Table of Contents
VTP pruning is a feature used to reduce unnecessary traffic in VLAN trunks by only forwarding broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast traffic to trunk links that require it. If you’re encountering issues with VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) pruning, here are some common problems and troubleshooting steps.
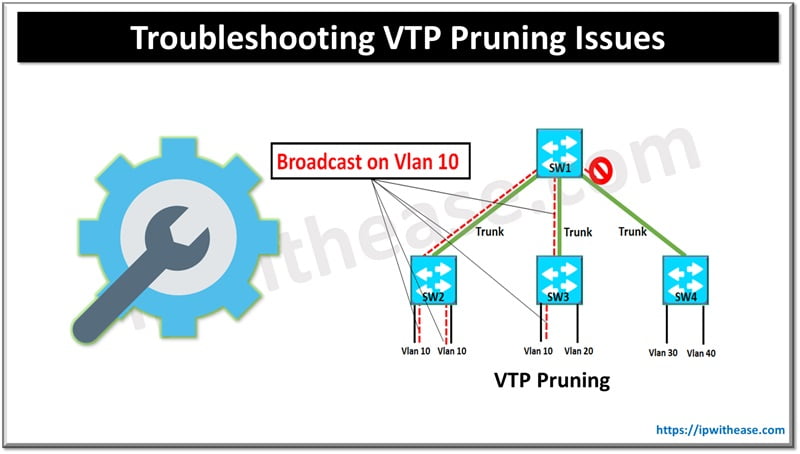
Common VTP Pruning Issues
1. VTP Pruning Not Working
- Issue: Traffic is still being forwarded on VLANs that should be pruned.
- Possible Causes:
- VTP pruning might not be enabled on the VTP server switch.
- Inconsistent VTP versions among switches.
- The VLAN might be active on the trunk link because it’s used by a host in that VLAN on another switch.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure VTP pruning is enabled on the VTP server with the command:
switch# show vtp statusCheck for VTP Pruning Mode: Enabled.
- Verify that all switches in the domain are running the same VTP version. Mismatched versions can lead to inconsistent pruning behavior.
- Use show interfaces trunk to check if the VLAN is actually being pruned. If not, investigate whether a device on that VLAN is using the link.
Related: How to Reset Revision Number in VTP?
2. VLANs Are Not Being Pruned as Expected
- Issue: Certain VLANs are not being pruned on trunk links.
- Possible Causes:
- The VLAN is not eligible for pruning (VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002–1005 cannot be pruned).
- The VLAN might have active traffic on the trunk.
- Troubleshooting:
- Check if the VLAN is part of the default or extended range. Pruning doesn’t apply to VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002–1005.
- Ensure that no devices are actively using that VLAN across the trunk link. Use the command:
switch# show vlan briefto check which VLANs are active and whether they’re passing traffic on the trunk.
3. VTP Pruning Causing Network Connectivity Issues
- Issue: Devices in certain VLANs lose connectivity after pruning is enabled.
- Possible Causes:
- Misconfigured pruning settings.
- A trunk link is improperly pruning traffic for a necessary VLAN.
- Troubleshooting:
- Disable pruning temporarily and verify if connectivity is restored. If so, review the VLANs being pruned on the affected trunk links.
- Use show interfaces trunk to identify which VLANs are being pruned and ensure important VLANs are not pruned.
- Check the pruning eligibility with:
switch# show vtp statusConfirm that only the intended VLANs are being pruned.
4. Inconsistent VLAN Information Across the Network
- Issue: VLANs are inconsistently available across different switches in the network.
- Possible Causes:
- VTP pruning may be causing VLAN information inconsistencies due to improper propagation.
- VTP domain name mismatch or VTP password issues.
- Troubleshooting:
- Verify that all switches belong to the same VTP domain using:
switch# show vtp status- Ensure VTP passwords (if configured) are correct on all switches.
- Review VLAN configurations and ensure that all intended VLANs are properly created and propagated.
5. Switches Not Synchronizing VLAN Database
- Issue: Some switches do not seem to be pruning VLANs even though VTP pruning is enabled.
- Possible Causes:
- VTP version mismatch or pruning is only enabled on some switches.
- Troubleshooting:
- Ensure all switches in the domain are running the same VTP version, preferably VTP version 2 or 3, as version 1 may not support pruning properly.
- Check that VTP pruning is enabled on the VTP server switch and propagated to all clients.
6. Multicast or Broadcast Traffic Still Traversing Trunk Links
- Issue: Despite enabling pruning, multicast or broadcast traffic is seen on trunk links where VLANs should be pruned.
- Possible Causes:
- Improperly configured VLANs or trunk links.
- Troubleshooting:
- Use show mac address-table to verify if any devices are registered in those VLANs.
- Confirm that pruning is properly enabled and VLANs are being pruned using the command:
switch# show interfaces trunkBest Practices
- Regularly monitor VTP status and VLAN pruning across switches.
- Ensure all switches run the same VTP version and are properly configured for the correct pruning behavior.
- Avoid using VLAN 1 and reserve it only for management if necessary, as it cannot be pruned.
By following these steps, you should be able to resolve most VTP pruning-related issues and ensure optimal traffic management across your network.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj