All network communication happens using the standard OSI framework. At each layer a set of protocols work which standardize the requirements of communication and prepare data which is universally acceptable to the next layer. Of network communication the most important aspect is data packet routing – there are several protocols available to support routing such as TCP/IP, OSPF etc. The one which gives the optimal route from source to destination is preferably considered for communication over large heterogeneous networks.
In today’s article we will look more in detail about how OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) link state routing protocols work over non broadcast networks (NBMA), how to configure OSPF over NBMA, its features and limitations.
OSPF Over Non-Broadcast Networks (NBMA)
OSPF is a link state routing protocol (used mostly widely) which uses information about the state of network links to ascertain or determine the best path for data packets. There are three types of network types in OSPF which determine how OSPF will route data packets across networks.
- Broadcast
- Point-to-Point
- No Broadcast
In addition to above there are two more Cisco proprietary network types
- Point to Multipoint
- Point to Multipoint Non broadcast
Since the point of focus in this article is No Broadcast networks (NBMA), we will go deeper into this. Non broadcast OSPF networks used in point-to-point links where multiple OSPF routers are connected such as frame relay, X.25, ATM virtual circuits (not used nowadays). For all hosts in a single NBMA network, data is sent from one host to another without broadcasting information across all hosts. Switched networks or virtual circuits provide direct routing of data packets. NMBA communicates directly to other hosts but on the same physical link other hosts can’t connect to it. NBMA uses next hop resolution protocol (NHRP) to find routes automatically through the network
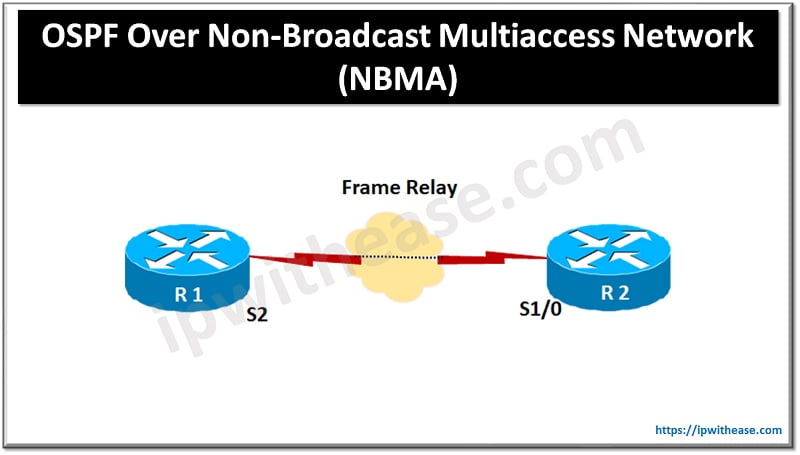
Configure OSPF Over Non-Broadcast Networks (NBMA)
Non broadcast Multiaccess (NBMA) broadcast model based on selection of designated router (DR) and a backup designated router (BDR). There are two ways to deploy this: defining the network type as broadcast with the IP OSPF network broadcast interface sub command or configure the neighbor statements using router OSPF command.
1. Configuration for NBMA (use Network Type Broadcast)
Router 1 Configuration
Ip address 168.0.2.3 255.255.255.255 ! ! Interface serial2 Ip address 168.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 Encapsulation frame-relay Ip ospf network broadcast No keepalive Frame-relay map ip 168.0.2.1 16 broadcast ! ! Router ospf 1 Network 168.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Router 2 Configuration
Ip address 168.0.0.2 255.255.255.255 ! Interface serial1/0 Ip address 168.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 Encapsulation frame-relay Ip ospf network broadcast No keepalive Clockrate 2000000 Frame-relay map ip 168.0.2.1 16 broadcast ! Router ospf 1 Network 168.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
2. Configuration for NBMA (use Neighbour statements)
Router 1 Configuration
Ip address 168.0.2.3 255.255.255.255 ! Interface Serial2 Ip address 168.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 Encapsulation frame-relay Ip ospf priority 2 No keepalive Frame-relay map ip 168.0.2.1 16 ! Router ospf 1 Network 168.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Neighbor 168.0.2.1 !
Router 2 Configuration
Ip address 168.0.2.2 255.255.255.255
!
Interface Serial0/1
Ip address 168.0.2.1 255.255.255.0
Encapsulation frame-relay
Ip ospf priority 2
No keepalive
Clockrate 2000000
Frame-relay map ip 168.0.2.1 16
!
Router ospf 1
Network 168.0.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Neighbor 168.0.2.1
!
Use show command to verify configuration
Router1#Show ip ospf neighbors
OSPF Non-broadcast Network Features
- Network can connect more than two routers but by default they cannot broadcast
- Multipoint frame relay interfaces are default network type for OSPF
- OSPF routers on NBMA networks choose a DR (Designated router) and a BDR (backup designated router), all OSPF packets are unicast between each neighbor specified with ‘neighbor’ command
- The next hop IP do not change and remains same as IP address of the router which sent the packet
- The assigned priority by default is ‘1’ and should be set to = 0 (turned off) on ALL SPOKES to stop spoke from becoming a blackhole DR/BDR
- 30 seconds is Hello interval and 120 seconds is dead interval in OSPF
Pros & Cons of OSPF over NBMA
PROS
- Easier to control traffic flow on network and also helpful to limit amount of traffic goes through a particular link
- Non broadcast network types are secure since hackers can easily intercept broadcast which will not happen here
CONS
- Difficult to configure as it requires manual neighbor configuration
- Difficult to scale on OPSF networks as compared to other network types
- Limited feature availability of OSPF features when this network type is used
- Susceptible to certain types of faults
Continue Reading:
OSPF Neighbor States Explained
OSPFv2 vs OSPFv3: Detailed Comparison
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj