Discover how hyperautomation makes industries work faster and smarter, changing the way we do business for the better!
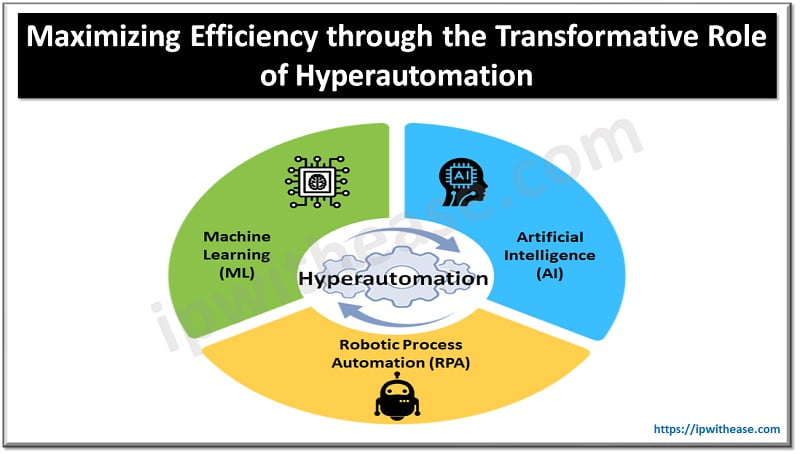
Hyperautomation is a transformative approach to business processes that combines advanced technologies like Machine Learning (ML), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), etc., to automate and optimize a wide range of tasks and processes. We will look into what hyperautomation is, how it is different from traditional automation, and its significant impact across various industries.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is a comprehensive automation strategy that aims to automate and evaluate as many business processes as possible. It goes beyond the limitations of traditional automation by integrating technologies. Key components of hyperautomation include:
- Process Discovery: The first step in hyperautomation involves identifying and documenting all possible processes within an organization. This approach ensures that no process is left unexamined, enabling organizations to maximize automation potential.
- Automation Tools: Hyperautomation leverages many advanced automation tools to execute tasks and processes.
- Data Integration: For hyperautomation to function flawlessly, it’s crucial to ensure that data from various sources can be integrated and utilized effectively. This integration enables informed decision-making and helps in optimizing processes further.
- Orchestration: With multiple technologies at play, orchestrating automation workflows across various systems and technologies becomes a critical aspect of hyperautomation. Proper orchestration ensures that different tools work in harmony to achieve business objectives.
- Analytics and Monitoring: Continuous improvement is the main purpose of hyperautomation. Analytics and monitoring tools are used to measure the performance of automated processes and make real-time adjustments to optimize efficiency.
How is Hyperautomation Different from Automation?
Hyperautomation goes beyond traditional automation in several ways:
- Scope: While automation focuses on individual, repetitive tasks, hyperautomation targets entire processes. This broader scope allows for comprehensive optimization and efficiency gains.
- Intelligence: Hyperautomation incorporates AI and ML to enable systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously. In contrast, automation follows pre-defined rules without the capacity to learn or adapt to changing circumstances.
- Data-Centricity: Hyperautomation prioritizes data integration and analysis to improve processes continually. While effective in specific tasks, automation may not emphasize data as extensively, potentially missing out on valuable insights and optimization opportunities.
The Role of Hyperautomation across Different Industries
Banking Services
- Hyperautomation plays a big role in banking by streamlining different operations. Automated document verification and background checks can significantly enhance Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
- Fraud detection benefits from the real-time analysis of vast datasets, enabling the rapid identification of suspicious transactions.
- Customer support and query resolution can be made more efficient through AI-powered chatbots that can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
- Automated loan approval processes speed up lending operations and improve accuracy by analyzing applicant data and creditworthiness efficiently.
Healthcare
- Patient data management is crucial for providing quality care in the healthcare sector. Hyperautomation can significantly reduce the administrative burden by automating data entry, record-keeping, and billing processes.
- Often complex and time-consuming, claims processing can be expedited with hyperautomation. AI algorithms can review and validate claims, leading to faster patient and healthcare provider reimbursement.
- Hyperautomation also extends to clinical applications. AI-driven diagnostics and predictive analytics can assist medical professionals in diagnosing illnesses, predicting disease progression, and recommending personalized treatment plans. This enhances patient care and contributes to cost savings by avoiding unnecessary tests and treatments.
Insurance
- The insurance industry relies heavily on data-driven decision-making. Hyperautomation enables insurance companies to process vast amounts of data efficiently, leading to more accurate risk assessment and competitive pricing.
- Claims processing, which involves assessing claims for validity and determining payouts, can be significantly expedited through automation. AI algorithms can analyze claims against policy details and historical data to make informed decisions.
- Underwriting, a critical function in insurance, can benefit from hyperautomation by automating the evaluation of applicants’ risk profiles. This speeds up the underwriting process and reduces the chances of human error.
Manufacturing
- Hyperautomation profoundly impacts manufacturing, where efficiency and quality control are paramount. Production lines can be optimized through automation, reducing downtime and minimizing defects.
- Predictive maintenance, another critical application of hyperautomation in manufacturing, utilizes sensor data and AI algorithms to predict when equipment will likely fail. This proactive approach helps manufacturers schedule maintenance optimally, avoiding costly breakdowns and production interruptions.
- Inventory management, a complex, and often manual process, can be automated with the help of hyperautomation. AI can analyze demand patterns, optimize reorder points, and reduce excess inventory, saving costs.
Information Technology (IT)
- IT operations involve numerous repetitive and rule-based tasks that are ideal candidates for automation. Tasks such as software testing, patch management, and incident response can be automated to increase efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
- AI-driven IT operations, often referred to as AIOps, are becoming increasingly prevalent. These systems use AI and ML to monitor and analyze IT infrastructure, predict potential issues, and automatically take corrective actions, improving system reliability and security.
Transportation and Logistics
- In the transportation and logistics sector, hyperautomation is vital in optimizing operations. Route optimization is a prime example, where AI algorithms analyze factors like traffic conditions, delivery schedules, and fuel efficiency to determine the most efficient vehicle routes.
- Inventory management is crucial for supply chain efficiency. Hyperautomation can help organizations maintain optimal inventory levels by automatically tracking inventory, predicting demand, and generating reorder requests when necessary.
- Real-time tracking and visibility are enhanced through automation. Organizations can track the location and status of their shipments in real time, allowing for better customer service and supply chain coordination.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation is a powerful force driving transformation across industries. Organizations can achieve efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction by using advanced technologies like AI and data analytics. As industries evolve in the digital era, hyperautomation will remain a crucial strategy for staying competitive and delivering exceptional customer value.
As we have explored, hyperautomation has many applications, from streamlining banking services to optimizing manufacturing operations. In the IT sector, it is driving the automation of routine tasks and improving system reliability.
Hyperautomation is a fundamental shift in how organizations operate and deliver value. Those who embrace it strategically and thoughtfully are poised to thrive in the digital era. At the same time, organizations that lag in adopting these advancements may find it increasingly challenging to remain competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.
Continue Reading:
What is ChatGPT And How Can You Use It?
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
IPwithease is aimed at sharing knowledge across varied domains like Network, Security, Virtualization, Software, Wireless, etc.