Overview
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) is a technology that supports multiple virtual routing instance on a single router (or layer-3 switch). This means a router can have multiple separate routing table and each one is completely independent. Whereas, an Access Control List (ACL) is a set of rules that is usually used to filter network traffic. ACLs contains a list of conditions that categorize packets and help you determine when to allow or deny network traffic based on subnet and port.
Basics of VRF
Virtual routing and forwarding feature is configured in Layer3 devices that allows multiple instances of a routing table to exist in a router/L3 Switch and these virtual routing tables work simultaneously and independently from each other. VRF allows network paths to be segmented without using multiple devices. Traffic is segregated and VRF increases network security, thus eliminating the need for encryption and authentication. Internet service providers create separate VRF for each customer’s virtual private networks and this is also called as VPN routing and forwarding.
Reated – VRF vs VRF LITE
Basics of ACL
ACL is acronym for Access Control List. ACL is used to filter the network traffic passing through the devices. ACL examines packets and takes decision as per policy decided in list.
- If match is found, it forwards the packet to associated interface.
- If match is not found, discards the packet immediately.
ACL is applied either to inbound or outbound of the interface:
- Outbound access lists – When an access list is applied on outbound of the interface, then packet will be processed at the outbound interface.
- Inbound access lists – When an access list is applied on inbound of the interface then packets will be processed according to the access list and then routed to the interface.
Related – Difference b/w ACL and Firewall
Types of ACL
- Standard Access list – Standard access list use the source IP address only. These ACLs permit and deny subnet. They don’t distinguish between the traffic type such as TCP, UDP and Https etc. For range from 1-99 and 1300-1999, router will understand it as a standard ACL and the specified address as source IP address.
- Extended Access-list – In case of extended ACL, it uses both source and destination IP address. Rules based on TCP port can be set for kind of traffic to be allowed or denied. Range is from 100-199 and 2000-2699.
Further, there are 2 categories of access list:
- Named access list – In named access list, a name is assigned to identify an access list. We can delete a named access list unlike numbered access list. It can be used with both standard and extended access list.
- Numbered access list – Numbered access list cannot be deleted once created i.e. if there is a need to remove any rule from an access list then this is not permitted and whole access list is required to be deleted. The numbered access list can be used with both standard and extended access list.
Case Study on VRF and ACL
In below scenario, we will configure VRF and ACL on DC_WAN Router and only VRF on Remote Site Routers A and B. With VRF, we will segregate routes from different remote sites or customers. With ACL, We will permit/deny type of traffic from different sites based on port number. So lets start with the configuration –
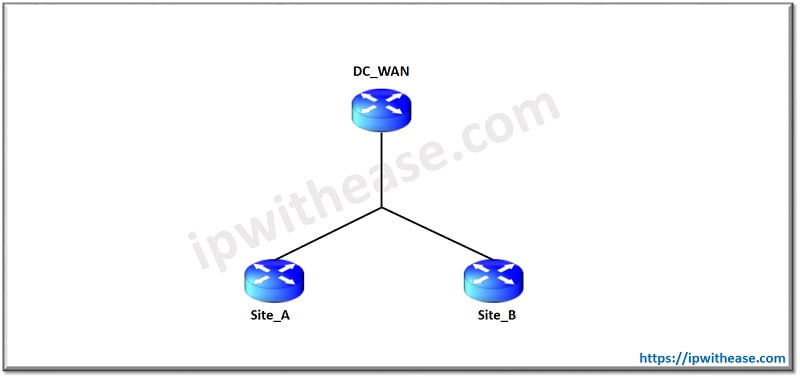
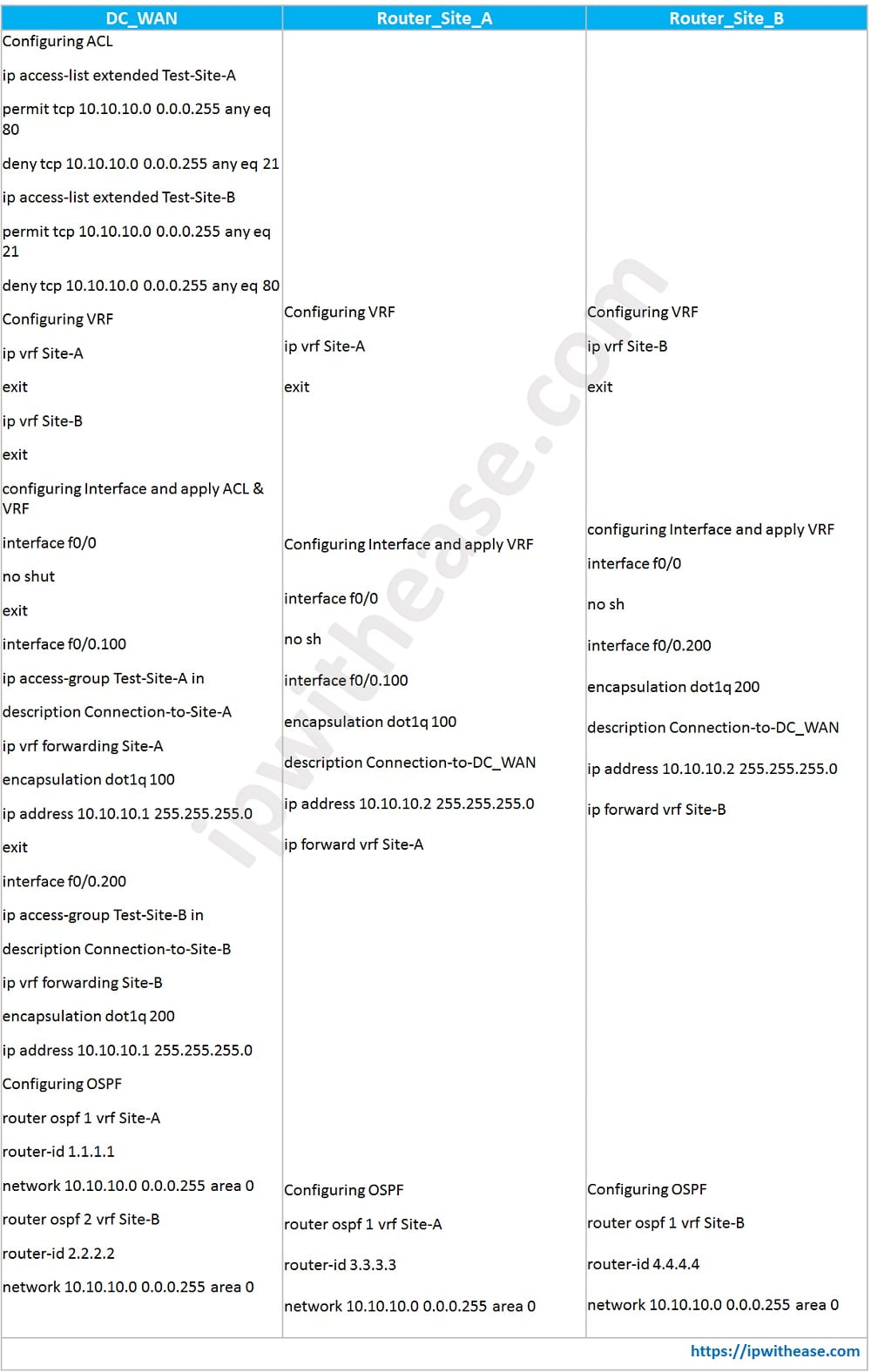
Key Differences : VRF vs ACL
- VRF stands for Virtual Routing and Forwarding. Whereas, ACL stands for Access Control List.
- VRF’s feature to allow multiple instances of IP routing table to exist in a layer 3 device and all routing instances work simultaneously. This allows network path to be segmented network path to be segmented without using multiple devices. Whereas, ACL used for permit and deny subnet/TCP port.
- VRF is local to Layer 3 device. ACL is also locally significant to device.
- VRF works on layer 3 of OSI model. Whereas, ACL works upto layer 4 of OSI model.
- VRF to VRF communication can be internally performed via route leaking without external port connections across VRFs. Whereas, Once ACL blocks or permit IP Subnet or TCP port, it will not be admitted until it gets removed from ACL list.
- VRF provides security of routes. ACL also provides security in network from unauthorized access.
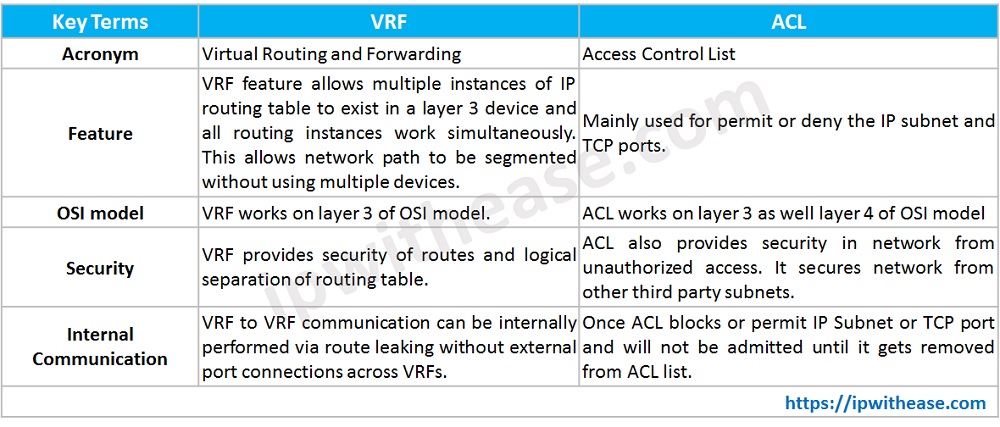
Comparison Table : VRF vs ACL
| KEY TERMS | VRF | ACL |
|---|---|---|
| ACRONYM | Virtual Routing and Forwarding | Access Control List |
| FEATURE | VRF feature allows multiple instances of IP routing table to exist in a layer 3 device and all routing instances work simultaneously. This allows network path to be segmented without using multiple devices. | Mainly used for permit or deny the IP subnet and TCP ports. |
| OSI MODEL | VRF works on layer 3 of OSI model. | ACL works on layer 3 as well layer 4 of OSI model |
| SECURITY | VRF provides security of routes and logical separation of routing table. | ACL also provides security in network from unauthorized access. It secures network from other third party subnets. |
| INTERNAL COMMUNICATION | VRF to VRF communication can be internally performed via route leaking without external port connections across VRFs. | Once ACL blocks or permit IP Subnet or TCP port and will not be admitted until it gets removed from ACL list. |
Download the comparison table here.
Conclusion
VRF is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to exist within the same router at the same time. Because the routing instances are independent and overlapped IP addresses can be used without conflicting with each other. An ACL is a set of rules for filtering traffic. Access control lists can be used to filter incoming and outgoing packets on an interface to control traffic.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj