Table of Contents
What is PoE?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is the ability for the LAN switching infrastructure to provide power over a copper Ethernet cable to an endpoint or powered device.
This capability was developed and first delivered by Cisco in 2000 in order to support the emerging IP Telephony deployments.
IP telephones, such as desktop PBX phones, need power for their operation, and PoE enables scalable and manageable power delivery and simplifies deployments of IP Telephony.

POE+ vs POE
Related- Perpetual POE vs Fast POE
The original IEEE 802.3af-2003 PoE standard provides up to 15.4 W of DC power (minimum 44 V DC and 350 mA) on each port. Only 12.95 W is assumed to be available at the powered device as some power dissipates in the cable.
Related- POE Interview Questions
What is PoE+?
Power Over Ethernet Plus (POE+) extends the support for more emerging end devices with higher power requirements. IEEE introduced a new standard, 802.3at, to scale up to 30W power delivery. This further expands the end devices coverage to a broader range including newer devices such as IEEE 802.11n wireless access points, security surveillance cameras, and so on. Cisco Catalyst 4500E was the first Ethernet switch in the industry to introduce 30W PoE technology in 2007, two years before the IEEE 802.3at standard introduction, and later become compliant with the IEEE 802.3at standard when it was ratified in 2009.
Related- UPOE vs POE+
Comparison: POE+ vs POE
The Difference between POE and POE+ standards has been enlisted in below table –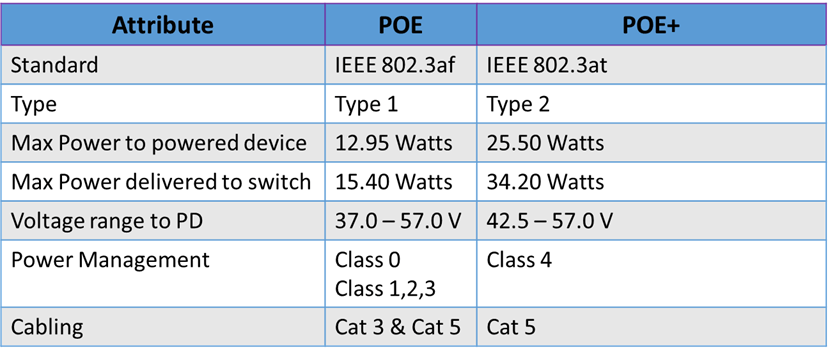
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj