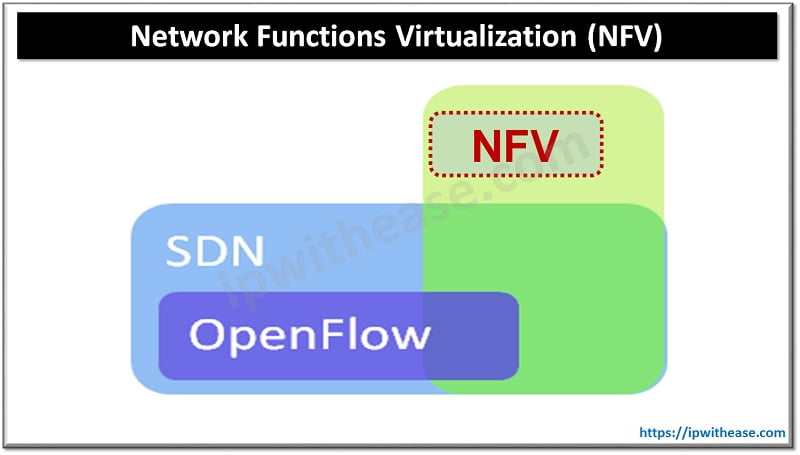
Introduction to NFV
Network functions virtualization (NFV) also called virtual network function (VNF) provides new paradigm towards designing, deploying and managing networking services. The goal of NFV is to decouple network functions from dedicated hardware devices and allow network services that are now being carried out by routers, firewalls, load balancers and other dedicated hardware devices to be hosted on virtual machines (VMs).
Some of network functions eligible for NFV decoupling include
- Network address translation (NAT)
- Firewalling
- Intrusion detection
- Domain name service (DNS)
- Caching
The above functions can be migrated from proprietary hardware appliances and run in software by NFV.
NFV is designed to consolidate and deliver the networking components needed to support a fully virtualized infrastructure – including virtual servers, storage, and even other networks. NFV utilizes standard IT virtualization technologies that run on high-volume switch and storage hardware to virtualize network functions. It is applicable to any data plane processing or control plane function in both wired and wireless network infrastructures.
Components of Network Functions Virtualization
The NFV framework consists of three main components –
- Virtualized network functions (VNFs) are software implementations of network functions that can be deployed on a network functions virtualization infrastructure (NFVI).
- Network functions virtualization infrastructure (NFVI) is the totality of all hardware and software components that build the environment where VNFs are deployed. The NFV infrastructure can span several locations. The network providing connectivity between these locations is considered as part of the NFV infrastructure.
- Network functions virtualization management and orchestration architectural framework (NFV-MANO Architectural Framework) is the collection of all functional blocks, data repositories used by these blocks, and reference points and interfaces through which these functional blocks exchange information for the purpose of managing and orchestrating NFVI and VNFs.
Advantages of NFV
- Lower hardware costs by replacing dedicated appliances with shared servers
- Speed revenue-generating services to market
- Reduce operational costs with fewer appliances to deploy and maintain
- Support on-demand pay-as-you go deployment models
- Enable Innovation by making it easier to develop network functions
- Deploy virtualized solutions on commercial, off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware
Continue Reading:
SDN vs NFV: Understand the difference
Static NAT vs Dynamic NAT- NAT Types
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj