Table of Contents
MacVLAN and Bridge are both network drivers, used mainly for connections on different Virtual Machine’s interfaces and network types. Let us deep dive and understand what both exactly stand for before drawing a comparison of MacVLAN vs Bridge.
What is MacVALN?
In the IT industry, MacVLAN driver allows IT engineers to configure multiple Layer 2 (i.e. Ethernet MAC) type addresses on a single physical interface. Also, MacVLAN allows the system administrator to configure sub interfaces (also known as slave devices) of a parent physical Ethernet interface (also termed upper device) with their own individual (randomly generated) MAC address and related IP address. Most applications, Virtual Machines and containers can then cohere to a specific sub interface in order to connect directly to the physical network, keeping their own MAC and IP addresses.
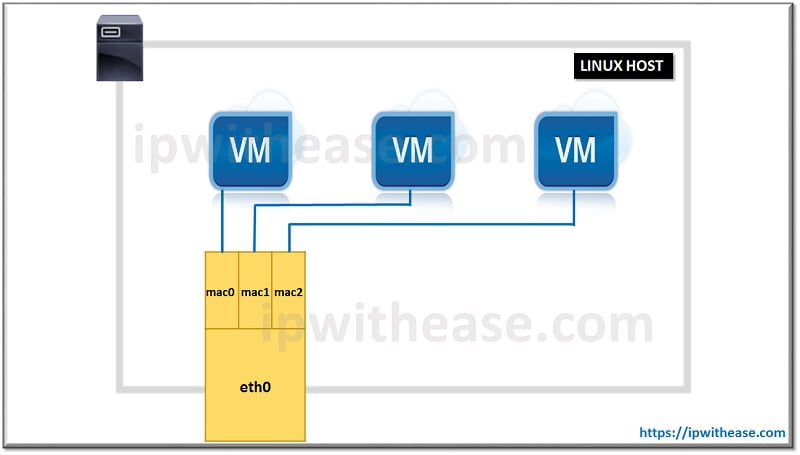
On the other hand, MacVLAN sub interfaces don’t have the ability to communicate directly with the parent interfaces and the Virtual Machines cannot directly communicate with the host accordingly. In case Virtual Machine host communication is required, the user should add another MacVLAN sub-interface and assign it to the host.
Finally, in some implementations, IT engineers use MacVLAN drivers in order to distinct sub interfaces by inserting a mac0@eth0 notation. This helps to identify the sub interface from its parent interface. Then the sub interface state is obligated to the parent’s state.
What is a Bridge?
In the IT industry, we define a bridge any kind of Layer 2 device that connects two Layer 2 (i.e. Ethernet) segments together. In general rule, the frames between these two segments are port forwarded based on the Layer 2 addresses (i.e. MAC addresses). Although the two terms are commonly used in different contexts, a bridge is commonly a switch and people confuse this technology for marketing purposes the last 20+ years.
The differentiation of a bridge is that it makes packet decisions based on the MAC address table contents. Firstly, Bridge learns MAC addresses by checking inside the Frames headers of the available communicating hosts.
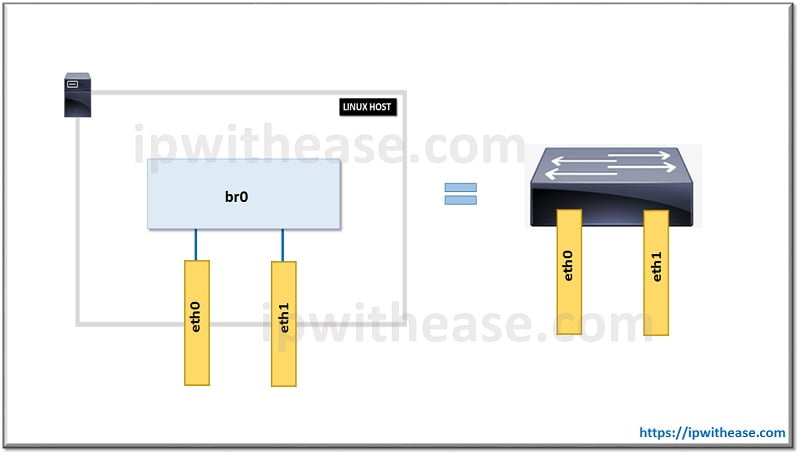
Despite the fact that a bridge can be a physical device or an implementation entirely created in software tools, most Linux kernels have been compatible to perform bridging since 1999. By creating a bridge, the user connects multiple physical or virtual interfaces into a single Layer 2 segment. Usually, a bridge that connects two physical interfaces on a Linux host effectively turns this host into a physical switch device.
MacVLAN vs Bridge: Difference
As a general rule, the MacVLAN is a bridge that doesn’t need to start learning anything, as it already knows all the mac addresses that it is able to receive. Therefore, it doesn’t need to implement learning techniques or use any spanning tree protocols.
Comparison Table
While both use the Layer 2 type addresses for connections, MacVLAN and Bridge differ in the following enlisted ways:
| PARAMETER | MACVLAN | BRIDGE |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity Interfaces | Physical Network Only | Complex Topologies And Hybrid Networks |
| Hardware Resources | Less CPU/RAM Usage | Normal CPU/RAM Usage |
| Administrative Skills | Normal to None | Advanced Flood Control and FDB Manipulation. |
| Implementation Cost | Cheap – No Expensive Technology Required. | Expensive, Advanced Technology Requirements. |
Download the Comparison Table: MacVLAN vs Bridge
Related FAQs
Q.1 What is MacVLAN used for?
MACVlan is useful for networking configurations where containers need to interact with the network as individual devices, providing both performance and flexibility benefits.
Q.2 What is a MacVTap device?
MacVTap device is a network interface in Linux that combines the functionality of MavVLAN with a tap device. It allows to create virtual network interfaces that can be used by containers or VMs, providing a way for these virtual interfaces to connect to the physical network.
Q.3 What is the difference between bridge and MacVTap?
– Bridge connects containers to a virtual network on the host, with shared IP addresses and communication through the host’s bridge interface.
– MacVTap gives containers their own unique MAC addresses, providing direct access to the physical network, bypassing the host’s network stack for improved performance and isolation.
Continue Reading
MacVLAN vs IPvlan: Understand the difference
What is MacVLAN? Detailed Expalnation
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

You can learn more about her on her linkedin profile – Rashmi Bhardwaj