Table of Contents:
One of the major functions in network computing is the creation of redundant and loop free network topologies at data link layer 2 of OSI model. In Ethernet networks several protocols are used to achieve network redundancy and loop prevention.
Today we look more in detail about two data link layer 2 spanning protocols – Spanning tree protocol (STP) and Rapid spanning tree protocol (RSTP), the advantages and disadvantages of both, their key differences, and similarities.
What is Spanning Tree protocol (STP)
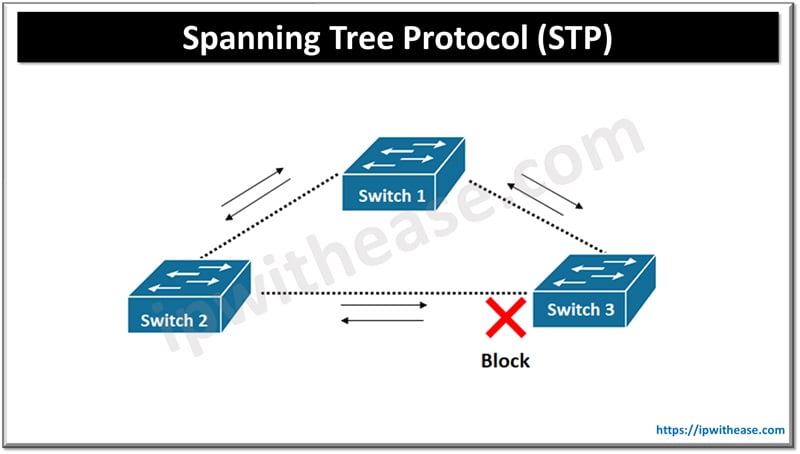
STP is layer 2 (data link layer) protocol which runs on switches and bridges. The IEEE standard 802.1D STP is used to prevent loops while using redundant network switches.
Related: Difference between UTP & STP
Pros and Cons of STP
PROS
- Mature protocol widely used in networks
- Effective handling of complex topologies and prevention of network loops by blocking redundant links
- It is a stable network topology which ensures only one path is active at any given time
- Supported by majority of network devices and easy to configure
- Does not require any special hardware or software to function
CONS
- Slow convergence timings which could result in network downtimes and performance glitches
- Lead to insufficient use of network resources by blocking links when they are not causing loops
- Can’t detect changes in network topology in quick manner which could result in network instability
- Require manual configuration and management in large networks
What is Rapid Spanning Tree protocol (RSTP)
RSTP is an enhanced version of STP and was designed to overcome the limitations of STP. The IEEE standard of RSTP is 802.1w. It is backward compatible with its counterpart STP. It averts network loops by blocking ports which are not required or unnecessary.
Related: Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Explained
Pros and cons of RSTP
PROS
- Faster convergence time to reduce network downtime and performance improvement
- Detect changes in network topology in quick manner and reconfigure network
- Uses link aggregation to provide faster network throughput with redundancy
- Supports VLANs and faster convergence over VLANs
CONS
- Require new network hardware and software for protocol support
- Require more memory and processing power to function
- More complex to configure and manage
Comparison: STP vs RSTP
Similarities
- Both prevent loops into networks by blocking redundant links
- Both protocols use root bridge to ascertain active path
- Both use metric to determine best path to reach root bridge
- Both protocols use BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) messages to reach other network devices
- Both protocols support VLANs
Differences
| Function | STP | RSTP |
| Standard | Governed by IEEE 802.1D standard | Governed by IEEE 802.1.w standard |
| Convergence | Supports slow convergence up to 30 seconds or more | Supports rapid convergence less than 1 second |
| Ports States | Supported port states •disabled •blocking •listening •learning •forwarding | Supported port states •discarding •learning •forwarding |
| Port Roles | Supported port roles •Root port, Designated port •Non designated / non root ports | Supported port roles •Root port •Designated port •Backup port •Alternative port •Non designated ports |
| Timers | Maximum age = 20 Forwarding delay = 15 seconds BPDU timer = 2 seconds | Maximum age = 20 Time to detect failure = 6 seconds Forwarding delay = 15 seconds BPDU timer = 2 seconds |
| Port Types | All ports are same | Edge – similar to STP port configured with fast port Non-edge – P2P or shared |
| Scalability | Supports only one spanning tree per VLAN | Supports multiple spanning trees per VLANs and per VLAN spanning trees |
| Forwarding State Transition | 30 seconds = 2 * forwarding delay (listening + learning) before forwarding starts by port after enablement | Proposal and agreement handshake on point-to-point links is used instead of timer |
| Failure Detection | 20 seconds (Maximum age) | 20 seconds (Maximum age) |
| BPDU Processing | Inferior BPDUs are ignored until old BPDU information is expired | On receiving Inferior BPDU , moves the alternate port to designated port role and sends superior BPDU from this new designated port. |
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj