Table of Contents
TCP FIN & RST
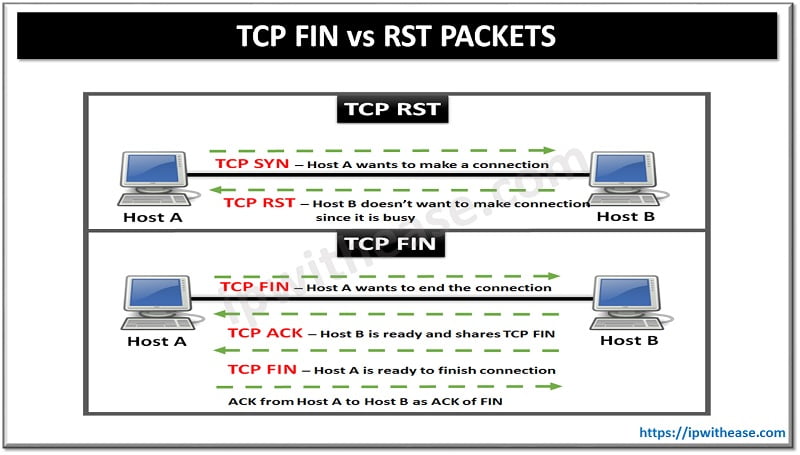
TCP FIN (Finish) and RST (Reset) are 2 ways in which TCP connection may be terminated. While TCP FIN is a pretty softer and graceful way of terminating the TCP connection, TCP RST is pretty straightforward and tends to immediately terminate the connection (TCP RST being less chatty than TCP FIN packet)
Related >> TCP/IP Port Numbers
TCP FIN Packet
Purpose
- Used to gracefully terminate a TCP connection.
Characteristics
- Indicates that the sender has finished sending data.
- Part of the four-way handshake to close a connection.
- Allows for any remaining data to be sent and acknowledged before closing the connection.
Process
- FIN Sent: The sender sends a FIN packet to the receiver.
- ACK Received: The receiver acknowledges the FIN packet with an ACK.
- FIN Sent: The receiver sends its own FIN packet once it has finished sending data.
- ACK Received: The sender acknowledges the receiver’s FIN packet with an ACK.
States Involved
- FIN-WAIT-1: When the sender has sent the FIN packet and is waiting for an ACK.
- FIN-WAIT-2: After receiving the ACK for the FIN packet.
- CLOSE-WAIT: When the receiver has received the FIN packet and acknowledged it.
- LAST-ACK: When the sender has received the FIN packet from the receiver and sent an ACK.
- TIME-WAIT: Ensures any delayed packets are handled before the connection is fully closed.
Use Cases
- Normal, orderly shutdown of a connection where both sides agree that no more data will be sent.
How a TCP FIN packet is sent
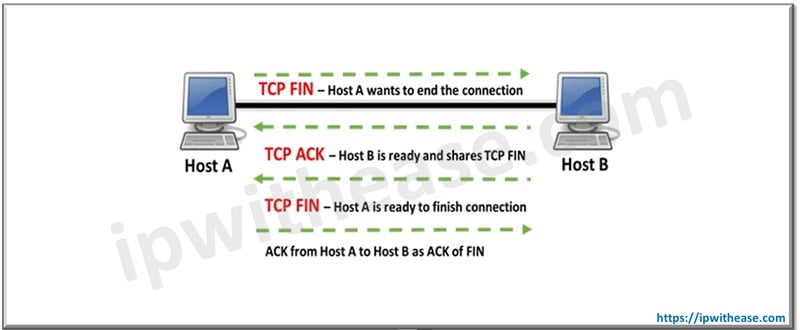
Figure: After establishing TCP 3-way handshake and successful data transfer, A FIN packet is usually sent from server or client to terminate a connection.
TCP RST Packet
Purpose
- Used to immediately terminate a TCP connection.
Characteristics
- Abruptly closes the connection without the need for a graceful shutdown.
- Does not wait for any remaining data to be sent or acknowledged.
- Can be sent by either side of the connection.
Process
- When a TCP endpoint sends a RST packet, the connection is immediately terminated without further communication.
States Involved
- There are no specific states associated with RST; it simply terminates the connection immediately.
Use Cases
- When an error occurs and the connection needs to be terminated immediately.
- When a connection is not recognized or is refused.
- In response to receiving unexpected or incorrect data.
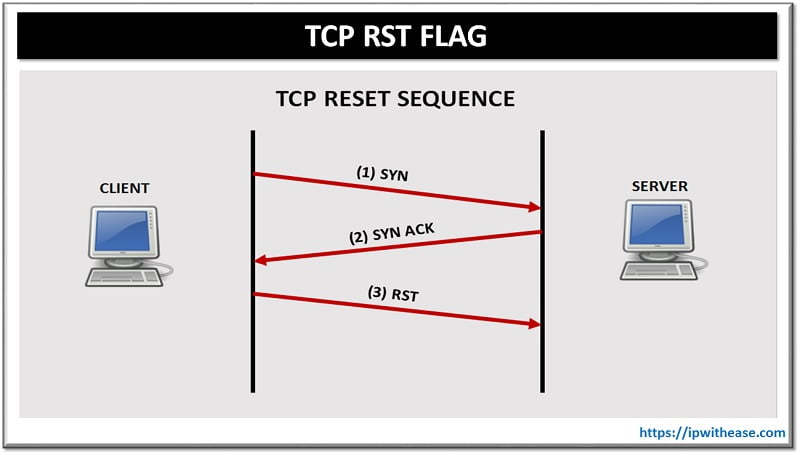
How a TCP RST packet is sent
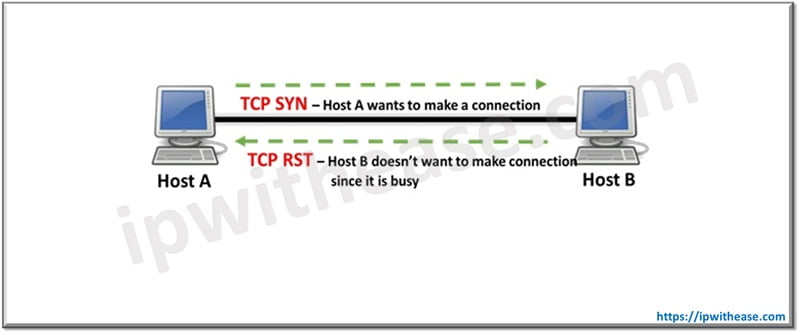
Figure: An RST packet is sent either in the middle of the 3-way handshake when the server rejects the connection or is unavailable OR in the middle of data transfer when either the server or client rejects further communication bypassing the formal 4-way TCP connection termination process.
Comparison: FIN Packet vs RST Packet
Below table articulates the difference between both FIN and RST packet types as part of the TCP connection termination process –
| PARAMETER | FIN PACKET | RST PACKET |
| Connection Termination Type | Graceful connection termination | Immediate connection termination |
| Confirmation | In case of FIN hosts get a confirmation. | RST causes immediate connection termination without any confirmation |
| Condition For Sending | Fin is sent when the application tells TCP that it wants to close so TCP does 4 way handshake and closes the connection gracefully | 1. Connection to a non-existent port 2. Server/Host is busy |
Download the difference table TCP FIN vs RST.
Final Words
FIN Packet ensures that all data is properly sent and acknowledged before closing the connection, used for a graceful shutdown.
Whereas, RST Packet immediately closes the connection without regard for any remaining data, used for error handling or immediate termination needs. Understanding the difference between these packets helps in diagnosing network issues and designing robust network protocols that handle connection terminations appropriately.
Continue Reading:
NETSTAT – TCP/UDP ACTIVE CONNECTION DISPLAY TOOL
For more information of TCP FIN & RST Flags watch this video –
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj