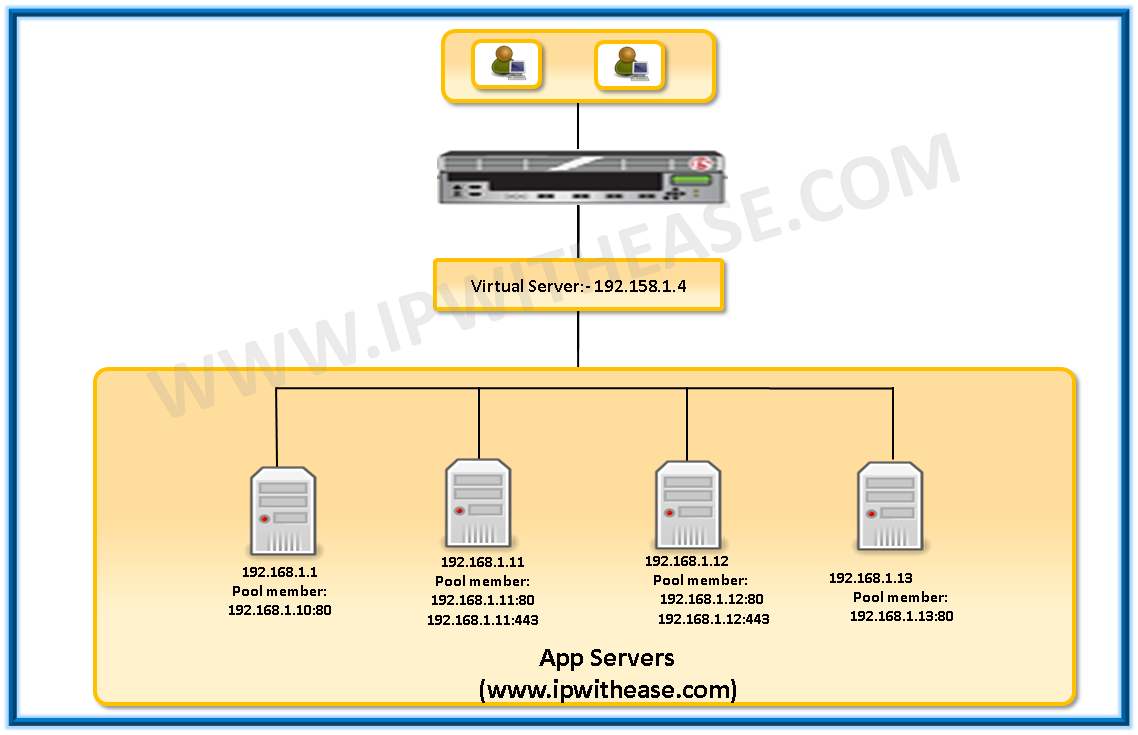
Virtual Server: – A virtual server is an IP address and server (port) combination that listens for client requests. BIG-IP LTM is a default deny device, the virtual server is the most common way allow client requests to pass through. Each virtual server will uniquely process client request that match its IP address and port. Each virtual server than directs the traffic, usually to an application pool. The Virtual server translates the destination IP address and port to the selected pool members. A Virtual server allows BIG-IP systems to send, receive, process and relay network traffic.
Related- F5 LTM Interview Questions
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj