Table of Contents
Ethernet interfaces are used to carry traffic over VLANs. They can carry traffic or a single VLAN or multiple VLANs over a single link and allow extension of VLANs across networks. Setting switch interfaces to access mode is required sometimes where there is a need to connect to endpoints as some switches have interfaces in a ‘dynamic desirable’ mode by default which is trunk state.
In today’s article we understand and compare Switchport Mode Access and Switchport Access VLAN.
Switchport Mode Access
When a port is configured in access mode, in a VLAN, we can specify which VLAN will carry traffic to that interface. If we do not configure VLAN for a port in ‘access’ mode the interface will carry traffic for default VLAN (VLAN 1). We can change the access port membership in VLAN by providing a new VLAN. We must create a VLAN before we assign it as an access VLAN for an access port.
If we change access VLAN on an access port to a VLAN which is not created, the access port will be shutdown by the system. If the access port receives a packet with 802.1Q tag in header instead of access port value, the packet will be dropped without learning MAC source address.
Use Cases for Switchport Mode Access
- Connecting endpoint devices such as PC, laptop, printers, scanners etc.
To configure switchport mode access use
Switch1(config)# interface FastEthernet 0/1
Switch1(config-if) # switchport mode access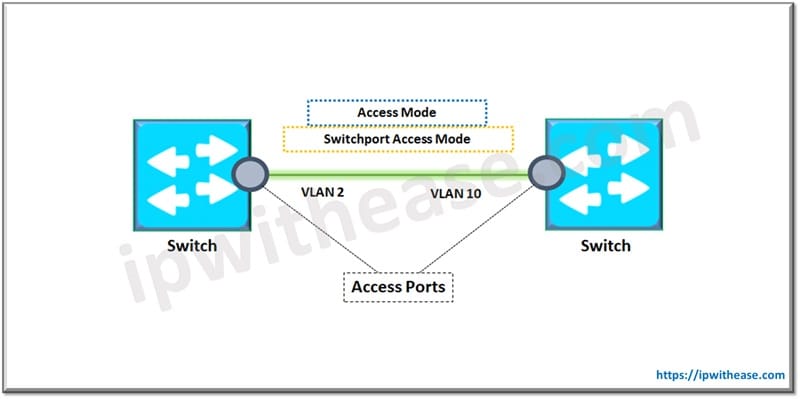
Related: Switchport Access Mode vs Trunk Mode
Switchport Access VLAN
The switchport access VLAN is a command which assigns layer 2 interface on a Cisco switch to specific VLAN. This command takes effect only if the interface is operating in switchport mode access.
Which means we first need to configure the interface to operate in access mode using ‘switchport mode access’ command and then assign interface to specific VLAN using switchport access vlan command.
Configuring switchport mode access disables dynamic trunking protocol on a given interface and turns off negotiation of trunking. This is an important command to access port settings as without this command the port can be set up as a trunk interface. Without this command if the neighbouring port is a trunk port, that port will be configured as a trunk.
To configure switchport access vlan
Switch1(config-if) # switchport access VLAN 2Port is set to member of VLAN 2
Cisco Switchport Mode Access vs Switchport Access VLAN
| Features | Switchport Mode Access | Switchport Access VLAN |
| Terminology | It is part of single VLAN and usually used to connect endpoints such as laptops, printers, scanners etc | It is a command to assign layer 2 interface on a Cisco switch to specific VLAN. |
| Support mode | This supports untagged single VLAN only | It is required after setting up switchport mode access as without this command access port setting can set as trunk interface |
| Use cases | PC, printers, switch, scanners etc | Single endpoint such as PC, printers, switch, scanners etc |
| Configuration | Designate port as access mode switchport mode access | After setting port as access mode it is required to establish access port in ‘access’ mode only |
| Protocols supported | Uses encapsulation protocol IEEE 802.1Q | Uses encapsulation protocol IEEE 802.1Q |
Download the comparison table: Switchport Mode Access vs Switchport Access VLAN
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj