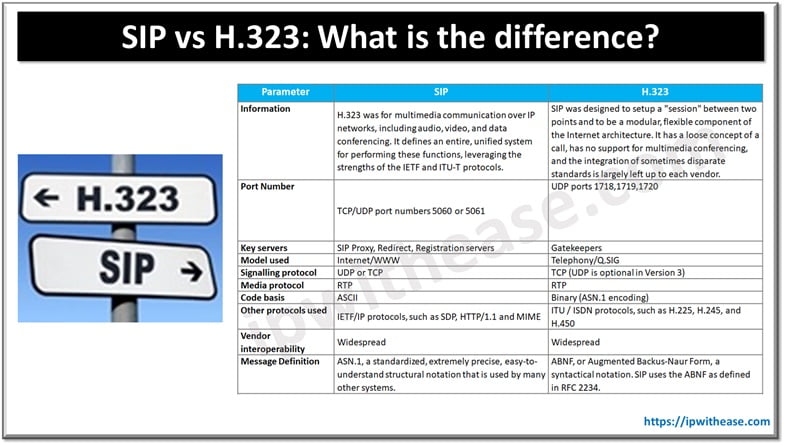
Table of Contents
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) are two common types of Ethernet cabling. Both are twisted pair cables used to transmit data in networks but they differ in how they handle interference, cost, and installation environments.
Let’s explore the key differences to help you decide which cable type suits your networking needs.
What is UTP
UTP is the most widely used cable type in Ethernet networks. It lacks any additional shielding around the wires, relying solely on the twisting of the pairs to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Features
- No shielding = more susceptible to interference.
- Lightweight and flexible.
- Lower cost compared to STP.
- Commonly used in LANs, offices, and homes.
What is STP
STP includes an additional shielding layer around each twisted pair or around all pairs together. This shielding helps block external electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for environments with high EMI.
Features
- Shielded with foil or braided mesh.
- Better performance in noisy environments.
- Slightly bulkier and more expensive.
- Requires proper grounding during installation.
Related – STP Interview Questions
Difference between UTP & STP
Both UTP and STP are widely used in transmitting information across distance.
UTP is a cable with wires that are twisted together to reduce noise generated by an external source. On the other hand, STP is a twisted pair cable with an additional mesh shield that guards the cable against electromagnetic interference. Thus it can also eradicate a phenomenon called crosstalk. Because of the incorporation of the additional shield, the data transfer rate of STP is higher than UTP.
The installation of STP cables is difficult as the cables are bigger, heavier, and stiffer. STP cables also require grounding, while no grounding is required in UTP. UTP cables are thus comparatively cheaper than STP.
Comparison: UTP vs STP
The differences between UTP and STP can be summarized as follows:
| Parameters | UTP | STP |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Unshielded Twisted Pair | Shielded Twisted Pair |
| Structure | cable with wires that are twisted together. | Twisted pair cable enclosed in foil / shield. |
| Cost | Cheaper than STP | Costlier than UTP |
| Weight | Lighter than STP | Heavier than UTP |
| Noise & interference | Prone to Noise and interference | Less prone to noise and interference |
| Data Speed | Supports slower speed than on STP | Support higher speed than UTP |
| Grounding of cable | Not required | Required |
| Target deployments | Locations less prone to interference like offices and homes. | Locations prone to interference like factories and airports |
Download the comparison table: utp vs stp
Related – Benefits of SFP Transceivers
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj