Process Switching and Fast Switching
These are 2 of widely discussed terms in IP Routing with both methods addressing the primary function of forwarding the packets to the destination. Process switching is the older of the 2 technologies.
What is Process Switching?
Process switching is responsible for inspecting every packet by the processor. This was the original switching mechanism available on Cisco routers. SNMP traps from the router and telnet packets destined for the router are always process-switched.
Related- Load Balancing- Per Packet & Per Destination
Since the process routing task is more processor-intensive, more complex, and introduces a longer latency, skipping this operation on all the packets except the first (all with the same destination address) is very advantageous and efficient. Fast Switching was introduced to offload CPU/processor for other key activities.
What is Fast Switching?
In Fast Switching, the first packet to a destination is process switched but subsequent packets are forwarded using the information stored in the fast cache.
Below table compares the terms Process Switching and Fast switching and shares the differences between each Routing mechanism type –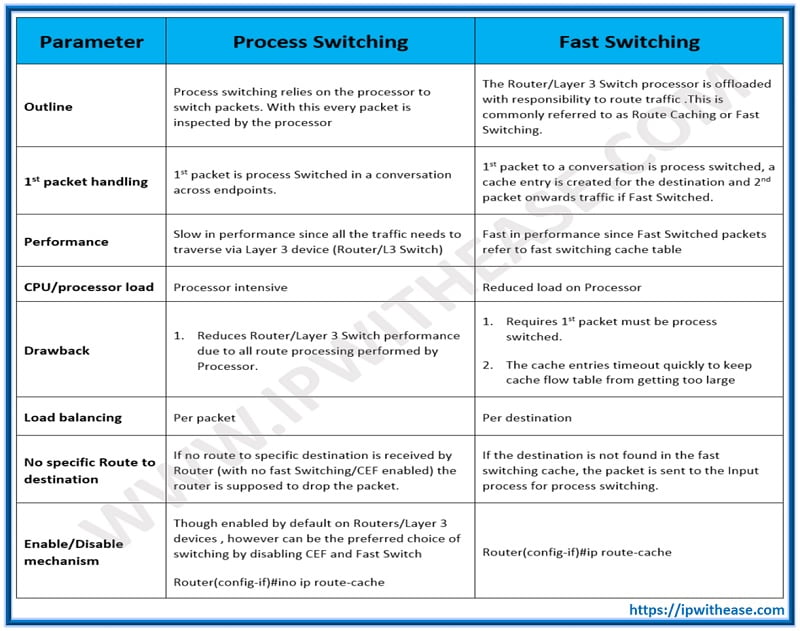
For subscribers interested in understanding the difference between CEF and Fast Switching, below link can be referred –CEF vs Fast Switching
Related- Function of Network Switch
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj