The need for IPV6 addressing is felt due to the fast depletion of the ipv4 address space.IPV6 address unlike IPV4 address is a 128 bit address or 16 byte address space.In IPV6 address there are 8 groups of 16 bit each.
Example of IPV6 address:
2002:0009:0012:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001
The above address in condensed form can also be written as 2002:9:12::1.
Note – we have used “::” in place of 4 blocks containing all zeroes. “::” can only be used once in the IPV6 address for example if we have address “2002:0009:0000:0000:0012:0000:0000:0001”
Incorrect Notation: 2002:0009::0012::0001
Correct Notation: 2002:0009:0000:0000:0012:: 0001 or 2002:0009:: 0012:0000:0000:0001
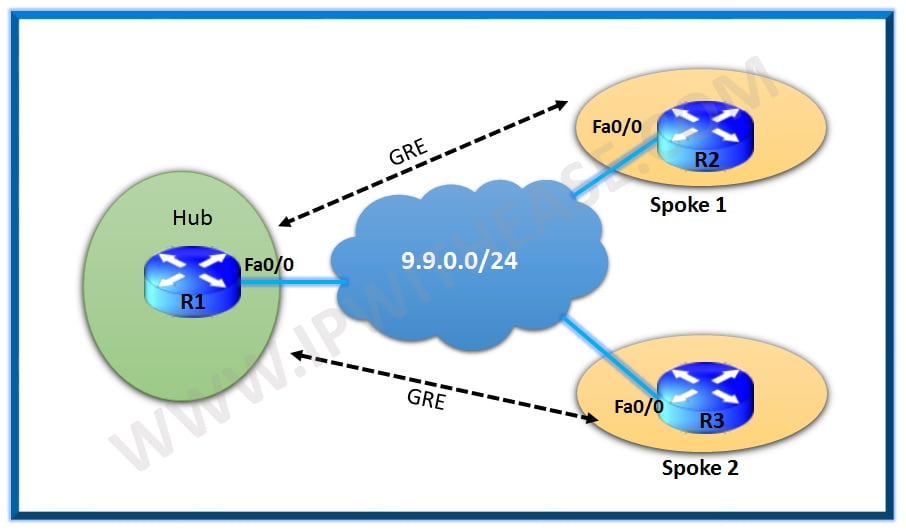
In this post we will configure IPv6 RIP, EIGRP and OSPF using the below topology:
R1 and R2 run RIPV6 between them.
CONFIGURATION:
R1:
ipv6 router rip abc
int fa0/0
ipv6 add 2002:9:12::1/64
ipv6 rip abc enable
no shut
int lo0
ipv6 add 2002:9:9::1/128
ipv6 rip abc enable
R2:
ipv6 router rip abc
int fa0/0
ipv6 add 2002:9:12::2/64
ipv6 rip abc enable
no shut
VERIFICATION:
R2#sh ipv6 route rip
B – BGP, R – RIP, H – NHRP, I1 – ISIS L1
I2 – ISIS L2, IA – ISIS interarea, IS – ISIS summary, D – EIGRP
EX – EIGRP external, ND – ND Default, NDp – ND Prefix, DCE – Destination
NDr – Redirect, O – OSPF Intra, OI – OSPF Inter, OE1 – OSPF ext 1
OE2 – OSPF ext 2, ON1 – OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 – OSPF NSSA ext 2, l – LISP
R 2002:9:9::1/128 [120/2]
via FE80::C801:FF:FE60:0, FastEthernet0/0
R2#ping 2002:9:9::1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/45/76 ms
We see above we have learnt the IPV6 route from R1 on R2 and are able to ping it.
R2 and R3 are running EIGRP between them
CONFIGURATION:
Note we have already enabled IPV6 routing above on R2 and hence not included here.
R2:
ipv6 add 2002:9:23::2/64
ipv6 eigrp 10
no sh
int lo0
ipv6 add 2002:9:9::2/128
ipv6 eigrp 10
R3:
ipv6 router eigrp 10
int fa0/0
ipv6 add 2002:9:23::3/64
ipv6 eigrp 10
no shut
VERIFICATION:
R2#sh ipv6 eigrp neighbors
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 Link-local address: Fa1/0 6 00:05:36 47 282 0 3
FE80::C803:1CFF:FE0C:0
The neighbor address is the link-local address of R3’s interface connecting to R2.
R3#sh ipv6 interface fa0/0
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Global unicast address(es):
2002:9:23::3, subnet is 2002:9:23::/64
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::A
FF02::1:FF00:3
FF02::1:FF0C:0
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds (using 30000)
ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified)
ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified)
ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds
ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds
ND advertised default router preference is Medium
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses.
We are able to see the R2’s loopback address learnt via EIGRP on R3.
R3#sh ipv6 route eigrp
B – BGP, R – RIP, H – NHRP, I1 – ISIS L1
I2 – ISIS L2, IA – ISIS interarea, IS – ISIS summary, D – EIGRP
EX – EIGRP external, ND – ND Default, NDp – ND Prefix, DCE – Destination
NDr – Redirect, O – OSPF Intra, OI – OSPF Inter, OE1 – OSPF ext 1
OE2 – OSPF ext 2, ON1 – OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 – OSPF NSSA ext 2, l – LISP
D 2002:9:9::2/128 [90/156160]
via FE80::C802:15FF:FE38:1C, FastEthernet0/0 # Highlighted is the link local address of R2’s interface
R3#ping 2002:9:9::2
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/39/84 ms
R3 and R4 run OSPF between them.
CONFIGURATION:
Note we have already enabled IPV6 routing above on R3 and hence not included here.
R3:
ipv6 add 2002:9:34::3/64
ipv6 ospf 5 area 0
int lo0
ipv6 add 2002:9:9::3/128
ipv6 ospf 5 area 0
R4:
ipv6 router ospf 5
router-id 9.9.0.4
int fa0/0
no ipv6 add 2002:9:34::4/64
no ipv6 ospf 5 area 0
no sh
VERIFICATION:
OSPF neighborship is up between R3 and R4
R4#sh ipv6 ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
9.9.0.3 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:36 3 FastEthernet0/0
We are able to see the route to R3’s loopback via OSPF and are able to ping it.
R4#sh ipv6 route ospf
B – BGP, R – RIP, H – NHRP, I1 – ISIS L1
I2 – ISIS L2, IA – ISIS interarea, IS – ISIS summary, D – EIGRP
EX – EIGRP external, ND – ND Default, NDp – ND Prefix, DCE – Destination
NDr – Redirect, O – OSPF Intra, OI – OSPF Inter, OE1 – OSPF ext 1
OE2 – OSPF ext 2, ON1 – OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 – OSPF NSSA ext 2, l – LISP
O 2002:9:9::3/128 [110/1]
via FE80::C803:1CFF:FE0C:1C, FastEthernet0/0
R4#ping 2002:9:9::3
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/48/84 ms
Note : In case of EIGRP and OSPF it is mandatory to configure the router-id manually for the neighbor ship to form.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj