Table of Contents
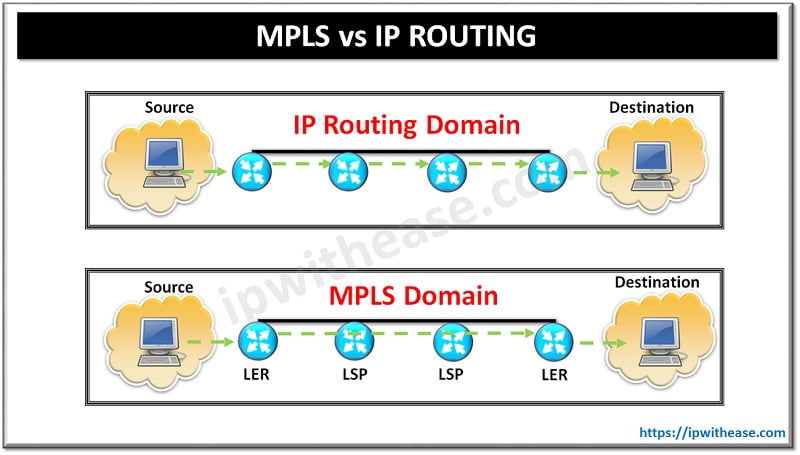
MPLS is a high-performance routing technique that uses short path labels instead of long network addresses to direct data through the network. IP Routing is a method of sending data across networks based on the destination IP address in each packet’s header. In this blog, we discuss the difference between MPLS and IP Routing in detail.
What is MPLS
MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching) has been in the IT market for quite some time now. Before its introduction, Service providers bore the burden of providing services to customers using IP routing, VPN and Layer 2 technologies. MPLS was welcomed by everybody and is now the de facto technology used in service provider and Large data Centers.
MPLS is a technology used for routing the network packets in a network. The forwarding of packets is done on the basis of the labels present on the packets following a fixed path called Label Switched Path (LSP).
Related – Top MPLS Interview Questions
What is IP Routing
While traditional IP Routing uses forwarding packets of packets based on the destination IP address, routing lookups are performed on every hop and every router may need full Internet routing information. Thus , the routing is done on the basis of IP address using hop-by-hop mechanism.
Related – MPLS vs Internet
Difference between MPLS and IP Routing
Let’s discuss the main points of differences between the two technologies.
- In MPLS, the switching of traffic is based on the labels assigned to the network packets. While in IP routing, it is based on the destination IP address.
- In MPLS, a fixed and dedicated path is established for the routing of network packets. This path is known as the LSP (Label Switched Path). While in IP routing, no such defined path is formed.
- MPLS Builds LFIB (Label Forwarding Information Base) table using LDP protocol. While in IP routing, the information is stored in routing table.
- In MPLS technology, the labels are inserted between layer 2 and layer 3 of TCP/IP model hence it lies at layer 2.5 (thus also known as “shim” protocol). While IP routing is a layer 3 protocol.
- MPLS is much faster than traditional IP Routing, as it is based on the concept of the label to allow forwarding (rather switching) of packets. This type of forwarding is more efficient as it avoids overloading the CPU.
- Traditional routing performs routing decision based on IP header, MPLS considers MPLS header with packets and hence takes all forwarding decisions based on the MPLS header, unlike traditional routing.
Related- Public IP vs Private IP
Comparison Table : MPLS vs IP Routing
Below table provides the detailed comparison between MPLS and IP routing:
| PARAMETER | MPLS | IP ROUTING |
|---|---|---|
| Switching/Routing principle | Switching traffic based on labels advertised by LDP | Routing based on the destination address for entries in the routing table. |
| Switching/Routing path | Establishes LSP (dedicated path) before data can flow. | No dedicated path is established, packet is routed based on IP addresses. |
| Tables usage | Builds LFIB (Label Forwarding Information Base) table using LDP protocol. | Stores IP routing table. |
| Layer of functioning | Labels inserted between layer 2 and Layer 3 (hence layer 2.5) | Performed at Layer 3 |
| Overlapping IP address | MPLS can allow communication across overlapping IP addresses of multiple customers | Does not allow communication across overlapping address of different customers |
| Related terms | LSP, LDP/TDP, VRF, LFIB, Push, Swap and Pop. | Route Lookup, IP protocol |
| Traffic Latency | Lower latency than traditional IP routing | Incurs higher latency than MPLS |
| Topology and services | With MPLS, providers can create (with use of different labels and label stacks) different topologies & services (MPLS-TE, MPLS VPNs). | Single topology can be created per IP routing domain. |
| Traffic Engineering | Scalable and proficient in service | Partially possible but not scalable solution |
| Separate Routing table | In MPLS network , each customer has separate routing network | Traditional IP routing can only have 1 Routing table for all customers |
| Scalability | Medium | High |
| Target scope | Service provider domain, Large & Multitenant Data Centers. | Home, Office, Service PTP/Underlay links, Data centers etc. |
| Traffic type | Allows non-IP traffic forwarding in addition to IP traffic | Allows forwarding of IP traffic |
Download the difference table: mpls vs ip routing
If you want to study more about MPLS, the please go through our FREE CHEATSHEET on MPLS in the downloadable pdf format. Its a ready reckoner to quickly brush up your MPLS basics.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj