Introduction to OSPF Network
An OSPF network can be divided into sub-domains called areas. A router within an area must maintain a topological database for the area to which it belongs. Since the router will not have detailed topology information of routers in other areas, this would greatly reduce the size of database.
Areas limit the scope of route information distribution. The link-state database (LSDB) of routers within the same area must be synchronized and be exactly the same. The main benefit of creating areas is a reduction in the number of routes to propagate—by the filtering and the summarization of routes.
Requirements of an OSPF Network
Each OSPF network that is divided into different areas must follow these rules:
- A backbone area—which combines a set of independent areas into a single domain—must exist.
- Each non-backbone area must be directly connected to the backbone area (though this connection might be a simple logical connection through a virtual link)
- The backbone area must not be partitioned—divided into smaller pieces—under any failure conditions, such as link or router down events.
OSPF Area Types
OSPF Areas are created to control the movement of LSAs across the OSPF network. There are different OSPF Area types, namely –
- Standard / Normal Area
- Backbone Area
- Stub Area
- Totally Stubby Area
- Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
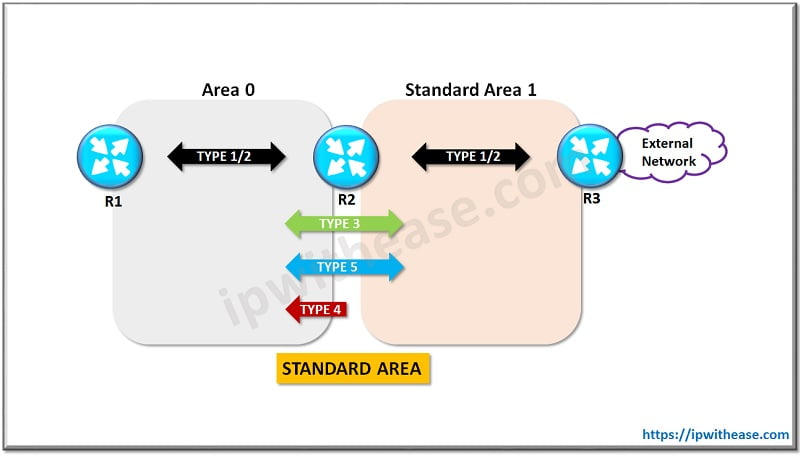
Standard Area:
LSA Type 1 and 2 are sent between routers within an area and thus help prepare the Shortest Path tree for an area. The LSA Type 3 which shares internal routes and LSA Type 5 that shares external routes flood through this area. Just note that the internal routes are by OSPF Router whereas the external routes are by the ASBR.
Standard areas help in optimizing routing as the information about all routes is with all routers. But this at times can be a burden to storing / maintain the full database.
Related- OSPF N1 and N2 Routes
To configure a normal area, we use the command:
R1 (config)# router ospf 10
R1 (config-router)# network <ip address> < wildcard mask> area <area no.>
Backbone Area:
Backbone area is similar to the standard area. All areas are connected to this area. This is also known as Area 0.
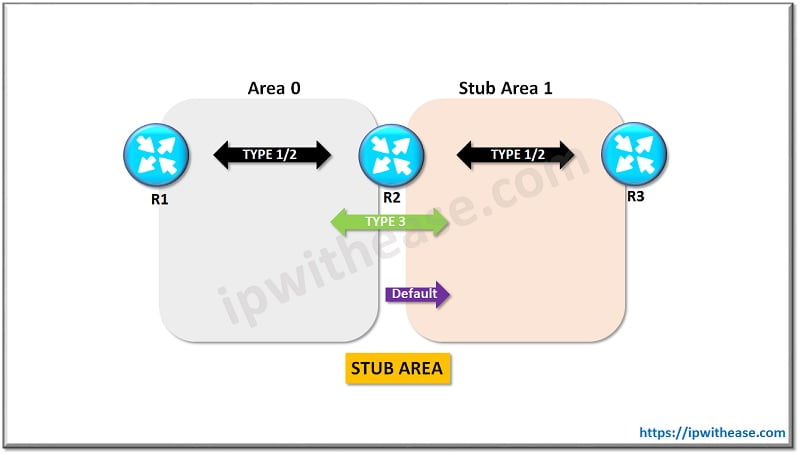
Stub Area:
In a Stub area the External LSAs i.e. LSA Type 5 is stopped. The LSA Type1 and Type can be used in a stub area so that a topology can be built. The main use of Stub Area is that the number of LSAs flowing in an area is under control which in turn will help consumption of CPU and bandwidth if the router.
In a Stub Area, a default route is injected by the ABR along with the Type 3 LSA. And this default route is helpful to reach external networks. All the routers in the area must be configured as stub in order to make an area stub.
The command used is as:
(Router-config)# area <area no.> stub
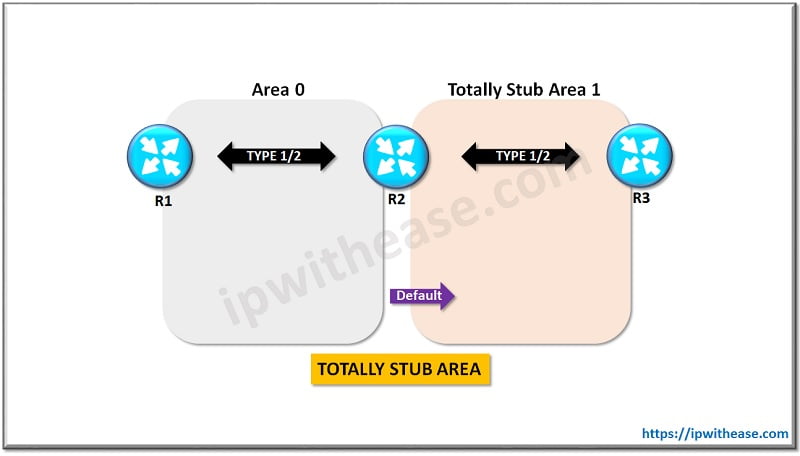
Totally Stubby Area:
As in a Stub area, in the Totally Stubby Area as well the External LSAs are stopped (Type 5 LSA.) In addition the LSA Type 3 i.e. Summary LSA is also not allowed in a Totally Stubby area. Thus this drastically reduces the size of the routing table as both internal and external routes are reduced and only default route is used.
The main use of Totally Stubby Area is also similar to a stub area, that the number of LSAs flowing in an area is under control which in turn will help consumption of CPU and bandwidth if the router.
Here also all the routers in the area must be configured as stub and the ABR of the stub areas will be configured as totally stubby.
The command used is as:
On the ABR:
(Router-config)# area <area no.> stub no-summary
On other routers:
(Router-config)# area <area no.> stub
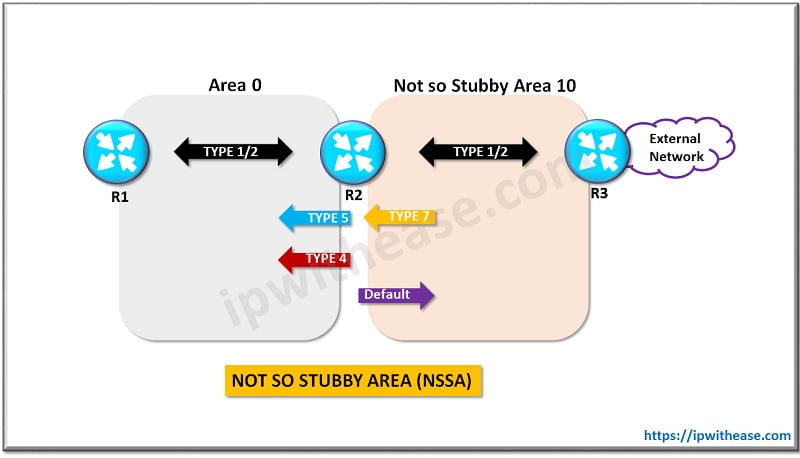
Not so Stubby Area (NSSA):
Here Type 7 LSAs are used which are similar to the type 5 LSA. Here the external links are advertised by the ASBR towards the ABR, which in turn will convert the LSA type 7 to LSA Type 5 and then flood it to the rest of OSPF network.
Similar to other areas, Type 1 and Type 2 LSAs are used to build the topology tables. The type 3 Network LSA are accepted by the NSSA thus can be used to reach other networks of other areas.
All the routers in the area must be configured as NSSA.
The command is:
(Router-config)# area <area no.> nssa
Continue Reading:
OSPF LSA Types The Ultimate Guide
Understanding OSPF LSA Data-Structure
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj