OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and IS IS stands for Intermediate System to Intermediate System.
OSPF and ISIS both are routing protocols for Internet Protocol Networks.
Similarities between OSPF and ISIS
Before going into the details of differences between OSPF and ISIS, let’s explore some similarities:
- OSPF and ISIS both are Link State Routing Protocols using the Dijkstra SPF Algorithm.
- Both are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) that distribute routing information between routers belonging to a single Autonomous System (AS).
- Both use Hello packets to create and maintain adjacencies between the neighboring routers.
- Both the protocols are classless protocols and support classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and Variable Subnet Length Masking (VLSM)
- Both support Authentication Mechanism
- Both support multipath.
- Both support IP unnumbered links.
Related – OSPF LSA types
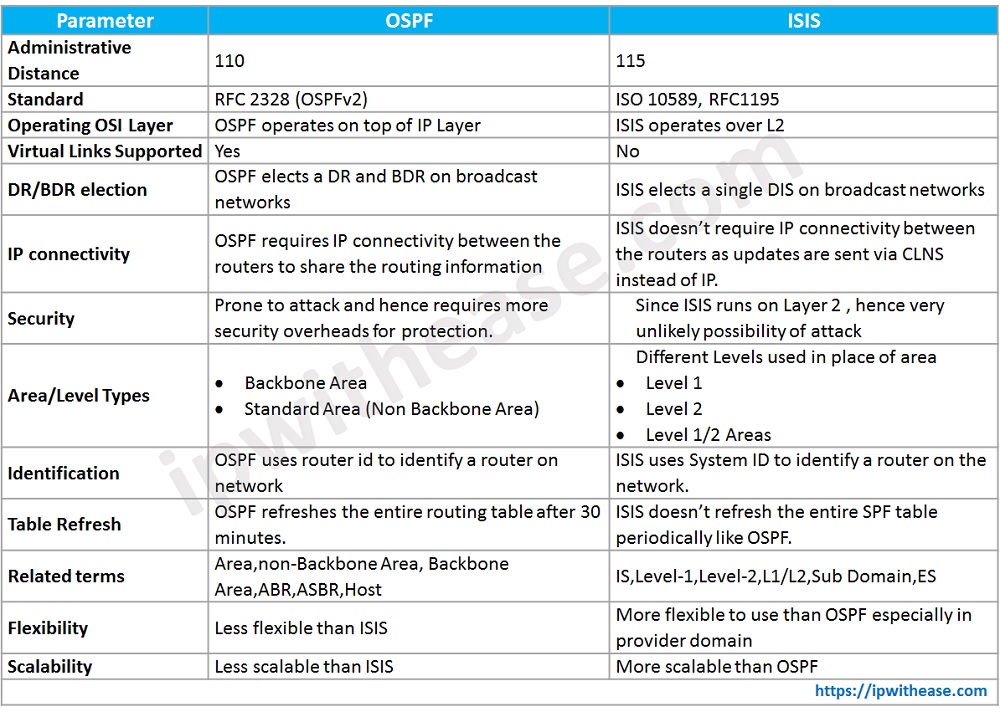
Differences between OSPF and ISIS
- OSPF operates on the top of IP layer whereas ISIS operates over Layer 2.
- OSPF can support virtual links but ISIS can not support (as it operates on Layer 2 directly).
- OSPF elects a DR and BDR on broadcast networks which can not be pre-empted however, ISIS elects a single DIS which can be pre-empted.
- IP connectivity between the routers to share the routing information is required in case of OSPF, while ISIS doesn’t require IP connectivity as the updates are sent via CLNS instead of IP.
- OSPF is prone to attacks hence security overheads are required for protection. The possibility of attacks is very less in case of ISIS as it runs over Layer 2.
- OSPF designates a backbone area and standard or non-backbone area for inter-area advertisements whereas ISIS organizes the domain into different levels.
- To identify a router on the network, OSPF uses Router ID and ISIS uses System ID.
- OSPF is less flexible with more strict requirements for forming neighbor adjacencies. The hello and dead intervals, and the subnet mask must match (except on point-to-point links).
Comparison Table: OSPF vs ISIS
Below table enumerates the differences between OSPF and ISIS protocols –
Download the comparison table: OSPF vs ISIS
Continue Reading:
OSPF Router Types: Detailed Explanation
OSPF Neighbor States Explained (OSPF States)
Are you preparing for your next interview
If preparing for your next interview, please go through the list of Top 100 OSPF Interview questions.
Watch our related video –
OSPF MTU Mismatch – Stuck in EXTART
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

I am here to share my knowledge and experience in the field of networking with the goal being – “The more you share, the more you learn.”
I am a biotechnologist by qualification and a Network Enthusiast by interest. I developed interest in networking being in the company of a passionate Network Professional, my husband.
I am a strong believer of the fact that “learning is a constant process of discovering yourself.”
– Rashmi Bhardwaj (Author/Editor)