In the evergrowing world of Internet users and all the business transactions happening over the Internet, it becomes imperative for Internet users to understand how secure Web sites work and how are HTTP and HTTPS protocols placed in this scenario. In this blog, we are going to talk about http vs https, how they are different from each other and what are the features of each.
People often ask how they can shop on a Web site, giving out personal information, and feel even remotely safe. After all, we’re sending confidential data over unsecured Web world. Hence, let’s understand the web related terms and how both HTTPS and HTTP protocols differ in functionality and scope.
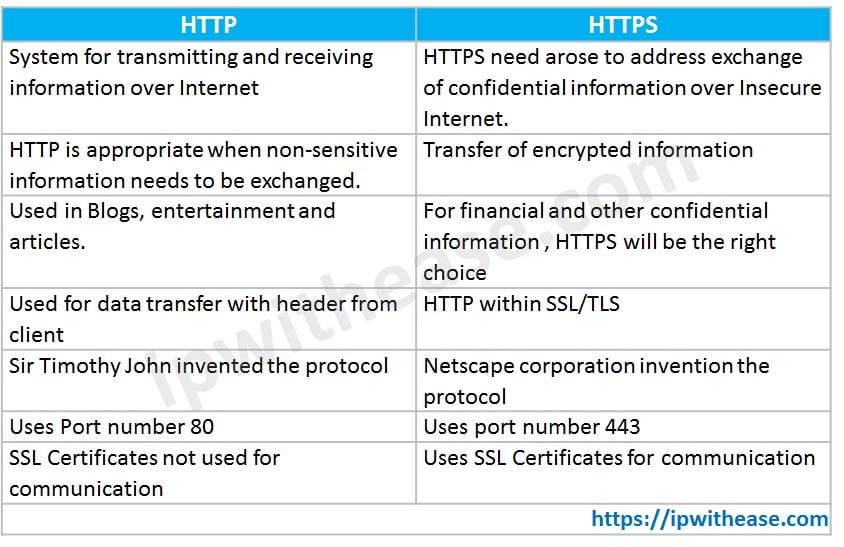
HTTP vs HTTPS
HTTP | HTTPS |
| System for transmitting and receiving information over Internet | HTTPS need arose to address exchange of confidential information over Insecure Internet. |
| HTTP is appropriate when non-sensitive information needs to be exchanged. | Transfer of encrypted information |
| Used in Blogs, entertainment and articles. | For financial and other confidential information , HTTPS will be the right choice |
| Used for data transfer with header from client | HTTP within SSL/TLS |
| Sir Timothy John invented the protocol | Netscape corporation invention the protocol |
| Uses Port number 80 | Uses port number 443 |
| SSL Certificates not used for communication | Uses SSL Certificates for communication |
Download the Comparison Table: http vs https
HTTP –
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol used in networking especially in client-server communication over the Internet and Intranet. When a user types a web address in the web browser, the browser acts as a client, and the computer having the requested information acts as a server. The request sent from client uses HTTP protocol to do so. The server responds back to the client after the request completes. The response comes in the form of the web page which user can see just after typing the web address and press “Enter”.
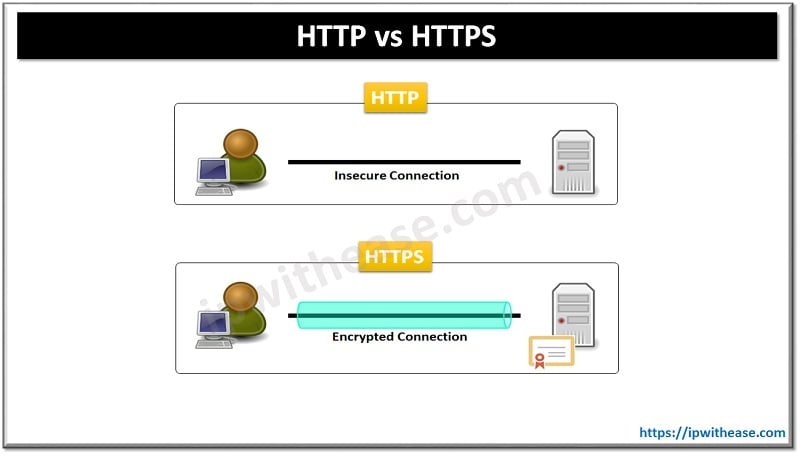
All communications sent over regular HTTP connections are in ‘plain text’ and can be read by any hacker that manages to break into the connection between your browser and the website. This presents a clear danger if the ‘communication’ is formed to give credit card of account details like password or OTP.
Related- Common Website HTTP Error Codes
The HyperText Transfer Protocol is an application layer protocol, which means it focuses on how information is presented to the user of the computer but doesn’t care a whit about how data gets from Source A to Destination B. It is stateless, which means it doesn’t attempt to remember anything about the previous Web session. This is great because there is less data to send, and that means speed. And HTTP operates on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Port 80 by default, meaning your computer must send and receive data through this port to use HTTP.
Related- FTP vs HTTP
HTTPS –
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, the protocol over which data is sent between your browser and the website that you are connected to. The ‘S’ at the end of HTTPS stands for ‘Secure’. It means all communications between your browser and the website are encrypted. HTTPS is often used to protect highly confidential online transactions like online banking and online shopping order forms.
When you request an HTTPS connection to a webpage, the website will initially send its SSL certificate to your browser. This certificate contains the public key needed to begin the secure session. Based on this initial exchange, your browser and the website then initiate the ‘SSL handshake’. The SSL handshake involves the generation of shared secrets to establish a uniquely secure connection between yourself and the website.
When a trusted SSL Digital Certificate is used during an HTTPS connection, users will see a padlock icon in the browser address bar. When a Validation Certificate is installed on a web site, the address bar will turn green.
With an HTTPS connection, all communications are securely encrypted. This means that even if somebody managed to break into the connection, they would not be able to decrypt any of the data which passes between you and the website.
The major benefits of an HTTPS are –
- Customer information, like credit card numbers, is encrypted and cannot be intercepted
- Visitors can verify you as a registered entity and own domain.
- More trust for customer with HTTPS communication protocol.
Related- Commonly Used Internet Terms and Concepts
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj